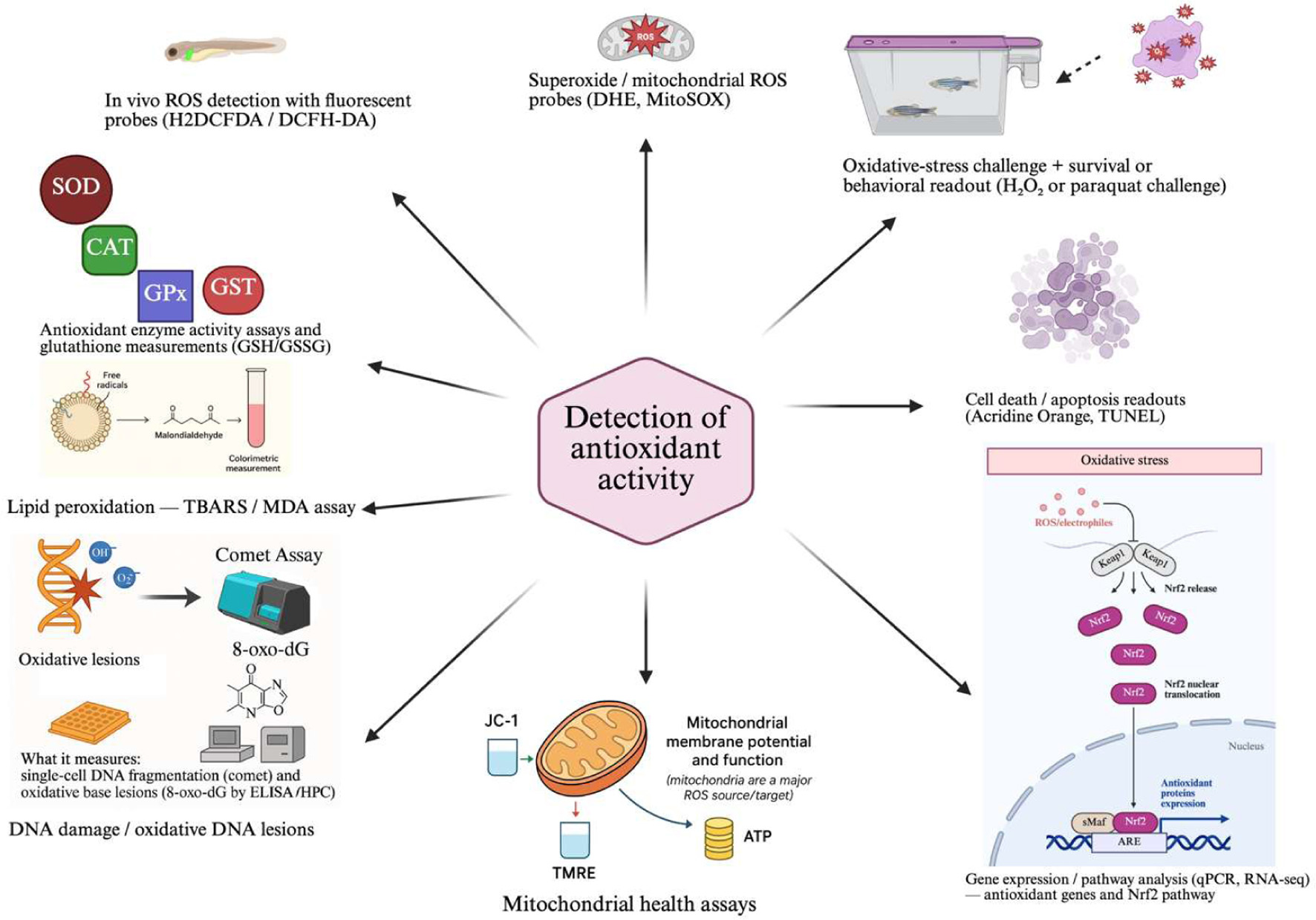
Figure 1. Different antioxidant detection methods using zebrafish models.
| Journal of Food Bioactives, ISSN 2637-8752 print, 2637-8779 online |
| Journal website www.isnff-jfb.com |
Review
Volume 31, September 2025, pages 41-62
Beyond petri dish: small animal models bridge in vitro and in vivo antioxidant assays
Figures

Tables
| Compound/Extract | Source | Key Findings in Zebrafish | Mechanisms/Pathways | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zebra fish model | ||||
| Water Extract of Citrus Pomace | Citrus Pomace | Improved survival rates; reduced heartbeat and ROS levels. | Scavenging of free radicals; reduction of cell death. | Wang et al., 2018 |
| Heat-killed LAB Strains | Various Lactic Acid Bacteria | Reduced H2O2-induced toxicity; all strains showed antioxidant activity. | Indirect antioxidant activity; activation of antioxidant enzymes. | Sato et al., 2024 |
| Rutin Trihydrate | Not specified | Increased GPx (9%), GSH (5%), GST (5%); countered doxorubicin effects. | Upregulation of key antioxidant enzymes; oxidative stress response. | Seethalakshmi and Kumar, 2024 |
| 6-Gingerol | Ginger | Reduced ROS and cell death; ↑SOD and CAT; ↓lipid peroxidation in larvae. | Direct antioxidant activity; regulation of ROS and H2O2. | Manjunathan et al., 2021 |
| Naringenin | Citrus, food sources | Protective against oxidative stress-induced lethality. | Induction of antioxidant pathways (e.g., Nrf2). | Arteaga et al., 2021 |
| Apigenin | Parsley, food sources | Protective against lethality and dysmorphogenesis. | Activation of cellular protective responses. | Arteaga et al., 2021 |
| Rutin | Buckwheat, food sources | Protective against lethality and dysmorphogenesis. | Enhanced oxidative stress resistance. | Arteaga et al., 2021 |
| Oleuropein | Olive, food sources | Protective against oxidative stress-induced lethality. | Modulation of oxidative stress mechanisms. | Arteaga et al., 2021 |
| Chlorogenic Acid | Coffee, food sources | Protective against oxidative stress-induced lethality. | Support of antioxidant defense systems. | Arteaga et al., 2021 |
| Curcumin | Turmeric, food sources | Protective against lethality and dysmorphogenesis. | Activation of Nrf2 and other protective pathways. | Arteaga et al., 2021 |
| Lycopene | Tomato, food sources | Protective against oxidative stress-induced lethality. | Enhancement of antioxidant pathways. | Arteaga et al., 2021 |
| Astaxanthin | Algae, food sources | Protective against oxidative stress-induced lethality. | Modulation of cellular oxidative stress response. | Arteaga et al., 2021 |
| β-Carotene | Carrot, food sources | Increased lethality and dysmorphogenesis at tested conditions. | Potential pro-oxidant effects at certain concentrations. | Arteaga et al., 2021 |
| Carnosine | – | Decreased ROS in larvae; rescued Hsp70 and MT expression altered by TiO2 NPs. | Antioxidant activity counteracting TiO2 nanoparticle-induced oxidative stress. | Caruso et al., 2023 |
| Phosvitin | Zebrafish Egg Yolk | Effective antioxidant; inhibited linoleic acid oxidation; non-cytotoxic. | Scavenges DPPH radicals; protects biomolecules from oxidation. | Hu et al., 2015 |
| Chlorogenic Acid | Sonchus oleraceus (Sowthistle) | Reduced phenotypic abnormalities in embryos exposed to pro-oxidant auranofin. | Protective effects against oxidative stress and malformation. | Chiu et al., 2020 |
| Nrf2 Inducers | Various Compounds | Induced expression of antioxidant genes (HO-1, NQO1, GSTs). | Activation of the Nrf2-ARE pathway. | Jung and Kwak, 2010 |
| Quercetin Nanocrystals | Nanosuspension | Enhanced survival rates (66.67–77.78%) in H2O2-treated zebrafish. | Reduced ROS levels; catalyzed increased CAT and GPx activity. | Wang et al., 2023a |
| Glutathione (GSH) | Endogenous System | Robust antioxidant system; oxidized by ROS forming GSSG. | Involves GPx and GR; key oxidative stress marker. | Massarsky et al., 2017 |
| N/A (Review on Drug Screening) | N/A | Review of zebrafish as a model for novel anti-inflammatory drug screening. | Analysis of inflammatory response and leukocyte behavior. | Xie et al., 2021 |
| Lignin-Carbohydrate Complexes | Wheat Stalk | Protected against BPA-induced neurotoxicity; reduced ROS and neuronal damage. | Suppressed nerve-related gene expression; reduced oxidative stress. | Gu et al., 2021 |
| Polyphenolic Extract | Condalia microphylla Fruits | Inhibited lipid oxidation by up to 40% under oxidative stress. | Antioxidant activity; reduction of oxidative stress. | Boeri et al., 2017 |
| Catechol | Experimental Compound | Increased ROS, reduced antioxidant capacity; decreased locomotor activity, increased anxiety. | Induction of redox imbalance; behavioral disruption. | Xiao et al., 2025 |
| Equol | Soy | Exerts strong antioxidant effects. | Functions through an Nrf2-independent mechanism. | Watanabe et al., 2022 |
| Total Particulate Matter (TPM) | Cigarette Smoke | Increased mortality, delayed hatching, deformities, and behavioral changes. | Disrupted angiogenesis; affected xenobiotic metabolism and oxidative stress. | Massarsky et al., 2015 |
| tBOOH | Oxidant (Positive Control) | Induces oxidative stress in zebrafish embryos. | Used as a model oxidant to test protective effects of antioxidants. | Boix et al., 2020 |
| TCHQ | Oxidant (Positive Control) | Induces oxidative stress in zebrafish embryos. | Used as a model oxidant to test protective effects of antioxidants. | Boix et al., 2020 |
| LPS | Escherichia coli | Induces oxidative stress in zebrafish embryos. | Used to model inflammatory/oxidative stress to test antioxidants. | Boix et al., 2020 |
| Momordica cochinchinensis Extract | Gac Fruit | Improved locomotor functions in an MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease model. | Not linked to significant change in antioxidant enzyme activities. | Singsai et al., 2023 |
| Formulated Agar 1 | Turbinaria conoides (Seaweed) | Higher antioxidant activity; lower teratogenic effects. | Demonstrates dose-dependent antioxidant potential. | Aavula et al., 2022 |
| Formulated Agar 2 | Turbinaria conoides (Seaweed) | Lower antioxidant activity; higher teratogenic effects. | Demonstrates dose-dependent toxicity. | Aavula et al., 2022 |
| Curcumin | Turmeric | Reduces hydrogen peroxide-induced toxicity. | Nrf2-dependent pathway activation. | Endo et al., 2020 |
| Diallyl Trisulfide | Garlic | Reduces hydrogen peroxide-induced toxicity. | Nrf2-dependent pathway activation. | Endo et al., 2020 |
| Quercetin | Various plants | Reduces hydrogen peroxide-induced toxicity. | Nrf2-dependent pathway activation. | Endo et al., 2020 |
| Cinnamaldehyde | Cinnamon | Reduces arsenite toxicity; exhibits antioxidant effects. | Nrf2-independent pathway. | Endo et al., 2020 |
| Carnosic Acid | Rosemary | Toxic at high concentrations; antioxidant analysis inconclusive. | Proposed Nrf2 pathway; confounded by toxicity. | Endo et al., 2020 |
| Troxerutin | Semi-synthetic flavonoid | Reduced MPO, NO, and LPO; protective against nicotine-induced lung fibrosis. | Scavenges free radicals; enhances defense; suppresses IL-10 & IL-1β expression. | Hobani, 2024 |
| Dieckol | Ecklonia cava (Brown seaweed) | Reduced ROS, nitric oxide, and cell death induced by UVB radiation. | Direct antioxidant activity; protective against UVB-induced damage. | Wang et al., 2021 |
| Antioxidant Peptides | C-phycocyanin (from algae) | Protective against H2O2-induced oxidative stress. | Activation of Nrf2 signaling pathway. | Xu et al., 2022 |
| Lignin–carbohydrate complexes (LCCs) | Bamboo and Poplar | Scavenged endogenous ROS effectively. | Prevented reduction of antioxidant enzyme activity (SOD, CAT). | Dong et al., 2019 |
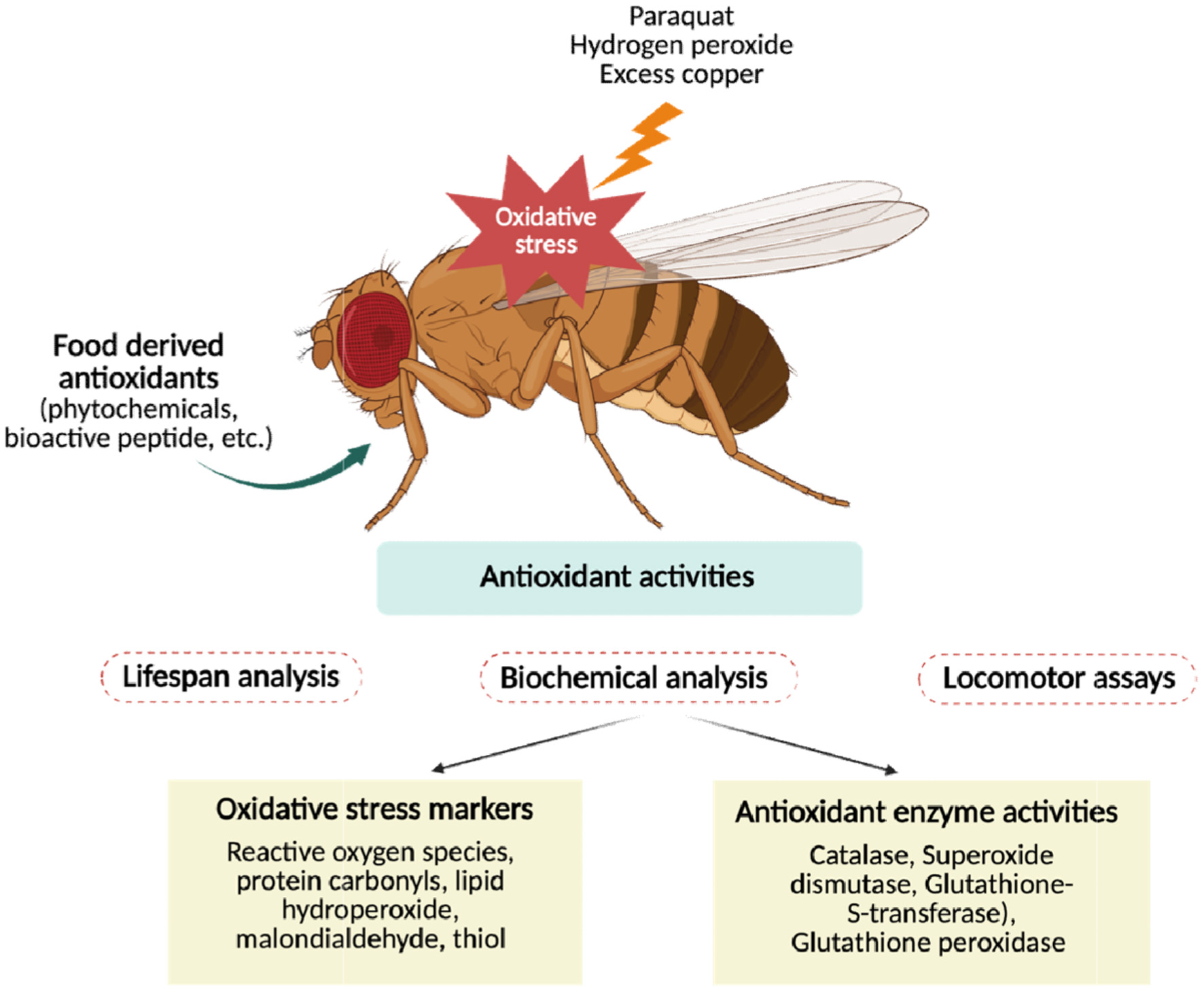
| Fruit fly model | ||||
| Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside (Anthocyanin) | Lonicera pallasii (Honeysuckle) | Increased lifespan and stress resistance; improved intestinal barrier integrity | Sirt6 activation; regulation of Hif1 & Keap1 | Golubev et al., 2022 |
| Mangifera indica leaf extract | Mangifera indica (Mango) | Enhanced survival; ↑GST, CAT activity; ↑thiol content | Enzyme induction (dose-sensitive) | Alexander et al., 2019 |
| Astragalus membranaceus extract (AME) | Astragalus membranaceus | Enhanced survival under H2O2 challenge; ↓ROS; ↑SOD, CAT; ↑Sod1, Cat, CncC | Enzyme induction; gene regulation | Dai et al., 2024 |
| Curcumin | Turmeric | Lifespan extension (males); reversed by SOD inhibitor | SOD-dependent pathway | Suckow and Suckow, 2006 |
| Flavonoids (icariin, epimedins A–C) | Epimedium pubescens | Enhanced radical-scavenging; boosted CAT, GSH-Px | Antioxidant enzyme activation | Yang et al., 2020 |
| Proanthocyanidin-rich fraction | Tamarindus indica | Improved lifespan, emergence rate, antioxidant enzyme activity; ↓AChE, caspase-3/9 | Antioxidant enzyme activation; neuroprotection | Jaafaru et al., 2024 |
| Artemisia argyi extract | Artemisia argyi | Prolonged lifespan; improved climbing; ↑stress tolerance; enzyme modulation; ↓MDA | SOD, CAT modulation | Yang et al., 2024 |
| Phlorizin | Apple | Lifespan extension; improved locomotion; ↑Nrf2/cnc, ↓methuselah | Nrf2 activator; stress regulation | Wang et al., 2019 |
| Crimson snapper scale peptides | Marine fish | Extended lifespan; ↓MDA, protein carbonylation; ↑SOD, CAT | Upregulation of SOD1, SOD2, CAT | Chen et al., 2020 |
| Rice protein hydrolysates | Rice | Increased lifespan; boosted SOD, Mn-SOD, CAT | Nrf2/Keap1, TOR/S6K, methuselah modulation | Yue et al., 2021 |
| Casein peptides | Milk protein | Improved survival; restored GSH, thiols, proteins; normalized oxidative markers | Keap1/Nrf2 regulation | Sadiq et al., 2023 |
| Lateolabrax japonicus peptides (LPH) | Japanese seabass | Extended lifespan; ↓ROS, MDA; ↑SOD, CAT, GSH-Px; preserved gut integrity | Nrf2 activation; mTOR downregulation; gut microbiota modulation | Li et al., 2023b |
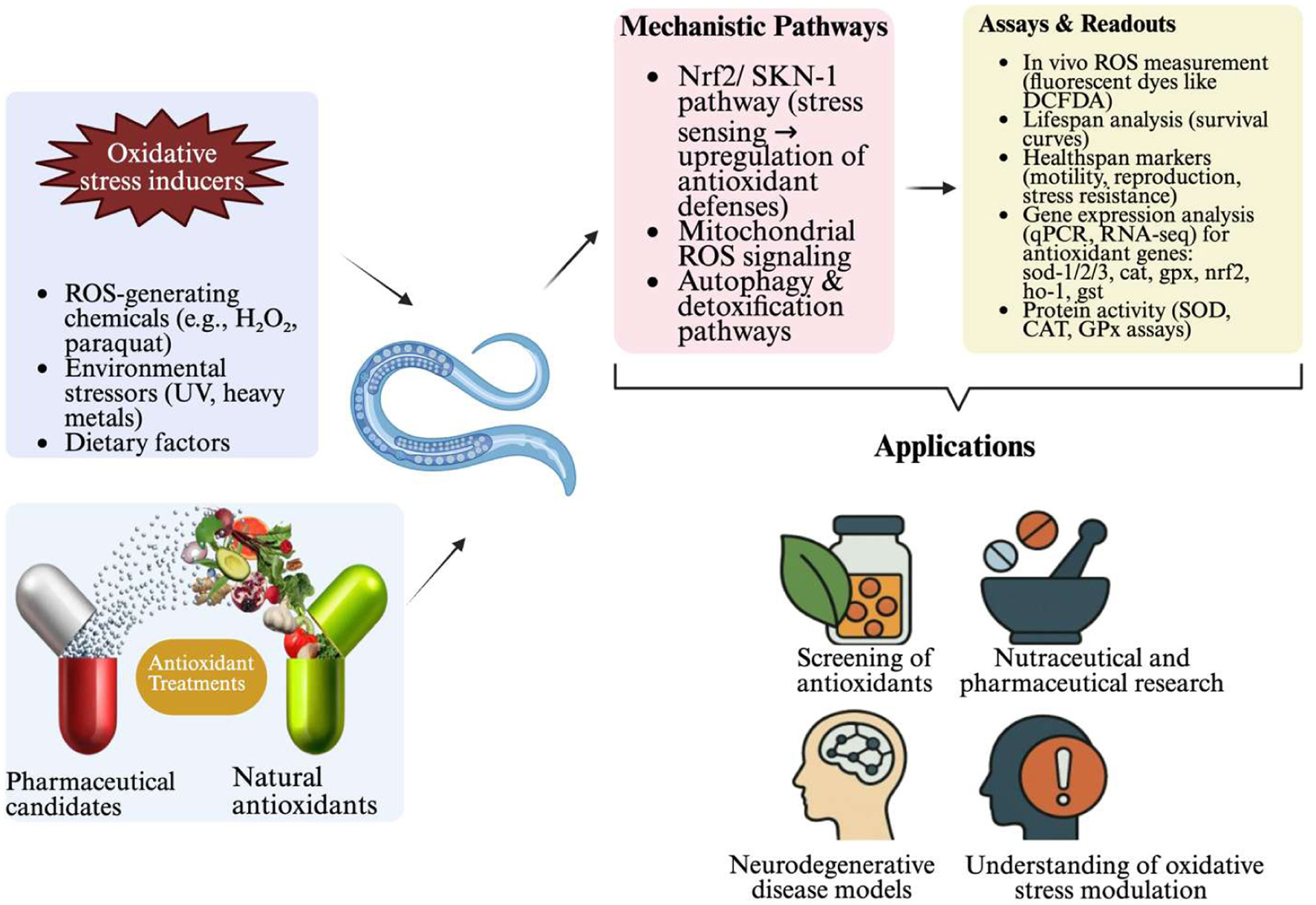
| C. elegans model | ||||
| Rhein Derivative 4b | Rhein | Increases lifespan & stress resistance; enhances GSH; reduces MDA & ROS | Targets Keap1-Nrf2 pathway | Wang, 2025 |
| Monascus-fermented Dioscorea (RMDE) | Yam | Increases survival during oxidative stress; reduces ROS | DAF-16/FOXO-dependent pathway; induces sod-3 expression | Shi et al., 2012 |
| Magnolol Derivative M27 | Houpoea officinalis | Prolongs lifespan; improves healthspan; increases stress resistance | IIS pathway (DAF-2, AGE-1, DAF-16) | Pang et al., 2023 |
| Polyphenols | Blumea laciniata | Extends lifespan (17.4%); enhances stress resistance; reduces ROS & MDA | Insulin/IGF-1 signaling; promotes DAF-16 nuclear translocation | Chen et al., 2021 |
| Caffeic Acid Phenethylester (CAPE) | Propolis | Increases stress resistance & lifespan (∼9–17%); reduces ROS | Modulates DAF-16 signaling pathway; SKN-1 independent | Havermann et al., 2014 |
| Methanol Extract | Camellia tenuifolia | Prolongs lifespan; reduces amyloid-β toxicity | Decreases intracellular ROS levels | Wei et al., 2014 |
| Kaempferol Glycosides | Camellia tenuifolia | Decreases ROS levels; prolongs lifespan | Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities | Wei et al., 2014 |
| Hot Water Extract | Chamaecyparis obtusa | Extends lifespan; decreases lipofuscin | Enhanced antioxidant activity via flavonoid absorption | Cheng et al., 2014 |
| Guarana | Paullinia cupana | Extends lifespan; antioxidant activity | DAF-16, HSF-1, SKN-1 pathways | Arantes et al. 2018 |
| Selenite | – | Protects from oxidative stress | DAF-16 and TRXR-1 dependent | Li et al., 2013 |
| Oleuropein | Olive | Prolongs lifespan (22.3%); increases survival against stress | Insulin/IGF-1 and SKN-1/Nrf2 signaling pathways | Fang and Miller, 2012 |
| Yeast Hydrolysate | Yeast | Enhances lifespan and stress resistance | Modulates tyrosine, glycerophospholipid, and glutathione metabolism | Li et al., 2023a |
| Guarana | Paullinia cupana | Lifespan extension; high antioxidant capacity | Indirect effects via altering E. coli metabolism | Reigada et al., 2022 |
| Phenolic Compounds | Sonchus arvensis, Hemerocallis citrina | Improves lifespan & health against nutrient stress | TGF-β signaling pathway; skn-1 | An et al., 2023 |
| Cassia fistula Extract | Cassia fistula | Improves survival; reduces ROS & proteotoxicity | DAF-16/FOXO and SKN-1/NRF2 pathways | Thabit et al., 2018 |
| Carbendazim | Fungicide | Inhibits growth & lifespan; damages reproduction & antioxidant systems | Impairs oxidative stress response; toxic | Li et al., 2020 |
| Liuwei Dihuang (LWDH) | Traditional Chinese Medicine | Delays β-amyloid paralysis; reduces ROS | Upregulation of HSPs; antioxidant activity | Sangha et al., 2012 |
| Ethyl Acetate Extract | Gastrodia elata | Protects from oxidative stress & Aβ toxicity; improves lifespan | Insulin/IGF-1 signaling (IIS) pathway | Shi et al., 2023 |
| Acrolein | Toxic Aldehyde | Shortens lifespan; increases ROS; decreases healthspan | Activates DAF-16/FOXO stress response | Jeayeng et al., 2024 |
| Leaf Extract | Anacardium occidentale (Cashew) | Enhances stress survival & lifespan; reduces lipofuscin | DAF-16/FoxO & SKN-1/Nrf-2 pathways; induces sod-3, gst-4 | Duangjan et al., 2019 |
| Polysaccharides | Dendrobium officinale | Prolongs lifespan; increases antioxidant enzyme activity | Upregulation of daf-16, skn-1, sir-2.1 | Tang et al., 2023 |
| Total Flavonoids | Sea Buckthorn | Increases lifespan (29.4%); enhances stress tolerance; delays paralysis | Radical scavenging; AChE/MAO-A inhibition | Wang et al., 2022 |
| Polysaccharides | Fermented Coix Seed | Increases lifespan (5.9%); enhances antioxidant enzymes | Downregulates daf-2, age-1; upregulates daf-16, sod-3, skn-1 | Zhao et al., 2023 |
| Cannabidiol (CBD) | Cannabis sativa | Extends lifespan & survival in AD model | Activates neural glyoxalase pathway; detoxifies methylglyoxal | Frandsen and Narayanasamy, 2022 |
| Extract | Anoectochilus roxburghii | Prolongs lifespan; reduces ROS; increases stress resistance | Activation of daf-16/FoxO pathway | Xu et al., 2024 |
| Model Organism | Key Strengths | Primary Limitations | Translational Value | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | High genetic and physiological similarity to humans (vertebrate model). Transparent embryos enabling real-time, live imaging of developmental and pathological processes. Rapid development and high fecundity. Well-suited for high-throughput genetic and drug screening. High conservation of immune and metabolic pathways. | Limited complexity of some organ systems compared to mammals. High lethality in severe genetic mutations. Differences in drug metabolism and anatomy. Limited genetic background diversity in some strains. Not ideal for long-term chronic studies due to lifespan. Limited studies on complex behaviors and mechanisms. | Highly valuable for drug discovery, toxicology, and safety evaluations. Excellent for modeling human diseases, particularly neurodegenerative, metabolic, and inflammatory conditions. Effective for studying developmental processes and in vivo oxidative stress dynamics. | Ali et al., 2022; Amen et al., 2020; Quelle-Regaldie, et al., 2023; Shreya et al., 2020 |
| Fruit Fly (Drosophila melanogaster) | Extremely short life cycle and rapid generation time. Vast array of well-established, powerful genetic tools for manipulation. Low cost and ease of maintenance. Well-characterized genome. Suitable for high-throughput screening. | Limited physiological and anatomical similarity to humans (invertebrate). Less relevance to complex mammalian systems (e.g., adaptive immunity, complex organ structures). Differences in metabolic pathways. Shorter lifespan can limit long-term studies. | Ideal for initial screening of compounds and for fundamental genetic studies. Provides crucial insights into the genetic basis of aging, oxidative stress mechanisms, and developmental biology. Strong model for gene-environment interactions. | Ajagun-Ogunleye and Ebuehi, 2020; Hamidu et al., 2022; Somegowda et al., 2021 |
| Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) | Simple, well-mapped nervous system and genetics. Transparent body allows for easy observation of cellular processes. Very short lifespan and rapid reproduction are ideal for high-throughput longevity and anti-aging studies. Low maintenance cost. Highly conserved genetic pathways. | Extremely simple anatomy lacks complex organ systems (e.g., no heart, liver, adaptive immune system). Limited relevance to vertebrate physiology and complex human diseases. Short lifespan may not model chronic conditions accurately. Limited behavioral complexity. | Exceptional model for screening antioxidants, anti-aging compounds, and neuroprotective agents. Unparalleled for understanding fundamental cellular mechanisms like apoptosis, stress response, and aging. High value in mechanistic studies of oxidative stress and lifespan extension. | de Araújo, 2025; Ayoub et al., 2024; von Mikecz, 2023; Roxo et al., 2020 |