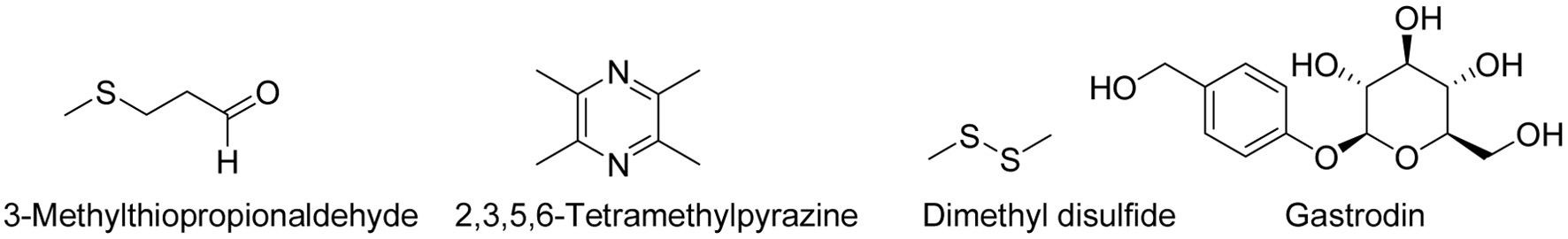
Figure 1. Structure of main compound associated with the horse-urine odor in Gastrodia elata.
| Journal of Food Bioactives, ISSN 2637-8752 print, 2637-8779 online |
| Journal website www.isnff-jfb.com |
Review
Volume 29, March 2025, pages 29-37
Progress in research on flavor compounds in Gastrodia elata
Figures

Tables
| No. | Category | Example Compounds | Chemical Formula | Odor/Flavor Description | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Aldehydes | Nonanal | C9H18O | Greasy fragrance | (Sun et al., 2022) |
| 2 | Hexanal | C6H12O | Floral, fruity fragrance | (Sun et al., 2022) | |
| 3 | Heptanal | C7H14O | – | (Sun et al., 2022) | |
| 4 | Hexadecanal | C16H32O | Cardboard-like odor | (Huang and Li, 2018) | |
| 5 | Benzaldehyde | C7H6O | – | (Sun et al., 2022) | |
| 6 | Phenylacetaldehyde | C8H8O | Hyacinth-like aroma | (Wang,et al.,2025; Sun et al., 2022) | |
| 7 | 2-Methylbutanal | C5H10O | Cocoa, almond-like odor | (Sun et al., 2022) | |
| 8 | 3-Methylbutanal | C5H10O | Chocolate, peach, and apple fragrances | (Li et al., 2025; Ma et al.,2024) | |
| 9 | 3-Methylthiopropionaldehyde | C4H8OS | Pungent, irritating odor | (Li et al., 2025) | |
| 10 | Alcohols | Campesterol | C28H48O | – | (Zhan et al., 2016) |
| 11 | β-Sitosterol | C29H50O | – | (ChP, 2020) | |
| 12 | Hexanol | C6H14O | – | (Sun et al., 2022) | |
| 13 | Alcohols | Butanol | C4H10O | – | (Sun et al., 2022) |
| 14 | 1-Octen-3-ol | C8H16O | – | (Duan,et al., 2023) | |
| 15 | Terpinen-4-ol | C10H18O | – | (Duan,et al., 2023) | |
| 16 | Phenethyl alcohol | C8H10O | Honey-like aroma | (Tan et al., 2025) | |
| 17 | Isoamyl alcohol | C5H12O | Nail polish and greasy odor | (Tan et al., 2025) | |
| 18 | Esters | Methyl palmitate | C17H34O | Waxy, fatty, iris-like odor | (Sun et al., 2022) |
| 19 | Ethyl palmitate | C18H36O2 | – | (Ma et al., 2024) | |
| 20 | Ethyl linoleate | C19H34O2 | – | (Ma et al., 2024) | |
| 21 | Acids | Acetic acid | C2H4O2 | – | (Han et al., 2018) |
| 22 | Hexanoic acid | C6H12O2 | Sweaty odor | (Han et al., 2018) | |
| 23 | Nonanoic acid | C9H18O2 | – | (Han et al., 2018) | |
| 24 | n-Hexadecanoic acid | C16H32O2 | – | (Ma et al., 2024) | |
| 25 | 1-Methoxyethyl hexadecanoate | C19H38O | – | (Zhan et al., 2016) | |
| 26 | Linolenic acid | C18H30O2 | – | (Han et al., 2018) | |
| 27 | Linoleic acid | C18H32O2 | – | (Zhan et al., 2016) | |
| 28 | Acids | Palmitic acid | C16H32O2 | – | (Zhan et al., 2016) |
| 29 | Linoleic acid | C18H32O2 | Mild fatty odor | (Huang and Li, 2018) | |
| 30 | Phenols | 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenol | C14H22O | Phenolic odor | (Huang and Li, 2018) |
| 31 | 4-Methylphenol | C7H8O | Narcissus, acacia, and mimosa-like fragrances | (Sun et al., 2022;) | |
| 32 | p-Cresol | C7H8O | Strong phenolic and tobacco-like aroma (urine-like odor) | (Tan et al., 2025;Han et al., 2018) | |
| 33 | Eugenol | C10H12O2 | Sweet, spicy, clove-like aroma with strong carnation and musk notes | (Huang and Li, 2018) | |
| 34 | Ketones | Acetone | C3H6O | – | (Sun et al., 2022) |
| 35 | 2-Butanone | C4H8O | – | (Sun et al., 2022) | |
| 36 | 3-Nonanone | C9H18O | – | (Sun et al., 2022) | |
| 37 | Acetophenone | C8H8O | Cheesy, sweet, almond-like | (Tan et al., 2025; Han et al., 2018) | |
| 38 | Alkanes | Isopentane | C5H12 | Pleasant aromatic odor | (Cao et al., 2018) |
| 39 | Alkanes | Tetradecane | C14H30 | Mild waxy odor | (Huang and Li, 2018) |
| 40 | Pentadecane | C15H32 | – | (Han et al., 2018) | |
| 41 | Hexadecane | C16H34 | Mild waxy odor | (Han et al., 2018) | |
| 42 | Eicosane | C20H42 | – | (Han et al., 2018) | |
| 43 | Triacontane | C30H62 | – | (Han et al., 2018) | |
| 44 | Farnesane | C15H26 | – | (Han et al., 2018) | |
| 45 | Aromatics | Naphthalene | C10H8 | Spicy, tar-like odor | (Huang and Li, 2018) |
| 46 | Phenanthrene | C14H10 | Spicy, tar-like odor | (Huang and Li, 2018) | |
| 47 | Others | Styrene | C8H8O | – | (Duan et al., 2023) |
| 48 | trans-Squalene | C30H50 | – | (Han et al., 2018) | |
| 49 | Limonene | C10H16 | Lemon-like aroma | (Ma et al., 2024) | |
| 50 | α-Pinene | C10H16 | Pine, coniferous, and resinous odor | (Duan et al., 2023) | |
| 51 | 2-Pentylfuran | C9H14O | Fruity, earthy, green, and vegetable-like aroma | (Ma et al., 2024) | |
| 52 | Others | 2,3,5,6-Tetramethylpyrazine | C8H12N | Musty odor | (Ma et al., 2024) |
| 53 | Dimethyl disulfide | C2H6S2 | Sulfurous, foul odor | (ChP, 2020) |
| Category | Technique | Description | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Techniques | Steam Distillation | Uses steam to carry volatile components from Gastrodia elata, followed by condensation and separation. | (Li et al., 2025) |
| Solvent Extraction | Employs organic solvents (e.g., ethanol, methanol) to extract flavor compounds. | (Li et al., 2019) | |
| Modern Techniques | Supercritical CO2 Extraction | Utilizes supercritical CO2 as a solvent for high-efficiency and residue-free extraction, preserving volatile components. | (Han et al., 2018) |
| Headspace-GC/MS | Directly analyzes volatile components in processed Gastrodia elata using headspace sampling coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. | (Wang et al., 2025) | |
| Solid-Phase Microextraction (SPME) | Adsorbs volatile components onto coated fibers, followed by GC-MS analysis for enrichment and identification. | (Wang et al., 2025) | |
| Microwave-Assisted Extraction | Enhances extraction efficiency through microwave irradiation. | (Jaouhari et al., 2025) | |
| Simultaneous Distillation-Extraction | Combines steam distillation and solvent extraction to simultaneously extract components. | (Huang and Li, 2018) |