| Journal of Food Bioactives, ISSN 2637-8752 print, 2637-8779 online |
| Journal website www.isnff-jfb.com |
Review
Volume 31, September 2025, pages 41-62
Beyond petri dish: small animal models bridge in vitro and in vivo antioxidant assays
Amal Samarasinghe, Sarusha Santhiravel*
Department of Biochemistry, Memorial University of Newfoundland, St. John’s, NL A1C 5S7, Canada
*Corresponding author: Sarusha Santhiravel, Department of Biochemistry, Memorial University of Newfoundland, St. John’s, NL A1C 5S7, Canada. E-mail: ssanthiravel@mun.ca
DOI: 10.26599/JFB.2025.95031420
Received: September 9, 2025
Revised received & accepted: September 22, 2025
| Abstract | ▴Top |
Dietary antioxidants, derived mainly from plant-based foods contribute to health promotion by supporting the body’s defense against oxidative stress-related disorders. In vitro assays are widely employed to evaluate the antioxidant capacities of food-derived compounds, providing rapid and cost-effective insights into their radical scavenging and reducing potential. However, these methods do not account for factors such as digestion, absorption, metabolism, and tissue distribution, which determine the physiological relevance of antioxidants. Therefore, in vivo models are essential to complement in vitro findings, enabling a more accurate assessment of bioavailability, mechanisms of action, and health benefits in a biological context. Small animal models provide versatile platforms to bridge this gap, offering genetic tractability, conserved pathways, and cost-effective tools for functional validation of dietary antioxidants. In this review, we summarize the antioxidant defense mechanisms and experimental approaches utilized in zebrafish, C. elegans, and fruit fly to investigate the impact of dietary antioxidants. Key outcomes of antioxidative action in these models include the reduction of reactive oxygen species, upregulation of endogenous defense systems, protection of biomacromolecules from oxidative damage, and lifespan extension. Furthermore, this review outlines future directions for utilizing these small animals as translational models in the investigation of food-derived antioxidants.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Zebrafish; C. elegans; Fruit fly; Oxidative stress
| 1. Introduction | ▴Top |
Antioxidants play a critical role in maintaining human health by mitigating oxidative stress, an imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the body’s antioxidant defences, which is a key contributor to the pathophysiology of chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disorders, neurodegenerative conditions, diabetes, cancer, and premature aging (Pizzino et al., 2017; Chandrasekara et al., 2024).The antioxidant compounds can be enzymatic (e.g., superoxide dismutase(SOD), Catalase(CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPx) or non-enzymatic (e.g., phenolics, certain vitamins, carotenoids), and maintain redox homeostasis by neutralizing ROS and preventing damage to DNA, proteins, and lipids (Kruk et al., 2022; Senadheera et al., 2023).The consumption of antioxidant-rich foods like fruits and vegetables can be recommended to avoid chronic diseases associated with oxidative stress. Bioactive compounds, which are natural chemicals responsible for antioxidant activity of foods, herbs, mushrooms, and other sources, have gained significant attention for their ability to improve health and help prevent disease beyond the basic roles of macro- and micronutrients. They exhibit diverse biological activities beyond the antioxidant activity, such as anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and immunomodulatory effects, making them more important in preventing and managing chronic conditions (Muscolo et al., 2024; Rahaman et al., 2023). For example, polyphenols in fruits and vegetables act as antioxidants with potential in obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer management. At the same time, resveratrol in grapes and red wine has demonstrated anticancer effects by inhibiting tumour cell growth and proliferation. Recent evidence supports this by showing an inverse correlation between the blood concentration of antioxidants like vitamins C and E and non-communicable disease rates. The glucose metabolism and blood pressure regulation, crucial in controlling hypertension and diabetes, are done by bioactive peptides derived from natural sources (Farhan and Rizvi, 2023; Ciupei et al., 2024). On the other hand, phytochemicals in herbs and spices show anti-obesity and lipid-lowering effects. This is evidenced by recent studies that further highlight their broad potential: mushrooms like Pleurotus ferulae and Chroogomphus rutilus reduce adiposity, improve lipid profiles, and exhibit antioxidant and antitumor effects; anthocyanin-rich berries (Vaccinium spp.) protect against inflammation and cancer; and yacon flour reduces colorectal cancer–related inflammation in animal models (Jeayeng et al., 2024).
Additionally, some marine microalgae, such as Chlorella, improve exercise performance through antioxidant and metabolic activities, while medicinal plants like Momordica charantia and Persea americana support glucose regulation and weight management (Lorenzo et al., 2023; Laczkó-Zöld et al., 2024). Nevertheless, compounds such as capsaicin from chilli peppers enhance thermogenesis, gut health, and antioxidant status, and bio actives like ω-3 fatty acids, sulforaphane, and bromelain have shown promise as adjuvants in breast cancer prevention and treatment. These examples highlight the varied roles in health and wellness, underscoring the need for more clinical research to confirm safety, efficacy, and long-term benefits. Therefore, bioactive compounds from natural sources have drawn increasing attention for their potential to promote health and prevent disease beyond basic nutritional functions (Corral-Guerrero et al., 2025).
The diversity of antioxidant assessments to evaluate the alleviating potential of oxidative stress from different sources is very important to understand. Researchers are looking for new effective methods to assess antioxidant capacity due to the difficulties of reliably predicting human physiological responses using traditional in vitro assays and mammalian models, which are usually applied in biomedical research, drug testing, and toxicity assessments (Shahidi and Danielski, 2024; Gulcin, 2025). The static cell cultures, which are also a kind of in vitro system, offer high capability of throughput but make the cellular environment oversimplified, which makes it hard to replicate critical dynamic processes like fluid flow, cellular interactions, and the complex metabolism and bioavailability of compounds that occur in vivo (Ryoo et al., 2024). Furthermore, their translational relevance is often limited by variability in environmental conditions, such as pH and oxygen levels, which can drastically affect outcomes. In case of oxidative stress assessment through mammalian models makes more beneficial with having biologically complex system their use is obstructed by ethical concerns, high costs, extended study durations, and crucial species differences; for example, transgenic mouse models can have significant genetic divergences that fail to replicate human disease mechanisms accurately (Liu et al., 2025). Additionally, some of the limitations of specific assays, such as the mouse aortic ring assay applied to angiogenesis, are exacerbated by their dependence on stressful surgical procedures and poor reproducibility due to variability in assay conditions and readouts. These shortcomings underscore the need to develop more predictive, human-relevant models, such as organ-on-chip technologies, to better mimic human physiology and pathology (Baker et al., 2012; Razmi et al., 2025).
The diversity of antioxidant assessments to evaluate the alleviating potential of oxidative stress from different sources is very important to understand. Researchers are looking for new effective methods to assess antioxidant capacity due to the difficulties of reliably predicting human physiological responses using traditional in vitro assays and mammalian models, which are usually applied in biomedical research, drug testing, and toxicity assessments (Shahidi and Zhong, 2015; Mendonça et al., 2022). The static cell cultures, which are also a kind of in vitro system, offer high capability of throughput but make the cellular environment oversimplified, which makes it hard to replicate critical dynamic processes like fluid flow, cellular interactions, and the complex metabolism and bioavailability of compounds that occur in vivo. Furthermore, their translational relevance is often limited by variability in environmental conditions, such as pH and oxygen levels, which can drastically affect outcomes (Ngo et al., 2023; Urzì et al., 2023). Even though mammalian models implies a more biologically complex, they are hampered by ethical concerns, high costs, extended study durations, and crucial species differences; for example, transgenic mouse models can have significant genetic divergences that fail to accurately replicate human disease mechanisms .Additionally some of the limitations of specific assays, such as the mouse aortic ring assay applying for angiogenesis, are more exacerbated by their dependence on stressful surgical procedures and poor reproducibility due to variability in assay conditions and readouts. These shortcomings underscore the need to develop more predictive, human-relevant models, such as organ-on-chip technologies, to better mimic human physiology and pathology (Urzì et al., 2023; Zhao and Bhattacharyya, 2018).
As a powerful and ethically favourable alternative for conventional methods in measuring oxidative stress, attention towards small model organisms like zebrafish (Danio rerio), Caenorhabditis elegans, and Drosophila melanogaster has become indispensable in antioxidant research. Their advantages are multifaceted: high genetic tractability, remarkably short life cycles, low cost, and a high degree of physiological conservation in fundamental redox and stress-response pathways with humans (Zhang et al., 2024a). These characteristics allow for high-throughput screening of oxidative stress and natural bioactive antioxidants, which are increasingly prioritized over synthetic options. Compared to the traditional in vitro systems, these small models provide a whole-organism context while mimicking complex cellular environments, including bioavailability and metabolism, to assess antioxidant efficacy from molecular activity to systemic health outcomes such as improved lifespan or stress resistance. Therefore, reviewing the applications of these small models is critical for rapidly validating the therapeutic potential of antioxidants derived from diverse natural sources, such as plant extracts, microalgae, and sea cucumbers, and for advancing their use in food preservation, nutraceuticals, and cosmetic applications (Zhang et al., 2024b).
| 2. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of antioxidant defense | ▴Top |
Antioxidant defence mechanisms are fundamental to cellular homeostasis, protecting against oxidative stress caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS). The Nrf2 signalling pathway primarily orchestrates this defence (Verma et al., 2023). Upon activation by oxidative stress, Nrf2 transcription factors move towards the nucleus and bind to antioxidant response elements (AREs), inducing the transcription of major antioxidant enzymes such as CAT, SOD, and GPx (Ngo and Duennwald, 2022; Hammad et al., 2023). This system is further fine-tuned through post-translational modifications, allowing cells to rapidly adjust their defences in response to fluctuating ROS levels. These enzymes are vital in vascular biology and manipulating Nrf2 as a promising therapeutic strategy for cardiovascular diseases, where their decreased activity is associated with endothelial dysfunction and inflammation (Liu et al., 2025).
The generation of ROS is a normal physiological process, but oxidative stress occurs when its production overwhelms the body’s antioxidant capabilities. However, conditions like chronic hyperglycemia, hypoxia, and substance abuse exacerbate the imbalance of ROS generation, leading to significant cellular damage through lipid peroxidation, DNA damage, and apoptosis and on the other hand, contributing to the pathogenesis of some neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s disease, cardiovascular complications via endothelial dysfunction, and metabolic syndromes. Furthermore, oxidative stress also significantly affects reproductive health, which presents a significant challenge to in vitro fertilization, where mitochondrial ROS production can damage oocytes and embryos (González et al., 2023; Bhatti et al., 2022).
To assess oxidative damage, specific biomarkers such as malondialdehyde (MDA) and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) to measure Lipid peroxidation, 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) to measure cellular DNA damage, and protein oxidation by protein carbonyls are utilized (AbuArrah et al.,2021). The analysis of these biomarkers provides critical insights into disease severity, as seen in conditions like COVID-19 and cancer, and helps elucidate the underlying pathological mechanisms. In addition to the application in patient diagnosis and stratification, the monitoring of these biomarkers also holds therapeutic promise for guiding interventions, such as the use of dietary polyphenols like resveratrol, which can enhance antioxidant defences through both Nrf2 activation and direct post-translational modifications of protective enzymes (Jain, 2010).
| 3. The zebrafish (Danio rerio) as a model for antioxidant and oxidative stress research | ▴Top |
The zebrafish (Danio rerio) has emerged as a preeminent model organism for investigating antioxidant mechanisms and oxidative stress, largely due to its unique combination of biological, genetic, and experimental advantages. A major strength is the optical transparency of its embryos and larvae, which permits direct, high-resolution, real-time imaging of physiological and pathological processes in vivo without invasive procedures (Srivastava et al., 2025).This feature is complemented by a high degree of genetic tractability; advanced genome-editing technologies like TALENs and CRISPR, along with a wide array of stable transgenic lines expressing fluorescent reporters, facilitate detailed mechanistic studies (Du et al., 2025). Furthermore, the zebrafish genome is fully sequenced and exhibits remarkable conservation with humans, with approximately 80% of human genes having a counterpart (Tasnim et al., 2024) .This is particularly true for genes governing oxidation, lipid metabolism, and inflammation, ensuring that findings are often translatable to mammalian systems (Teame et al., 2019).
These attributes make zebrafish an unparalleled platform for toxicological and pharmacological research, allowing for the real-time observation of oxidative stress responses during their rapid embryonic development (Zhang et al., 2021). The model has been effectively used to demonstrate the physiological implications of oxidative stress, such as acute sensitivity to ROS. Consequently, numerous studies have utilized zebrafish to screen and evaluate the efficacy of various antioxidants. For instance, quercetin nanocrystals, tamarind shell extract, and Cassia fistula stem bark have all been shown to mitigate hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress, demonstrating significant reductions in ROS production and protective roles against cellular damage (Li et al., 2023b; Wang et al., 2023a).
At the molecular level, zebrafish research has elucidated key pathways like the Nrf2-Keap1 signaling cascade, which regulates the expression of antioxidant genes in a manner that parallels mechanisms in mammals (Nguyen et al., 2018). Studies consistently highlight the activation of critical antioxidant enzymes, including CAT and GPx, as essential for maintaining redox homeostasis (Wang et al., 2023b). The use of fluorescent probes has further enabled the visualization of metabolic dynamics, such as cysteine metabolism, under oxidative stress in living organisms (Yu et al., 2025). This utility extends to environmental toxicology, where zebrafish have been instrumental in linking pollutant exposure (e.g., bisphenol A) to oxidative damage and in documenting the protective effects of potential therapeutic compounds like antioxidant peptides (Guru and Arockiaraj, 2023).Thus, the combined attributes of transparency, genetic manipulability, and physiological homology make the zebrafish an indispensable platform for advancing both basic and therapeutic research into redox biology. Figure 1 summarizes in vivo, in vitro, and molecular approaches that have been applied in zebrafish for evaluating antioxidant capacity and oxidative stress mechanisms.
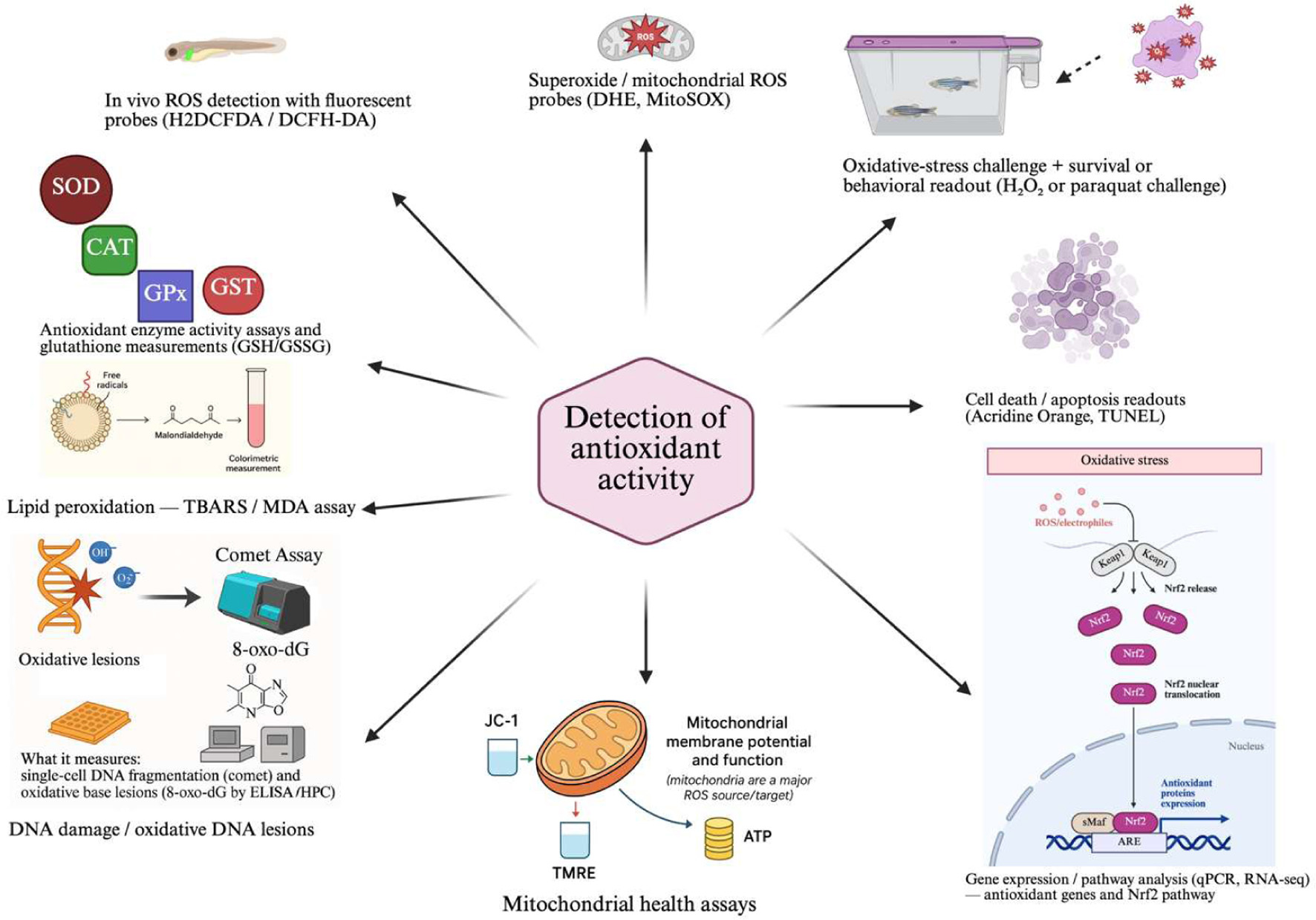 Click for large image | Figure 1. Different antioxidant detection methods using zebrafish models. |
3.1. Zebrafish in oxidative stress toxicology
One of the most significant applications of the zebrafish model lies in toxicological research, where it is extensively employed to evaluate the oxidative stress potential of environmental contaminants and to elucidate underlying molecular pathways. For instance, exposure to perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) induces a concentration-dependent increase in ROS and markedly upregulates the activity of key antioxidant enzymes—SOD, CAT, and GPx—as a cellular defense mechanism (Shi and Zhou, 2010). The primary mechanism for this response involves the Nrf2 pathway, a central regulator of antioxidant defenses. Activation of Nrf2 mitigated PFOS-induced damage, whereas its knockdown exacerbated oxidative stress (Shi and Zhou, 2010).
Similarly, nanotoxicology studies have shown that titanium dioxide nanoparticles (NM-TiO2), particularly in anatase-rich forms, exhibit significantly enhanced toxicity under simulated solar radiation due to elevated ROS generation, resulting in oxidative tissue damage (Faria et al., 2014). These findings emphasize the zebrafish model’s value in revealing how pollutants disrupt oxidative homeostasis and in identifying the protective mechanisms involved.
The zebrafish is also well suited for experimental setups designed to mimic oxidative stress conditions. For example, exposure to pro-oxidants such as tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BHP) allows researchers to simulate oxidative stress in vivo (Li et al., 2023a). In one study, tamarind shell extract was shown to protect zebrafish against t-BHP–induced oxidative damage, confirming its antioxidant potential (Li et al., 2023a). Likewise, carnosine has demonstrated protective effects against titanium dioxide–induced oxidative stress in zebrafish embryos, further supporting the model’s utility for drug discovery and antioxidant screening (Caruso et al., 2023).
Moreover, the genetic manipulability of zebrafish—particularly through CRISPR-based approaches—enhances its role in dissecting molecular mechanisms of oxidative stress. Loss- and gain-of-function mutants of the Nrf2a gene have been used to clarify how this pathway regulates antioxidant gene expression and mediates toxicity responses (Mills et al., 2019). These genetic tools also allow researchers to assess how natural compounds influence oxidative stress responses. For example, soy-derived equol has been investigated in zebrafish larvae, revealing both Nrf2-dependent and independent mechanisms of antioxidant protection (Watanabe et al., 2022).
3.2. Screening therapeutic antioxidants and evaluating bioactive compounds
Beyond toxicology, the zebrafish has emerged as an invaluable model for screening and evaluating the efficacy of natural and synthetic antioxidants, offering critical functional and safety data. Research on sulfated polysaccharides from the brown alga Sargassum tenerrimum demonstrated potent radical-scavenging activity in vitro and a strong cytoprotective effect in vivo, significantly decreasing H2O2-induced ROS production and cell death in embryos while improving survival and heart rates (Raguraman et al., 2019). The model also enables insights into the therapeutic potential of compounds for complex disorders. For instance, nicotine metabolites were found to alleviate scopolamine-induced anxiety and memory deficits in zebrafish, with their effects attributed to robust antioxidant properties that enhanced the activity of key antioxidant enzymes and glutathione levels while reducing lipid peroxidation (Popovici et al., 2025).
Importantly, the zebrafish model is crucial for safety assessment, as high antioxidant capacity in vitro does not necessarily translate to safety in vivo. This was illustrated in a study of native Australian fruits, where Kakadu plum extract—with high antioxidant activity—was among the least toxic, whereas Muntries extract—with lower antioxidant metrics—proved the most toxic, causing significant mortality and hatching delays (Ali et al., 2022). Such findings underscore the importance of zebrafish in validating both the efficacy and the safety of potential antioxidant therapies.
Focusing on specific natural antioxidants, several studies have identified effective food-derived phytochemicals. Compounds such as curcumin and diallyl trisulfide have shown significant protective effects against oxidative stress in zebrafish larvae (Watanabe et al., 2022). Similarly, chlorogenic acid supplementation demonstrated benefits for exposed zebrafish embryos, highlighting the therapeutic promise of dietary antioxidants (Chiu et al., 2020). Moreover, the antioxidant Riboceine successfully rescued craniofacial defects in zebrafish exposed to auranofin, showcasing the practical applications of antioxidant research in developmental biology (Leask et al., 2021).
Zebrafish models also support high-throughput screening of antioxidant compounds, enabling the identification of those with substantial protective effects against oxidative stress. For example, fucoidan from Undaria pinnatifida exhibited protective properties in AAPH-induced oxidative stress assays (Oh et al., 2020). Additionally, research has revealed that phosvitin, a protein isolated from zebrafish, possesses potent antioxidant activity, suggesting that the amino acid composition of zebrafish proteins contributes significantly to their capacity to mitigate oxidative damage (Hu et al., 2015). Collectively, these studies demonstrate how zebrafish-based research, combined with modern genetic tools, can elucidate the mechanisms through which natural compounds exert their antioxidative effects.
3.3. Integrative omics for antioxidant research in zebrafish
The application of integrative omics approaches, such as transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, in zebrafish (Danio rerio) research underscores the utility of this model organism in evaluating the antioxidant potential of natural sources. Zebrafish are increasingly utilized in studies assessing oxidative stress due to their genetic similarities to humans and their transparent embryos, which permit real-time observation of biological processes. A significant area of research involves the use of natural extracts to mitigate oxidative stress. For example, the antioxidant effects of Moringa oleifera leaf extract have been demonstrated in zebrafish exposed to imidacloprid toxicity. The extract has been shown to enhance levels of antioxidant enzymes, thereby alleviating the harmful effects associated with oxidative damage in liver tissues (Yadav et al., 2020). Moreover, Moringa compounds, which are rich in essential amino acids, have been indicated to promote protein synthesis and mitigate oxidative damage, further highlighting their pharmacological relevance (Yadav et al., 2020).In addition, the effects of various antioxidants, including nanoparticles such as selenium (Se) and zinc oxide (ZnO), on zebrafish growth and modulation of oxidative stress have been explored. Research indicates that the incorporation of these nanoparticles significantly enhances growth performance and modulates gene expression related to oxidative stress, indicating their potential as nutraceuticals in fish feeds aimed at improving aquaculture outcomes (Fasil et al., 2021). These findings suggest that integrative omics can elucidate the mechanisms by which natural antioxidants operate at molecular and cellular levels, revealing pathways implicated in growth and stress responses. Natural sources of antioxidants extend beyond traditional medicinal plants. Marine resources, such as astaxanthin, have emerged as potent antioxidants. Carotenoids like astaxanthin are recognized for their role in mitigating oxidative stress and enhancing immune responses in fish, thus improving the health and resilience of fish stocks under farming conditions (Akhmedzhanova et al., 2022; Córdova et al., 2018). In this context, zebrafish serve as an optimal model for studying the effects of such antioxidants, allowing for precise metabolic profiling and comparative studies of antioxidant efficacy under various environmental conditions. Furthermore, the role of phenolic compounds from diverse natural sources in preserving the quality of fish has been investigated. Research indicates that extracts rich in phenolics provide antioxidant activity comparable to synthetic alternatives, thus improving oxidative stability in seafood products (Pezeshk et al., 2015). The assessment of these natural antioxidants through omics approaches could lead to a deeper understanding of their mechanisms and efficacy in real-world scenarios, particularly within the aquaculture industry (Taşbozan and Erbaş, 2023).
3.4. As a model for diet-induced oxidative stress research
This model organism’s favorable characteristics, such as its genetic and physiological similarity to higher vertebrates, allow researchers to effectively test dietary components for their antioxidant capacity and metabolic impacts. Recent studies underscore the role of specific micronutrients in boosting the antioxidant defenses of zebrafish. For instance, Fasil et al. demonstrate that the supplementation of zinc oxide (ZnO) and selenium significantly enhances growth performance by modulating oxidative stress and influencing gene expression relevant to growth, such as growth hormone (GH) and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) (Fasil et al., 2021). The interplay between these nutrients reinforces the synergistic effects of antioxidants in promoting overall fish health. Further investigations have illustrated how external environmental factors, such as exposure to contaminants, can adversely affect the oxidative status of aquatic organisms. For example, Velanganni et al. documented that exposure to benzophenone-3, a common water pollutant, triggered oxidative stress in zebrafish, evidenced by altered antioxidant enzyme activities and increased lipid peroxidation markers (Velanganni et al., 2021). Such environmental stressors highlight the necessity for dietary interventions that enhance antioxidant capacities, as seen in the comparative analyses of synthetic versus natural antioxidants in fish diets conducted by Pereira et al. They found that natural sources, particularly from vegetables like tomatoes, exhibit promising antioxidant potential under both standard and stress-challenged conditions (Pereira et al., 2022).Moreover, various dietary proteins have been explored for their bioactive peptide content, contributing to antioxidant activities. The peptide VY6 derived from β-lactoglobulin was shown to modify lipid metabolism in zebrafish, leading to significant reductions in liver triglycerides and free cholesterol while enhancing HDL levels (Mohammed-Geba et al., 2016). This suggests a pathway by which dietary proteins can be strategically utilized to ameliorate lipid-related oxidative stress in fish. Furthermore, antioxidants sourced from natural plants and microorganisms are garnering attention for their application in fish diets. The study by Vargas-Sánchez et al. highlights the potential of propolis extract as a natural antioxidant, supporting the idea that a diet enriched with natural antioxidants can enhance the oxidative stability of fish products during storage (Vargas-Sánchez et al., 2019). This aligns with the broader literature emphasizing the extraction and application of natural antioxidants from various sources, which, according to Xu et al., are integral in mitigating oxidative stress effects at molecular levels and promoting overall health (Xu et al., 2017).
| 4. Drosophila melanogaster (fruit fly) | ▴Top |
Drosophila melanogaster, also known as fruit fly, has emerged as a powerful in vivo model for nutritional and biomedical research due to its genetic tractability, short lifespan (average three months at 25 °C), cost effectiveness, and conserved molecular pathways involved in oxidative stress responses (Atoki et al., 2025). It is an economical choice because of its rapid reproduction (30–50 eggs per day), short generation time (around ten days at 25 °C), and minimal maintenance cost. For decades, D. melanogaster has served as a highly valuable animal model for investigating genetics, evolutionary processes, and developmental biology. Although D. melanogaster is evolutionarily distant from humans, many aspects of its development, physiology, biology, and metabolism closely resemble those of mammals (Lopez-Ortiz et al., 2023). In particular, recent studies highlight parallels in metabolic regulation, including insulin signaling, nutrient sensing, and energy homeostasis, which are relevant to metabolic disorders such as diabetes and obesity (Mattila and Hietakangas, 2017). Recently, fruit flies are being increasingly used in antioxidant studies since flies share homologous antioxidant defense mechanisms with mammals, including SOD, CAT, and glutathione (GSH)-based systems, making them biologically relevant for evaluating antioxidant interventions (Yi et al., 2024). Furthermore, dietary compounds can be readily incorporated into fly food, enabling controlled studies of dose-dependent effects on stress resistance, longevity, and physiological health.
Previous studies have established D. melanogaster as a suitable model for antioxidant research on food-derived bioactives (Lopez-Ortiz et al., 2023). Oxidative stress is commonly induced in flies using agents such as paraquat, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), or excess copper, providing a consistent framework to evaluate stress resistance and survival (Demir et al., 2022). Experimental outcomes are typically assessed through lifespan analysis, locomotor assays such as negative geotaxis, and biochemical measurements of oxidative stress markers, including reactive oxygen species (ROS), protein carbonyls, lipid hydroperoxides, malondialdehydes (MDA), and thiol content, as well as antioxidant enzyme activities such as CAT, SOD, glutathione-S-transferase (GST), and GPx as shown in Figure 2. Furthermore, disease models in D. melanogaster, including α-synuclein–based Parkinson’s disease models, exhibit elevated oxidative stress and motor impairments, making them particularly valuable for testing antioxidant interventions (Aryal and Lee, 2019). Overall, D. melanogaster models are widely applied to investigate the antioxidant potential of dietary phytochemicals and bioactive peptides, which are discussed in the following sections (Table 1).
 Click to view | Table 1. Use of Zebrafish, Fruit Fly, and C. elegans for Antioxidant Discovery |
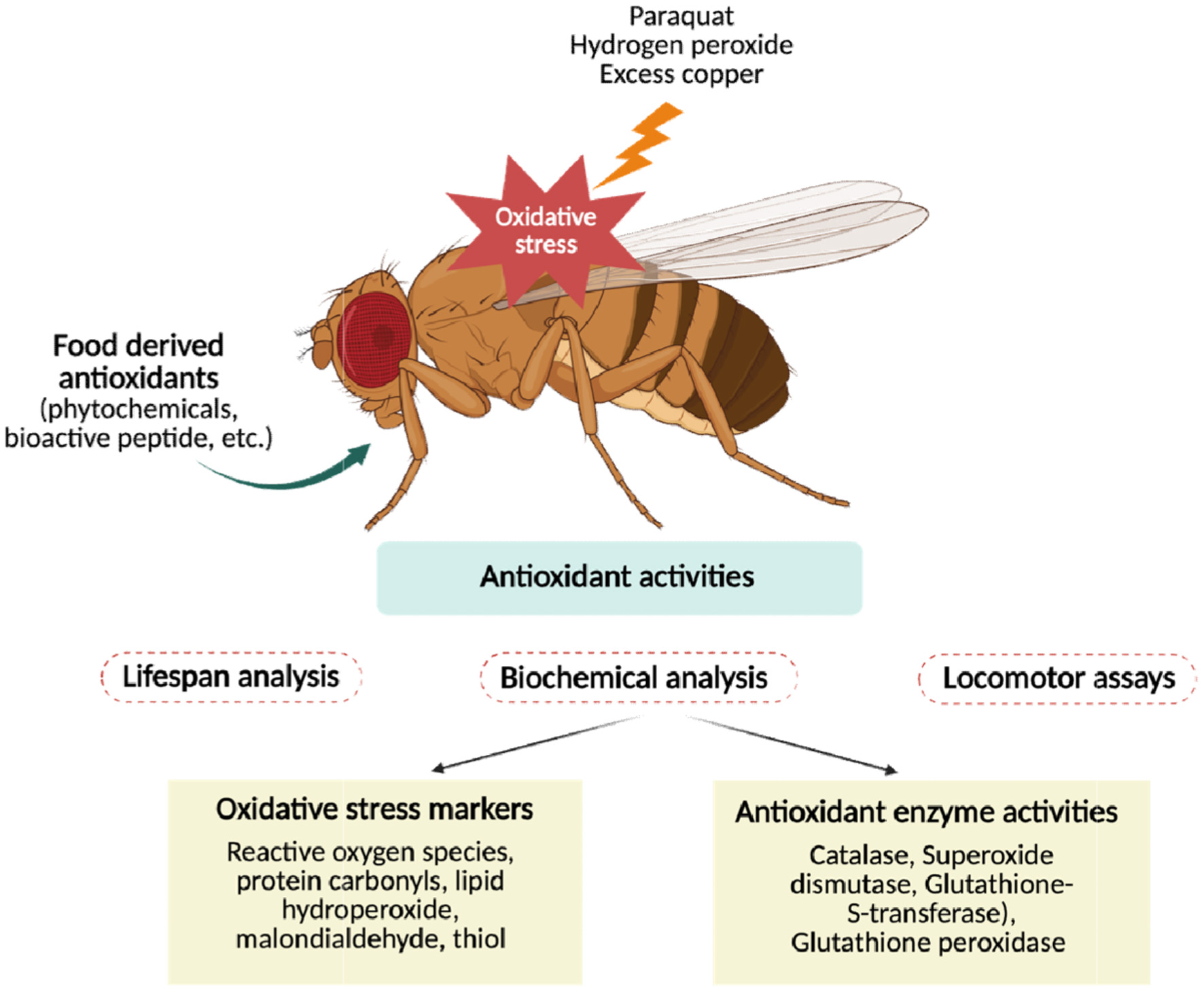 Click for large image | Figure 2. D. melanogaster as a small in vivo model to study antioxidant activities of food derived antioxidants. |
4.1. Plant-based antioxidants and oxidative stress modulation
Phytochemicals are naturally occurring bioactive compounds present in fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, and other plant-based foods, where they contribute to health promotion through their antioxidant and protective properties. These compounds, including phenolics, carotenoids, and alkaloids, can neutralize ROS, chelate transition metals, and stimulate the body’s endogenous antioxidant defense systems. A growing body of evidence demonstrates that dietary phytochemicals can extend lifespan, enhance stress resistance, and improve antioxidant capacity in fruit flies, offering insights relevant to human health. Several studies highlight the role of individual compounds and plant extracts in modulating oxidative stress in D. melanogaster. For example, Golubev et al. (2022) demonstrated that Lonicera pallasii (honeysuckle) extract and its major anthocyanin, cyanidin-3-O-glucoside, modestly increased lifespan and stress resistance while improving intestinal barrier integrity, effects linked to Sirt6 activation and regulation of pro- and anti-longevity genes (Hif1 and Keap1). Together, these findings suggest that phytochemicals can promote longevity and health span through antioxidant and gene-modulatory mechanisms.
Other investigations have focused on plant extracts rich in diverse phytochemicals. Mangifera indica cold aqueous leaf extract enhanced fly survival and increased activities of GST and CAT as well as thiol content, although effects were dose-dependent, emphasizing the importance of dose optimization (Alexander et al., 2019). In addition, Astragalus membranaceus extract and its bioactive compounds improved oxidative stress resistance by enhancing survival under H2O2 challenge, lowering ROS levels, increasing antioxidant enzyme activity (SOD, CAT), and upregulating related genes (Sod1, Cat, CncC) (Dai et al., 2024). Curcumin supplementation significantly extended lifespan in male flies, with the effect reversed by a SOD inhibitor, suggesting that curcumin acts through SOD-dependent pathways (Suckow and Suckow, 2006). Likewise, flavonoids extracted from Epimedium pubescens, including icariin and epimedins A–C, showed strong radical-scavenging activity and boosted antioxidant enzyme activities (CAT and GSH-Px) in both sexes, reinforcing their potential as natural antioxidants (Yang et al., 2020).
One prominent area of research focuses on how various plant extracts modulate antioxidant enzyme activity and reduce oxidative stress in Drosophila melanogaster. For instance, selenium-enriched Chrysanthemum morifolium has been shown to significantly influence lifespan and upregulate key antioxidant enzymes, including superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase, both of which play crucial roles in mitigating oxidative stress (Feng et al., 2022). Similarly, Spirulina platensis extract has been demonstrated to enhance overall antioxidant levels and decrease oxidative damage in fruit flies exposed to toxic compounds, further supporting its protective role (Salim et al., 2019). Collectively, these findings suggest that such natural sources may serve as promising anti-aging and neuroprotective agents.
Research has also investigated the effects of individual dietary components on oxidative stress regulation. For example, phlorizin, a bioactive compound from apples, was reported to increase both SOD and catalase activity in Drosophila, strengthening the organism’s defenses against reactive oxygen species (ROS) (Wang et al., 2023b). In a similar vein, dietary supplementation with chili pepper extract produced a concentration-dependent extension of lifespan in fruit flies, suggesting that such extracts influence metabolic and stress-response pathways that govern longevity (Semaniuk et al., 2022a).
The implications of these findings are particularly relevant to neurodegenerative disease research, especially Parkinson’s disease (PD). In a Drosophila PD model involving ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase (dUCH) knockdown, antioxidants such as curcumin have been found to alleviate PD-like symptoms by reducing oxidative stress (Nguyen et al., 2018). Likewise, natural antioxidants from Portulaca oleracea have shown neuroprotective effects in the same model, underscoring their potential as therapeutic candidates for neurodegenerative conditions driven by oxidative damage (Huynh et al., 2019).
In addition to these physiological outcomes, recent studies have shed light on the genetic mechanisms underlying antioxidant responses in Drosophila. Pathways involving transcription factors such as FOXO and Nrf2 play central roles in regulating antioxidant enzyme expression in response to dietary antioxidants (Semaniuk et al., 2022b). A deeper understanding of these molecular mechanisms not only supports the effectiveness of plant-derived antioxidants but also lays the groundwork for developing strategies to harness these natural compounds for human health benefits.
More recent studies have expanded the scope of phytochemical testing in D. melanogaster. A proanthocyanidin-rich fraction from Tamarindus indica improved lifespan, emergence rate, and antioxidant enzyme activities while reducing acetylcholinesterase and caspase-3/9 activities, indicating both antioxidant and neuroprotective effects (Jaafaru et al., 2024). Similarly, supplementation with Artemisia argyi extract significantly prolonged lifespan, improved climbing ability, and increased tolerance to oxidative stress while modulating key antioxidant enzymes and reducing MDA levels (Yang et al., 2024). Apple-derived phlorizin also exhibited strong antioxidant and anti-aging properties, including lifespan extension, improved locomotor performance, upregulation of Nrf2/cnc and related genes, and downregulation of methuselah. Computational analysis further suggested that phlorizin functions as a Nrf2 activator, linking its effects to endogenous stress response pathways (Wang et al., 2019). Collectively, these findings underscore the utility of D. melanogaster as a model for studying the antioxidant and anti-aging effects of phytochemicals and provide mechanistic insights with translational potential.
4.2. Bioactive peptides
Bioactive peptides, short protein fragments released from dietary proteins, have emerged as important natural antioxidants with health-promoting effects that extend beyond basic nutrition. Their antioxidant activity is attributed to free radical scavenging, transition metal chelation, and regulation of endogenous defense systems. Owing to these properties, Drosophila melanogaster has been increasingly employed as an in vivo model to investigate the antioxidant and anti-aging effects of food-derived peptides.
Several studies have demonstrated the ability of dietary peptides to enhance stress resistance and prolong lifespan in D. melanogaster. Chen et al. (2020) reported that crimson snapper scale peptides significantly extended lifespan in a dose-dependent manner, reduced MDA and protein carbonylation levels, and enhanced antioxidant enzyme activities (thiol modified-SOD and CAT), while upregulating antioxidant-related genes (SOD1, SOD2, CAT). Similarly, supplementation with rice protein hydrolysates (0.2 and 3.2%) increased lifespan, boosted antioxidant enzyme activities (SOD, Manganese-SOD, CAT), and modulated key signaling pathways, including Nrf2/Keap1, TOR/S6K, and the longevity gene methuselah (Yue et al., 2021). Casein supplementation has also been shown to counteract oxidative stress: Sadiq et al. (2023) demonstrated that 1% casein improved survival, restored GSH, thiols, and protein levels, and normalized oxidative stress biomarkers in flies, potentially through Keap1/Nrf2 pathway regulation.
More recently, Lateolabrax japonicus peptides (LPH) have been evaluated for their antioxidant potential in flies subjected to H2O2-induced oxidative stress. LPH supplementation extended lifespan, reduced ROS and MDA levels, enhanced antioxidant enzyme activities (SOD, CAT, GSH-Px), and preserved intestinal structure by regulating stem cell proliferation. Mechanistically, LPH activated Nrf2-related genes, downregulated mTOR, and modulated gut microbiota composition, suggesting a multifaceted mechanism of action (Chen et al., 2025). Collectively, these findings highlight the strong potential of food-derived bioactive peptides as functional ingredients for enhancing oxidative stress resilience and delaying aging, with D. melanogaster serving as a powerful model for mechanistic insight.
4.3. Integrative omics of antioxidants in Drosophila
Integrative omics studies using Drosophila melanogaster have become a powerful approach for assessing the antioxidant potential of natural sources, offering valuable insights into the identification and quantification of bioactive compounds. The advantages of using Drosophila include their short life cycle and well-characterized genetics, which enable rapid evaluation of the physiological effects of natural antioxidants. For example, curcumin tested in Drosophila has demonstrated significant pharmacological effects linked to its antioxidant activity, underscoring the relevance of this model for in vivo efficacy studies (Rumata et al., 2023). Such approaches also shed light on the role of diet in health and longevity, as shown by studies investigating the impact of antioxidant-rich diets on lifespan extension in fruit flies (Liedo et al., 2012).
The mechanisms by which natural antioxidants mitigate oxidative stress are also being actively explored in fruit fly models. Research indicates that Drosophila can serve as experimental platforms for evaluating the therapeutic potential of diverse antioxidant sources, including mushrooms, which are rich in bioactive compounds with strong antioxidant capacity (Sánchez et al., 2015). Similar findings in related species, such as the Mexican fruit fly (Anastrepha ludens), reveal a positive correlation between consumption of antioxidant-rich nutraceutical compounds and improvements in longevity and overall health (Sánchez et al., 2015).
The integration of advanced omics technologies—such as metabolomics and transcriptomics—further enhances understanding of the biochemical pathways influenced by antioxidants. Multi-omics approaches reveal specific metabolic and gene-expression shifts in response to antioxidant supplementation, as demonstrated in studies examining fruit fly responses to different antioxidant treatments (Lazzari et al., 2020). These integrative data analyses provide a holistic view of the interactions between metabolic pathways and antioxidant compounds, facilitating the identification of health-promoting mechanisms (Rodrigues et al., 2024).
Additionally, comparative studies of antioxidant activity among different food sources have highlighted variations in bioactive compound profiles, which are shaped by both genetic and environmental factors. Such research underscores the value of Drosophila as a model not only for biomedical applications but also for agricultural and nutritional studies aimed at improving food quality and promoting health (Ismail et al., 2023). Together, the synergy between integrative omics and fruit fly models opens new avenues for antioxidant research, functional food development, and translational applications for human health.
4.4. Oxidative stress and dietary interventions
The use of Drosophila melanogaster in dietary intervention research has proven highly effective for evaluating the antioxidant properties of various natural sources, particularly fruits and their derivatives. This organism, commonly known as the fruit fly, serves as a robust model due to its genetic similarity to humans and its short life cycle, which allows for rapid investigation of dietary effects on health and longevity (Hof-Michel et al., 2025; Staats et al., 2018).
A key focus in this field is identifying beneficial fruit-derived compounds with potent antioxidant properties. Polyphenols, carotenoids, and other bioactive antioxidants from fruits have been shown to improve health outcomes in Drosophila models. For example, Spirulina platensis extracts, rich in antioxidants, have been demonstrated to mitigate oxidative stress, enhance resistance to FeSO4-induced toxicity, reduce mortality rates, and improve locomotor function in fruit flies (Salim et al., 2019). Similarly, diets high in antioxidants are positively associated with extended lifespan and improved metabolic profiles in Drosophila (Jo and Imm, 2017).
Phenolic compounds, particularly abundant in cherries, berries, and other fruits, are of notable interest due to their ability to lower oxidative stress markers and reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disorders (Zujko et al., 2022). The concept of total antioxidant capacity (TAC) has emerged as a valuable metric for evaluating diet quality, with studies linking high-TAC diets to reduced oxidative damage and enhanced overall health metrics in Drosophila models (Xu et al., 2017; Frakchi et al., 2024; Mancini et al., 2017).
In addition, research highlights that specific dietary components, such as sucrose, can modulate the oxidative defense system in Drosophila, suggesting that dietary moderation plays a significant role in influencing oxidative stress responses, tissue damage, and longevity (Sánchez et al., 2015). The inclusion of natural antioxidants from açaí berries has also been associated with positive health outcomes, reinforcing their potential as functional food components in targeted dietary interventions (Strilbytska et al., 2022).
Furthermore, studies integrating Drosophila models into nutrigenomics research emphasize the importance of understanding how dietary interventions interact with genetic factors to optimize health outcomes (Ferreira et al., 2016). This area of research holds promise for guiding policymakers and nutrition experts in developing dietary guidelines that strategically leverage the antioxidant potential of natural foods to promote health and longevity.
| 5. Use of C. elegans in antioxidant and oxidative stress research | ▴Top |
The nematode Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) has emerged as a prominent model organism for studying oxidative stress and antioxidant mechanisms, largely due to its genetic similarities to humans, short lifespan, and well-characterized biology. This review aims to synthesize existing knowledge regarding C. elegans as a model for investigating antioxidant properties, elucidating mechanisms through which various compounds exert protective effects against oxidative stress.
The utilization of C. elegans in antioxidant research is well-supported by its well-mapped genome and the availability of numerous mutant strains, facilitating targeted studies on specific pathways related to oxidative stress resistance and aging. Significant advancements have been made in understanding the role of specific molecular pathways, particularly those involving transcription factors like DAF-16/FOXO. DAF-16 has been shown to mediate the oxidative stress response, with studies indicating that modulation of this pathway through dietary compounds can enhance the organism’s stress resistance and longevity (Shi et al., 2012; Chen et al., 2021; Ayuda-Durán et al., 2020). Moreover, the connection between the antioxidant potential of phytochemicals and lifespan extension via the insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathway has been emphasized (Zhao et al., 2017; Chen et al., 2021; Ayuda-Durán et al., 2020).
Numerous studies demonstrate that various natural products exhibit antioxidant capacities when tested in C. elegans. For example, flavonoids and polyphenols have shown protective effects, primarily through their antioxidative activities (Shi et al., 2012; (Ayuda-Durán et al., 2020). In particular, the antioxidant effects of quercetin were enhanced when combined with sugar moieties, suggesting that the biomass composition of such compounds plays a crucial role in their bioavailability and efficacy (Cheng et al., 2014). Similarly, studies of polysaccharides from sources like Auricularia auricular and Brassica chinensis have highlighted their potential to mitigate oxidative stress and promote healthier aging in this nematode model (Fang et al., 2019; Chen et al., 2016b).
Moreover, the enzymatic activity related to the detoxification of reactive oxygen species (ROS) has also been studied extensively, revealing that antioxidant enzymes such as SOD and CAT play significant roles in the survival of C. elegans under oxidative stress conditions. Studies noted the induction of these enzymes in response to various stressors, suggesting that the organism’s innate defense mechanisms are robust and can be influenced by dietary antioxidants or environmental conditions (Song et al., 2014; Li et al., 2013). The interaction between these enzymes and genetic modulators underscores the complexity of oxidative stress response networks that can potentially be targeted for therapeutic interventions against aging and associated oxidative damage Zhu et al., 2022; Li et al., 2013). Figure 3. Overview of Caenorhabditis elegans as an antioxidant model presented in this review. The figure highlights how C. elegans has been utilized to investigate antioxidant activity, oxidative stress pathways, and physiological responses relevant to antioxidant research.
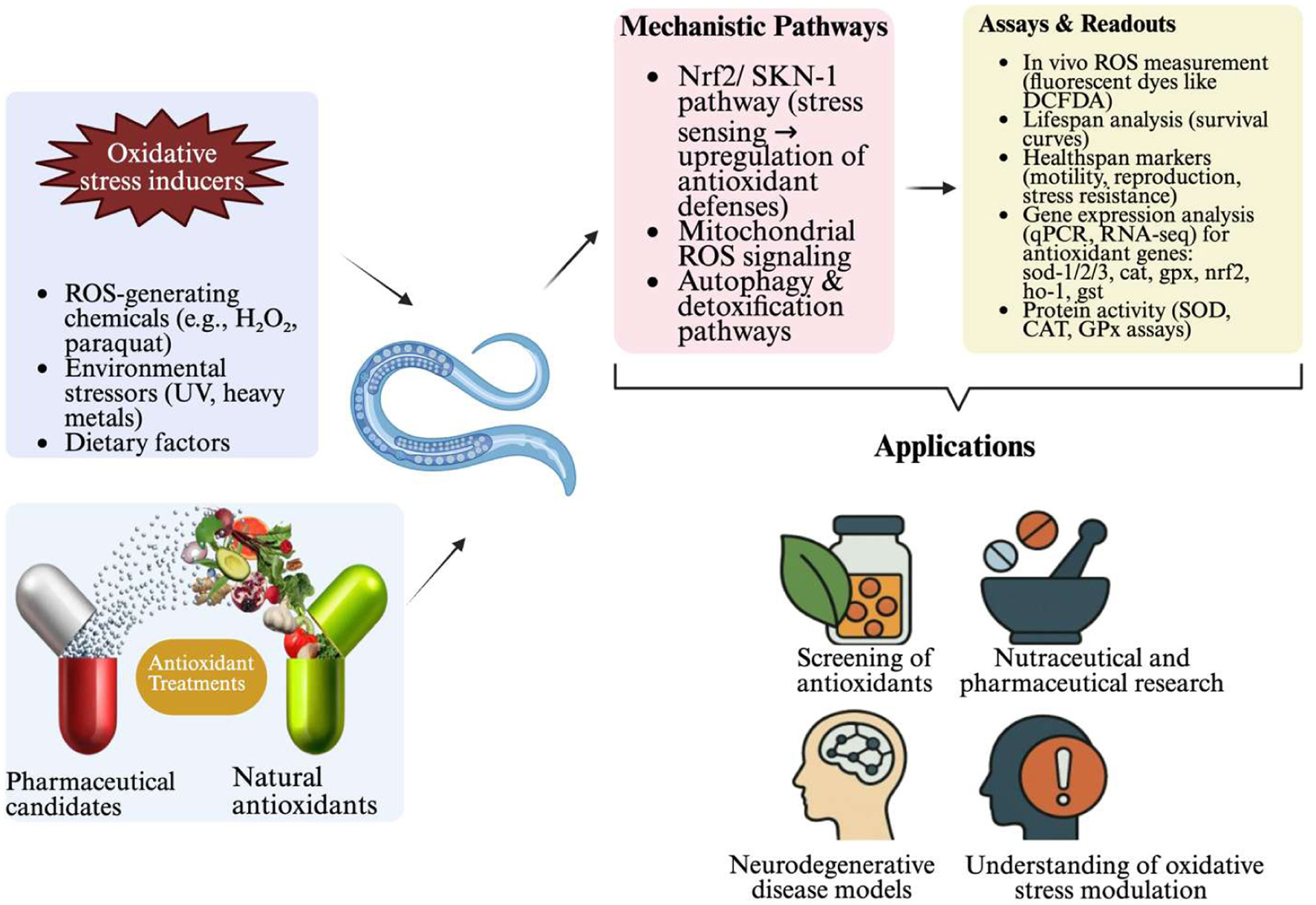 Click for large image | Figure 3. Overview of Caenorhabditis elegans as an antioxidant research model |
5.1. Genetic insights into antioxidant activity
Research demonstrates that C. elegans offers valuable insights into how antioxidant compounds modulate cellular stress mechanisms. The nematode has been widely employed to assess the antioxidant potential of diverse natural products, including polyphenols and polysaccharides (Ayuda-Durán et al., 2020; Pang et al., 2024; Zhu et al., 2022). For example, polysaccharides isolated from Dendrobium officinale exhibited significant antioxidant activity when tested in C. elegans, highlighting the organism’s utility in evaluating plant-derived antioxidants and their effects on oxidative stress (Pang et al., 2024). Similarly, compounds such as quercetin have demonstrated multiple biological activities, including neuroprotective effects, indicating that natural antioxidants can function via several pathways, many of which have been validated using C. elegans models (Schiavi et al., 2023).
The antioxidant pathways activated in C. elegans, such as the SKN-1/Nrf signaling pathway, are particularly important for mediating oxidative stress responses. Understanding these pathways is essential for elucidating mechanisms related to longevity, stress resistance, and metabolic health (Blackwell et al., 2015). One advantage of C. elegans lies in its genetic tractability; techniques like RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) have enabled the identification of key genes and regulatory networks involved in antioxidant defense, providing a molecular framework for studying these protective processes (Shen, 2025).
Natural antioxidants have also been shown to enhance the organism’s resistance to oxidative stress. For instance, treatments with various selenium species have been reported to boost antioxidative defenses in C. elegans, with early supplementation producing long-lasting improvements in stress response capabilities (Rohn et al., 2019). Such findings suggest that dietary antioxidants can exert persistent beneficial effects on healthspan and resilience to oxidative damage.
Furthermore, the availability of transgenic C. elegans lines expressing fluorescent markers allows for dynamic visualization of antioxidant effects on cellular and physiological states. These tools enable real-time monitoring of how natural compounds influence oxidative stress and cellular function, deepening the mechanistic understanding of antioxidant action in vivo (Li et al., 2023b).
5.2. Integrative omics of antioxidant mechanisms
Integrative omics studies utilizing Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) as an experimental model have become a crucial approach for evaluating the antioxidant potential of various natural sources. By employing multi-omics strategies, including genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, researchers can gain a comprehensive understanding of antioxidant mechanisms, particularly in the context of oxidative stress and aging.
C. elegans is an effective in vivo model for antioxidant research due to its well-characterized genetics and conserved metabolic pathways. Critical signaling pathways associated with oxidative stress responses, such as the insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathway involving DAF-2/IGF-1R, AGE-1/PI3K, and DAF-16/FOXO, have been well established. Manipulation of these pathways has been shown to enhance lifespan and stress resistance, reflecting the organism’s antioxidant capacity (Pang et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2022). Moreover, natural compounds have been reported to modulate these pathways, contributing to improved oxidative resistance and longevity in C. elegans (Zeng et al., 2021).
In integrative omics studies, the antioxidant effects of natural extracts have been assessed through metabolomic analyses. For instance, polysaccharides derived from mushrooms such as Auricularia auricular and Lactarius deliciosus demonstrated significant antioxidant activities, improving survival rates of C. elegans exposed to oxidative stress (Fang et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2022). Such studies commonly evaluate parameters including malondialdehyde levels, reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation, and the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as catalase and superoxide dismutase to determine the efficacy of natural compounds (Fang et al., 2019). Additionally, C. elegans serves as a reliable model for investigating the bioavailability and mechanistic action of these antioxidants (Lin et al., 2018).
The application of advanced omics technologies further clarifies the molecular pathways underlying antioxidant activity. Comprehensive multi-omics profiling has revealed metabolic remodeling in response to oxidative stress, including the upregulation of key antioxidant genes and stress-response markers (Wu et al., 2023). This integrative approach not only identifies potential antioxidants but also elucidates their biological effects, such as modulation of metabolic pathways and activation of stress response mechanisms (Wu et al., 2023).
Furthermore, studies using C. elegans have demonstrated the beneficial effects of dietary compounds, such as trigonelline, in enhancing oxidative stress resistance and promoting longevity (Zeng et al., 2021). These findings underscore the significance of diet-derived antioxidants in supporting healthspan, and integrative omics approaches provide a powerful framework for linking metabolic shifts to longevity and stress resilience in this model organism.
5.3. Dietary interventions for stress resistance
The exploration of dietary interventions to assess the antioxidant potential of natural sources using Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) has gained considerable attention in pharmacological and nutraceutical research. C. elegans is valued as a model organism due to its genetic tractability, well-characterized biology, and the relevance of its oxidative stress response to human health.
A key aspect of using C. elegans for evaluating antioxidant activity is the modulation of crucial antioxidant enzymes, including superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT), which are essential in mitigating oxidative stress. For example, Liu et al. (2016) demonstrated that stereoisomeric forms of astaxanthin enhance the expression of these enzymes, thereby improving C. elegans resistance to oxidative stress induced by paraquat. Similarly, flavonoid compounds such as rutin from Myrciaria tenella have been shown to reduce reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels significantly, with Ribeiro et al. (2019) reporting notable reductions in ROS following rutin treatment. These studies highlight the critical influence of dietary compound structure and function on antioxidant efficacy.
Plant extracts have also been shown to modulate oxidative stress responses in C. elegans. Chen et al. (2016a) reported that Centella asiatica extract activates antioxidative defenses and may influence amyloid beta accumulation, suggesting potential neuroprotective effects, although further research is required. In addition, Arantes et al. (2018) observed that guarana extract downregulates stress-response genes, likely due to its inherent antioxidant properties, indicating a direct impact on cellular repair mechanisms. Collectively, these findings demonstrate how dietary interventions can influence aging processes and enhance the antioxidative capacity of C. elegans.
Various plant-derived compounds have also been associated with longevity and resilience against oxidative damage in C. elegans. Zhao et al. (2017) characterized emodin as a compound capable of stimulating insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathways, leading to increased lifespan and activation of antioxidant enzymes. Similarly, Zou et al. (2024) demonstrated that extracts from Hemerocallis citrina promote lifespan extension by regulating antioxidant enzymes and related genes. These results align with broader literature suggesting that dietary antioxidants can modulate signaling pathways, contributing to age-related health benefits.
| 6. Challenges and limitations | ▴Top |
Our comparative analysis (Table 2) underscores that the three cornerstone model organisms—zebrafish, fruit fly, and C. elegans—each occupy a distinct niche in the research pipeline. Zebrafish, as vertebrates, are exceptionally valuable for direct translational applications in toxicology and disease modeling, leveraging their genetic homology and suitability for live imaging. Conversely, D. melanogaster and C. elegans serve as powerful discovery engines for initial screening and mechanistic inquiry; the fly excels in genetic dissection of pathways, while the worm is the premier model for high-throughput lifespan and stress resistance studies. This tiered approach, from simple invertebrates to more complex vertebrates, allows for efficient triaging of compounds and hypotheses before committing to higher-cost mammalian models.
 Click to view | Table 2. Summary of the strengths, limitations, and translational value of zebrafish, fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster), and Caenorhabditis elegans in antioxidant research |
The zebrafish (Danio rerio) model has gained prominence in antioxidant research due to its suitability for in vivo experimentation. Its advantages include rapid development, genetic similarities to humans, and the visibility of phenotypic changes through its transparent embryos (Wang et al., 2023a; Kim et al., 2021). However, several limitations exist when using zebrafish for antioxidant studies.
One primary concern is the potential variability in physiological responses among zebrafish. This variability can arise from factors such as genetic background, environmental conditions, and developmental stages. Variations in methodologies—such as exposure times and concentrations of tested compounds—may lead to inconsistent results in antioxidant assays (Arteaga et al., 2024). Different protocols can yield vastly different outcomes, amplifying the need for standardized procedures in zebrafish studies. This lack of standardization complicates the comparison of findings across different research groups and can hinder the reproducibility of antioxidant effects.
Another significant limitation is the disconnect between in vitro and in vivo responses. For instance, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) failed to induce the Nrf2 pathway in tested zebrafish cell lines, which contrasts with responses observed in mammalian cells and in whole zebrafish embryos. This demonstrates that even optimized in vitro systems require validation in the whole organism to ensure physiological relevance (Lungu-Mitea et al., 2018). Moreover, a high antioxidant potential does not always guarantee a safe toxicological profile. Studies on Australian fruit extracts revealed that despite strong antioxidant activity, in vivo assessments still demonstrated potential toxic effects, underscoring the importance of comprehensive toxicological screening before pharmacological or nutraceutical application (Ali et al., 2022).
Additionally, the robustness of the zebrafish model in simulating human metabolic processes must be carefully evaluated. While zebrafish share many genetic and physiological similarities with humans, their responses to oxidative stress and antioxidant interventions are not always analogous. Some studies indicate that zebrafish exhibit a higher resistance to harmful agents compared to mammalian systems, which may lead to an underestimation of cytotoxic effects (Jaja-Chimedza et al., 2012; Wang et al., 2020). Zebrafish are also ectothermic, relying on glycolysis under fluctuating oxygen conditions and possessing a higher proportion of unsaturated fatty acids in their membranes, which makes them more prone to oxidative damage—traits that may not directly translate to human physiology (Fang and Miller, 2012).
Environmental variables can further confound experimental results. Water parameters, such as temperature and pH, significantly influence oxidative stress responses and metabolic rates, potentially skewing antioxidant assessments (Kim et al., 2021; Arteaga et al., 2024). Maintaining controlled laboratory conditions is crucial but challenging, particularly in large-scale experiments. Developmental stage differences also influence outcomes, as antioxidant responses observed in embryos may not reflect those in adult zebrafish due to differing metabolic states (Nguyen et al., 2018).
Finally, while the transparency of zebrafish embryos allows real-time imaging of oxidative stress markers, visual assessment methods yield largely qualitative data, which may not always correlate with quantitative biochemical measures. This raises the risk of overinterpreting antioxidant efficacy and highlights the need for complementary quantitative assays (Wang et al., 2023a; Arteaga et al., 2024).
Similar challenges exist in ecotoxicological research, where predicting the risk of chronic, low-level contaminant exposure is complex. Compounds such as arsenic trioxide and maduramicin can induce significant oxidative stress and cellular damage even at concentrations considered safe by regulatory standards, underscoring the need for improved risk assessment models in aquatic systems (Sarkar et al., 2014; Ni et al., 2019).
The fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) is also widely used in oxidative stress and antioxidant studies due to its genetic tractability and short lifespan. However, its simpler biological systems can limit translational relevance. For example, studies investigating antioxidants such as curcumin or vitamin C in Drosophila models of neurodegenerative diseases mimic human conditions only partially, with significant differences in pathophysiology (Nghi et al., 2022; Anh et al., 2019). This raises concerns about the direct applicability of findings to humans, as certain cellular pathways and regulatory mechanisms may differ substantially (Hwang et al., 2013; Mockett et al., 1999).
Genetic manipulation is common in Drosophila research but can introduce unintended phenotypes that confound results. Overexpression of antioxidant enzymes such as glutathione reductase altered longevity and stress resistance under hyperoxic conditions but did not fully represent mild oxidative stress responses (Mockett et al., 1999; Aigaki et al., 2004). Similarly, transgenic models of human disease may not capture the full genetic and environmental variability of human populations (Jahromi et al., 2013).
Methodological issues also arise from the use of chemical assays such as DPPH radical scavenging tests, which may not capture the complexity of oxidative stress in living organisms (Nwachukwu et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2021). Antioxidants showing strong in vitro activity may display very different efficacy in vivo due to metabolism and bioavailability differences (Dias-Santagata et al., 2007; Zhong et al., 2022). Furthermore, acute oxidative stress models (e.g., paraquat exposure) may not reflect the chronic oxidative stress that underlies most human diseases, risking a bias toward short-term protective mechanisms (Seong et al., 2015).
The nematode Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) is another valuable model for oxidative stress research due to its genetic tractability and conserved stress response pathways. However, strain-specific responses to oxidative stress inducers such as H2O2, paraquat, and sodium arsenite can complicate interpretation (Lee et al., 2006; Chen et al., 2024). Moreover, antioxidants may exert dual effects, enhancing resistance at certain doses but inducing stress at others (Kim and Park, 2020; Liu et al., 2021a; Wu et al., 2022; Chen et al., 2022). Genetic modifications—such as transgenic overexpression of stress-related genes—can further skew results and limit extrapolation to wild-type organisms (Ma et al., 2016; Benedetto et al., 2010).
Beyond these methodological challenges, C. elegans studies face general limitations regarding translatability to human biology. Despite sharing conserved signaling pathways such as DAF-2/IGF-1R and DAF-16/FOXO, species-specific differences in pathway regulation can impact the interpretation of results (Pang et al., 2023; Zou et al., 2024). The nematode’s short lifespan (2–3 weeks) restricts long-term aging studies, and its laboratory environment fails to replicate key factors such as gut microbiota interactions, which are critical for antioxidant metabolism in humans (Reigada et al., 2022; Barreto et al., 2020). Furthermore, dose-response relationships often fail to correspond to physiologically relevant human intakes (Pang et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2022).
Finally, C. elegans lacks behavioral and physiological complexity, limiting its usefulness in studying the neurological and systemic impacts of oxidative stress (Zou et al., 2024; Arantes et al., 2018). Therefore, while C. elegans provides mechanistic insights into oxidative stress and aging, validation in more complex mammalian models remains essential for translating findings to human health (Morcos and Hutter, 2009; Zhang et al., 2021).
| 7. Applications and future direction | ▴Top |
Scientists often use simple animals to study how antioxidants work. These animals are useful because they are easy to grow and their genes are easy to study. Table 1 shows how three common animals—the zebrafish, fruit fly, and a tiny worm called C. elegans—are used to find and test new antioxidants. A significant direction in antioxidant research involves the development of sophisticated in vitro assays using zebrafish cell lines. The establishment of Nrf2-responsive reporter gene assays in lines such as ZFL and ZF4 offers an effective alternative to in vivo testing. This aligns with the 3Rs principle (Replacement, Reduction, and Refinement), enabling high-throughput screening of chemicals and environmental samples for oxidative stress potential, thereby accelerating toxicological risk assessment (Lungu-Mitea et al., 2018). In parallel, the screening of natural antioxidants from sources like marine algae is gaining momentum. For instance, sulfated polysaccharides from Sargassum tenerrimum have shown efficacy in mitigating oxidative damage in both cellular and whole-organism models, pointing to novel nutraceutical and pharmaceutical candidates (Raguraman et al., 2019). Zebrafish are also increasingly used to evaluate the therapeutic potential of novel compounds for complex diseases. Studies on metabolites such as cotinine and 6-hydroxy-L-nicotine demonstrate their utility in assessing multi-target agents that improve cholinergic function, reduce oxidative stress, and enhance neuroprotective gene expression, making them promising leads for cognitive disorders like Alzheimer’s disease (Szychlinska and Marino Gammazza, 2025).Furthermore, the integration of CRISPR/Cas9-based genetic manipulation enables precise investigation of disease mechanisms and treatment responses, advancing personalized medicine approaches with zebrafish models (Hong and Luo, 2021) (Table 1).
Similarly, Drosophila melanogaster provides unique opportunities for advancing antioxidant research beyond traditional lifespan and stress-resistance assays. Emerging studies advocate incorporating multi-omics strategies—transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics—to map molecular networks modulated by dietary antioxidants. These approaches can identify target genes, signaling pathways, and molecular interactions underlying antioxidant effects while also clarifying the long-term impact of sustained phytochemical exposure on oxidative stress–related diseases. Comparative analyses across diverse Drosophila strains or closely related species may further reveal how genetic variability contributes to antioxidant responses, enriching our understanding of gene–diet interactions. Such efforts will not only highlight protective effects but also uncover potential adverse impacts of prolonged antioxidant intake, thereby enhancing the translational value of Drosophila in functional food and nutraceutical research.
The nematode Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) also remains central to oxidative stress research, particularly in aging and antioxidant defense studies. Future directions include probing gene regulation mechanisms, where transcription factors like DAF-16 (FoxO orthologue) and NHR-49 mediate stress tolerance and longevity by activating detoxification genes such as gst-4 and gcs-1 (Hu et al., 2018; Chen et al., 2024; Liu et al., 2021b). Natural antioxidants such as rosmarinic acid and phenolic compounds modulate insulin signaling pathways, enhance antioxidant defenses, and extend healthspan (Lin et al., 2019; Saier et al., 2018). Polyphenols and carotenoids further exhibit dual functions in scavenging ROS and enhancing endogenous defenses, though their effects depend on dose and gut microbiota interactions (Llopis et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2019; González-Peña et al., 2021; Ayuda-Durán et al., 2022). Beyond longevity, oxidative stress intersects with neurodegenerative models, where early oxidative damage has been shown to precede β-amyloid accumulation in Alzheimer’s disease models (Moliner et al., 2019; Chin et al., 2024). Advanced technologies such as microfluidics now facilitate high-throughput drug screening, accelerating the discovery of compounds targeting oxidative stress pathways (Wang et al., 2019). Collectively, these advances highlight the expanding role of C. elegans in deciphering oxidative stress biology and identifying therapeutic interventions.
| 8. Conclusion | ▴Top |
Small animal models such as zebrafish (Danio rerio), Caenorhabditis elegans, and fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) remain invaluable in vivo systems for studying dietary antioxidants. Their short lifespans, rapid reproduction, ease of genetic manipulation, conserved molecular pathways, and genetic homology to humans make them ideal for mechanistic investigations and high-throughput screening. These models enable detailed evaluation of bioavailability, absorption, metabolism, and antioxidant mechanisms, while providing functional insights into resistance to oxidative stress, age-related disorders, metabolic and neurological health, and potential lifespan extension.
However, translation of these findings to human health requires careful consideration of interspecies differences, including metabolism, gut physiology, microbiota composition, and dose scaling. For instance, differences in intestinal absorption rates, enzymatic biotransformation, and systemic distribution of antioxidants may lead to variability in efficacy between model organisms and humans. Standardization of assay conditions, dietary delivery, and exposure protocols is essential to improve reproducibility and comparability across studies.
Importantly, data from these models can guide the design of human trials and functional food development by identifying candidate bioactive compounds, elucidating molecular targets, and predicting safety profiles before advancing to mammalian models or clinical research. Advances in CRISPR-based genome editing, live imaging, metabolomics, and multi-omics integration continue to enhance the translational relevance of these models, bridging the gap between discovery science and evidence-based nutritional interventions. Collectively, these organisms represent cost-effective, ethically viable platforms that not only accelerate antioxidant research but also inform precision nutrition strategies and the rational design of functional foods and nutraceuticals for mitigating oxidative stress–related diseases in humans.
| References | ▴Top |