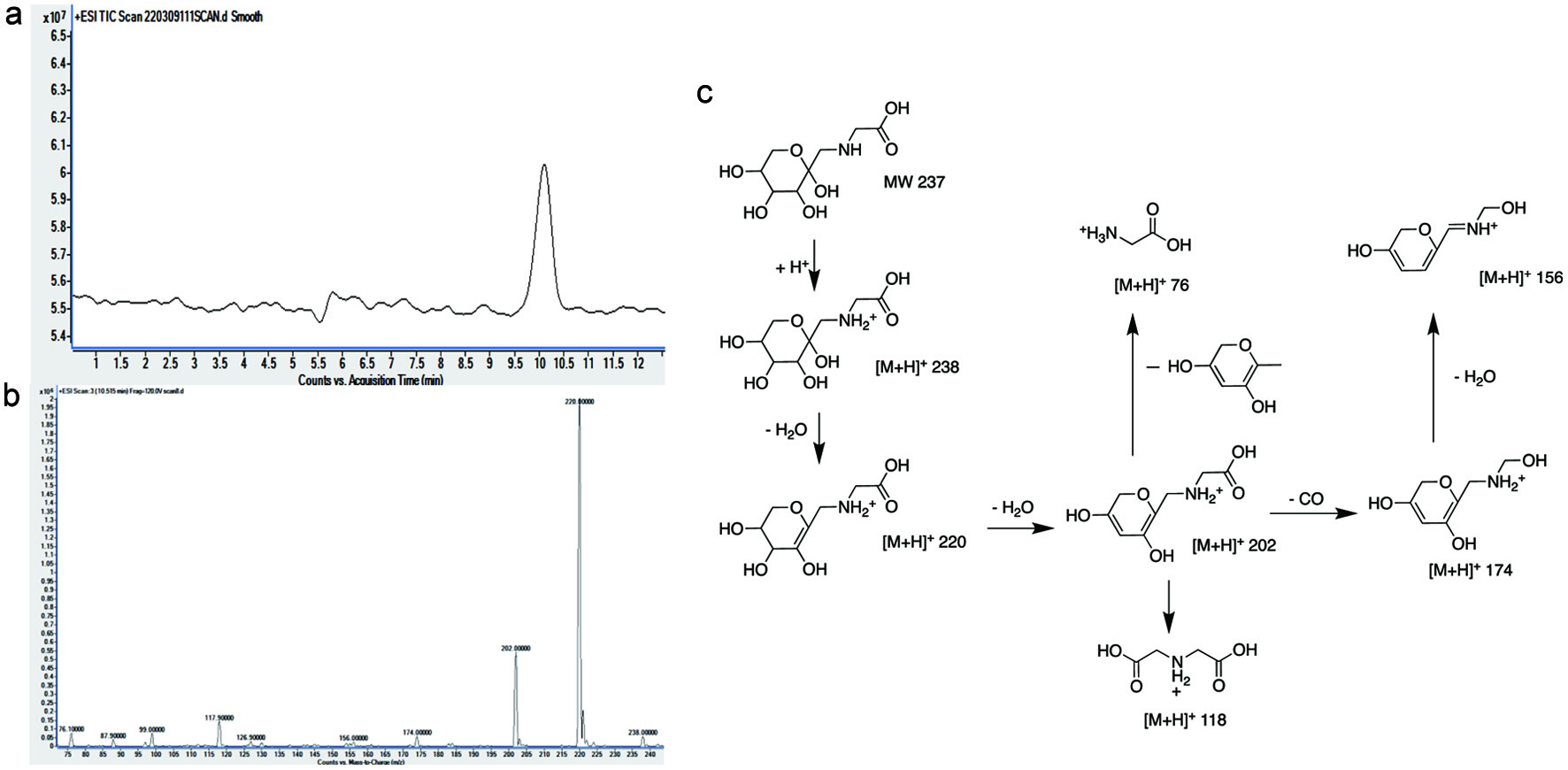
Figure 1. LC/MS/MS analysis of glycine-ARP: full scan spectrum (a); secondary spectrum (b); proposed fragmentation pathway (c). (120.0 v–m/z: 76.1, 118.0, 156.1, 174.0, 202.0, 220.0, 238.0)
| Journal of Food Bioactives, ISSN 2637-8752 print, 2637-8779 online |
| Journal website www.isnff-jfb.com |
Original Research
Volume 20, December 2022, pages 90-97
Reactivity comparison of Amadori rearrangement product formation of glycine, diglycine, and triglycine in a competing Maillard system
Figures

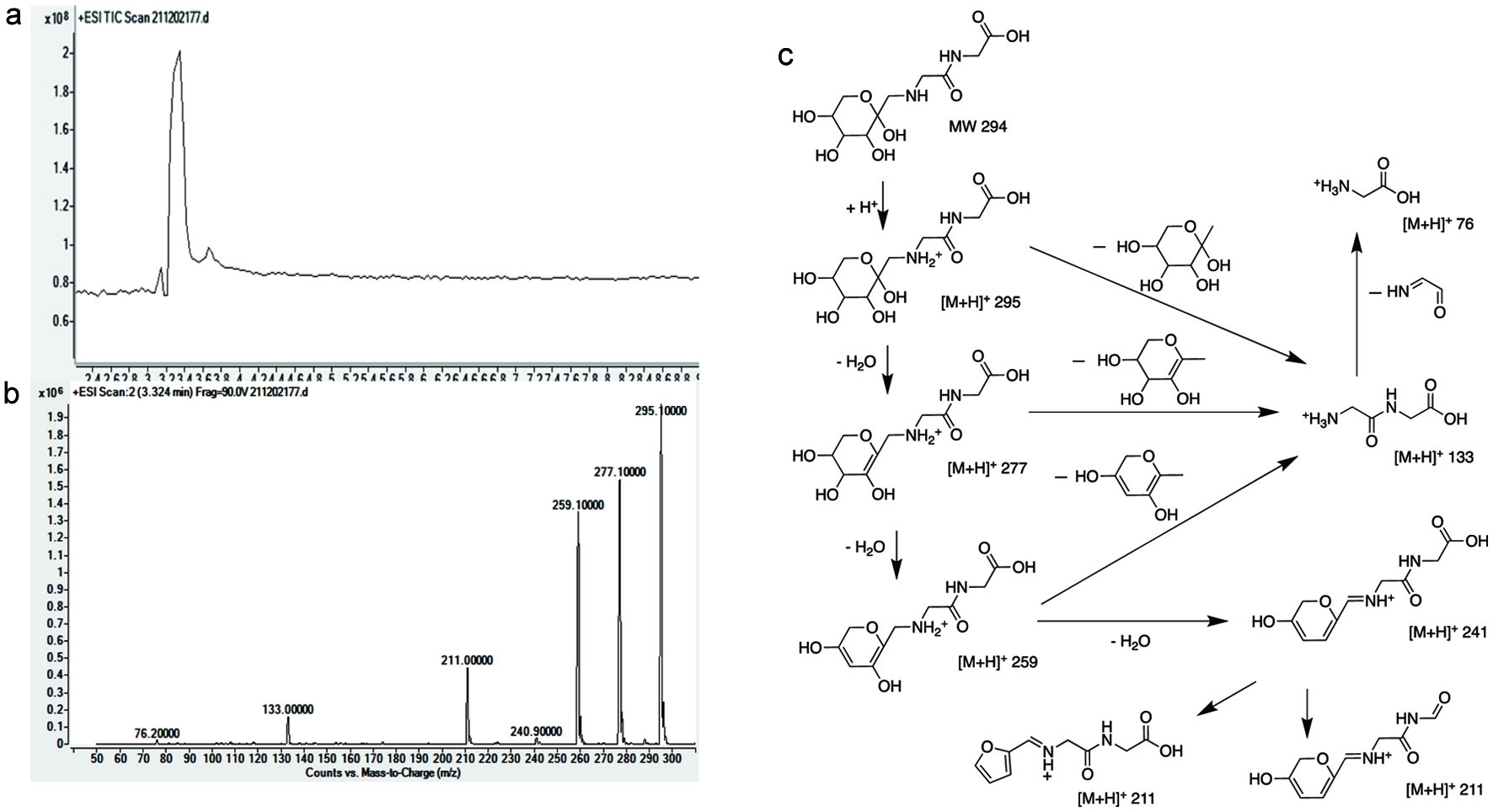
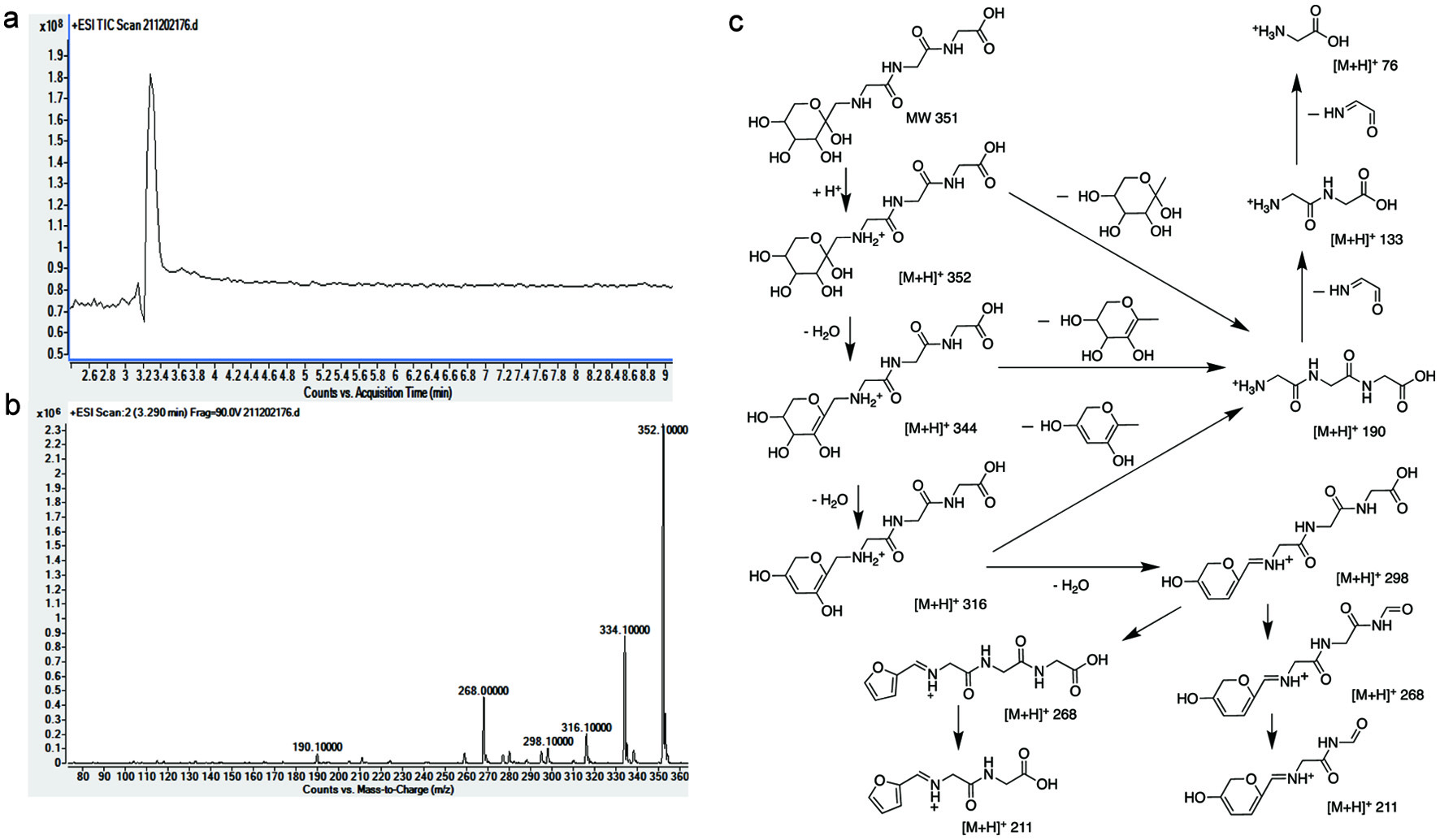
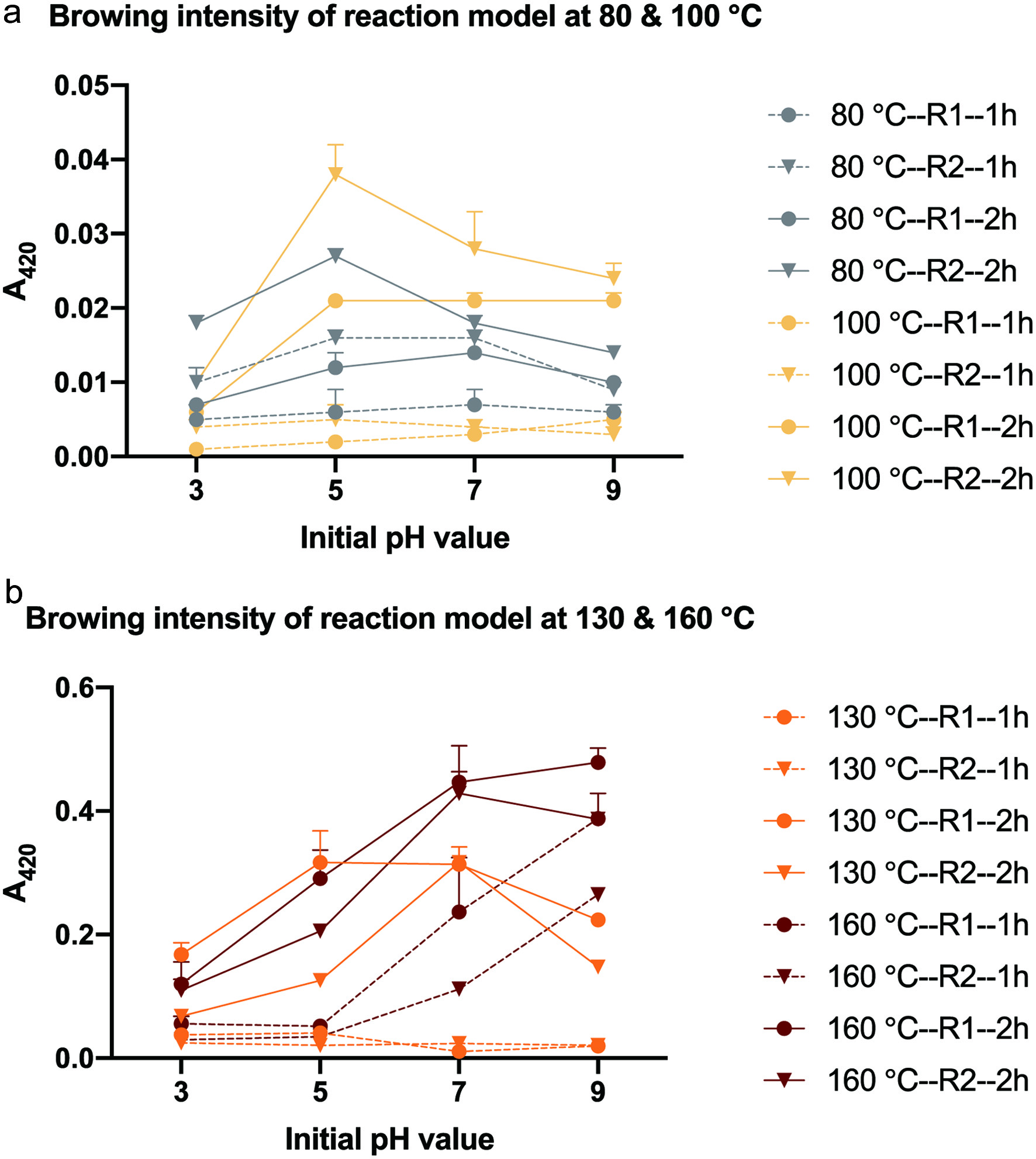
Tables
| GA (R1) | DA (R1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH 3 | pH 5 | pH 7 | pH 9 | pH 3 | pH 5 | pH 7 | pH 9 | |
| *1H and 2H means thermal treatment of 1 hour and 2 hours, receptivity. *R1 means the model system of glucose/glycine/diglycine = 1:1:1 (molar ratio). | ||||||||
| 80 °C 1H | 0.0021 | 0.0033 | 0.0035 | 0.0695 | 0.0025 | 0.0035 | 0.0068 | 0.0059 |
| 80 °C 2H | 0.0021 | 0.0043 | 0.0058 | 0.1099 | 0.0021 | 0.0043 | 0.0081 | 0.0092 |
| 100 °C 1H | 0.0049 | 0.0061 | 0.0063 | 0.1905 | 0.0047 | 0.0088 | 0.0146 | 0.0143 |
| 100 °C 2H | 0.0080 | 0.0172+ | 0.0218 | 0.3049 | 0.0077 | 0.0159 | 0.0282 | 0.0254 |
| 130 °C 1H | 0.0563 | 0.2000 | 0.3825 | 0.2724 | 0.0465 | 0.1029 | 0.1235 | 0.1469 |
| 130 °C 2H | 0.0637 | 0.3514 | 0.3238 | 0.2520 | 0.0479 | 0.0981 | 0.1121 | 0.1440 |
| 160 °C 1H | 0.0543 | 0.1832 | 0.0793 | 0.0260 | 0.0523 | 0.0690 | 0.0739 | 0.0462 |
| 160 °C 2H | 0.0326 | 0.2963 | 0.2223 | 0.0421 | 0.0315 | 0.0397 | 0.0439 | 0.0136 |
| GA (R2) | TA (R2) | DA (R2, from TA degradation) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH 3 | pH 5 | pH 7 | pH 9 | pH 3 | pH 5 | pH 7 | pH 9 | pH 3 | pH 5 | pH 7 | pH 9 | |
| *1H and 2H means thermal treatment of 1 hour and 2 hours, receptivity. *R2 means the model system of glucose/glycine/triglycine = 1:1:1 (molar ratio). | ||||||||||||
| 80 °C 1H | 0.0053 | 0.0128 | 0.0105 | 0.0876 | 0.0042 | 0.0123 | 0.0101 | 0.0129 | ||||
| 80 °C 2H | 0.0042 | 0.0065 | 0.0091 | 0.1166 | 0.0055 | 0.0065 | 0.0080 | 0.0198 | ||||
| 100 °C 1H | 0.0065 | 0.0161 | 0.0251 | 0.1604 | 0.0053 | 0.0129 | 0.0107 | 0.0213 | ||||
| 100 °C 2H | 0.0085 | 0.0211 | 0.0262 | 0.2502 | 0.0074 | 0.0189 | 0.0139 | 0.0222 | ||||
| 130 °C 1H | 0.0854 | 0.1662 | 0.1773 | 0.1319 | 0.0758 | 0.0988 | 0.1711 | 0.1299 | 0.0027 | 0.0029 | 0.0031 | 0.0073 |
| 130 °C 2H | 0.1205 | 0.1231 | 0.1164 | 0.0788 | 0.0623 | 0.0996 | 0.1108 | 0.0896 | 0.0026 | 0.0025 | 0.0034 | 0.0069 |
| 160 °C 1H | 0.0326 | 0.2506 | 0.0642 | 0.0520 | 0.0132 | 0.0111 | 0.0107 | 0.0209 | 0.0034 | 0.0048 | 0.0029 | 0.0056 |
| 160 °C 2H | 0.0156 | 0.0593 | 0.0568 | 0.0487 | 0.0143 | 0.0018 | 0.0010 | 0.0024 | 0.0048 | 0.0030 | 0.0031 | 0.0035 |
| pH 3 | pH 5 | pH 7 | pH 9 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DA/GA | TA/GA | DA/GA | TA/GA | DA/GA | TA/GA | DA/GA | TA/GA | ||||||
| *1H and 2H means thermal treatment of 1 hour and 2 hours, receptivity. | |||||||||||||
| 80 °C 1H | 1.21 | 0.78 | 1.06 | 0.96 | 1.96 | 0.97 | 0.08 | 0.15 | |||||
| 80 °C 2H | 1.01 | 1.32 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 1.40 | 0.88 | 0.08 | 0.17 | |||||
| 100 °C 1H | 0.96 | 0.82 | 1.44 | 0.80 | 2.33 | 0.43 | 0.08 | 0.13 | |||||
| 100 °C 2H | 0.96 | 0.87 | 0.92 | 0.90 | 1.30 | 0.53 | 0.08 | 0.09 | |||||
| 130 °C 1H | 0.83 | 0.89 | 0.51 | 0.59 | 0.32 | 0.96 | 0.54 | 0.98 | |||||
| 130 °C 2H | 0.75 | 0.52 | 0.28 | 0.81 | 0.35 | 0.95 | 0.57 | 1.14 | |||||
| 160 °C 1H | 0.96 | 0.40 | 0.38 | 0.04 | 0.93 | 0.17 | 1.15 | 0.40 | |||||
| 160 °C 2H | 0.97 | 0.92 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0.20 | 0.02 | 0.32 | 0.05 | |||||
| pH 3 | pH 5 | pH 7 | pH 9 | ||||||||||
| DA/TA | DA/TA | DA/TA | DA/TA | ||||||||||
| *1H and 2H means thermal treatment of 1 hour and 2 hours, receptivity. | |||||||||||||
| 80 °C 1H | 1.6 | 1.1 | 2.0 | 0.6 | |||||||||
| 80 °C 2H | 0.8 | 1.0 | 1.6 | 0.5 | |||||||||
| 100 °C 1H | 1.2 | 1.8 | 5.4 | 0.6 | |||||||||
| 100 °C 2H | 1.1 | 1.0 | 2.4 | 0.9 | |||||||||
| 130 °C 1H | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.3 | 0.5 | |||||||||
| 130 °C 2H | 1.5 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | |||||||||
| 160 °C 1H | 2.4 | 8.5 | 5.6 | 4.4 | |||||||||
| 160 °C 2H | 1.1 | 4.4 | 11.8 | 6.6 | |||||||||