Figures
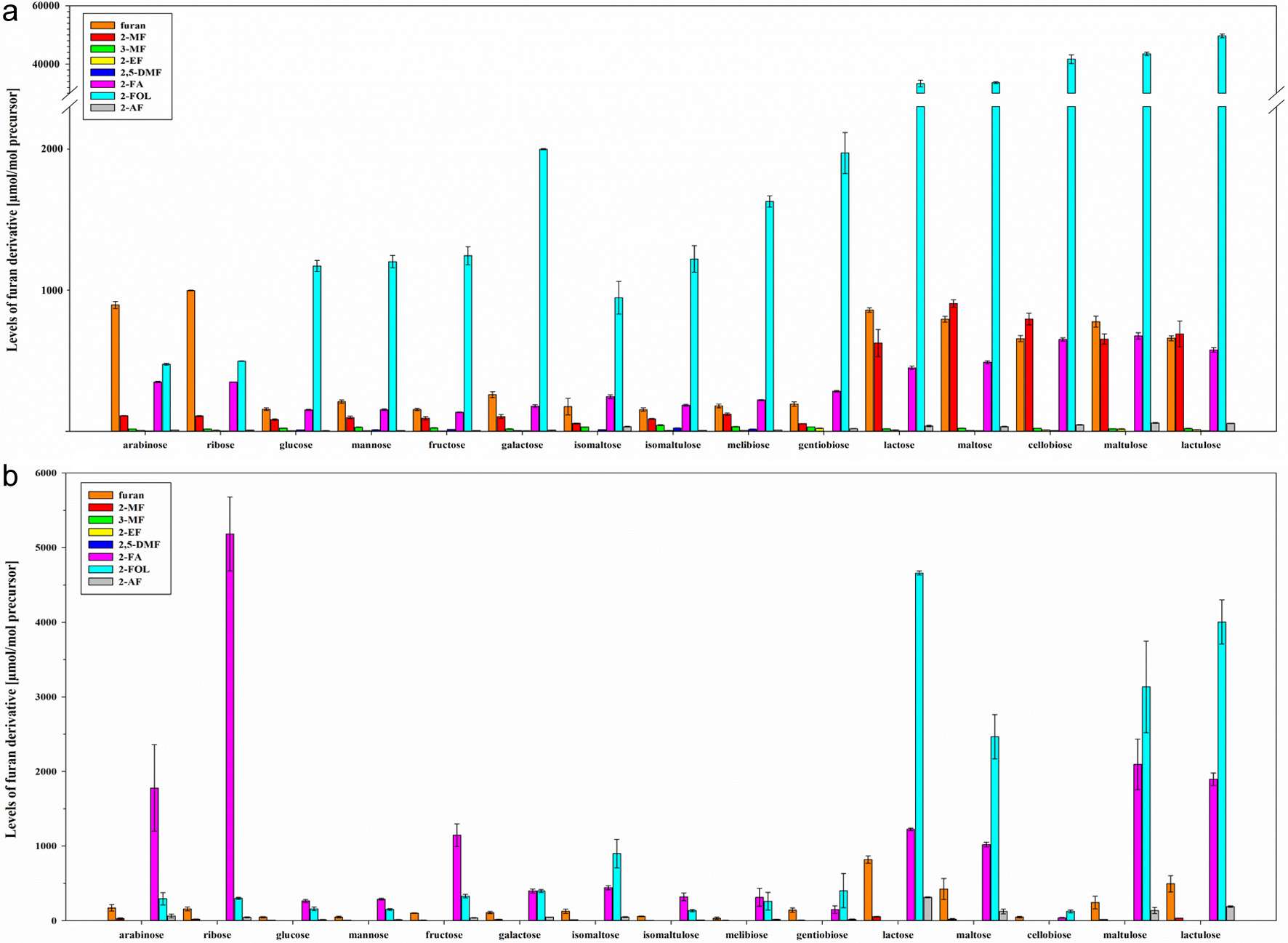
Figure 1. Levels [µmol/mol precursor] of furan, 2-methylfuran (2-MF), 3-methylfuran (3-MF), 2-ethylfuran (2-EF), 2,5-dimethylfuran (2,5-DMF), furfural (2-FA), furfuryl alcohol (2-FOL), and 2-acetylfuran (2-AF) (mean ± SD, n = 3) obtained by heat treatment of mono- and disaccharides in model A at pH 7 (a) and model B (b).
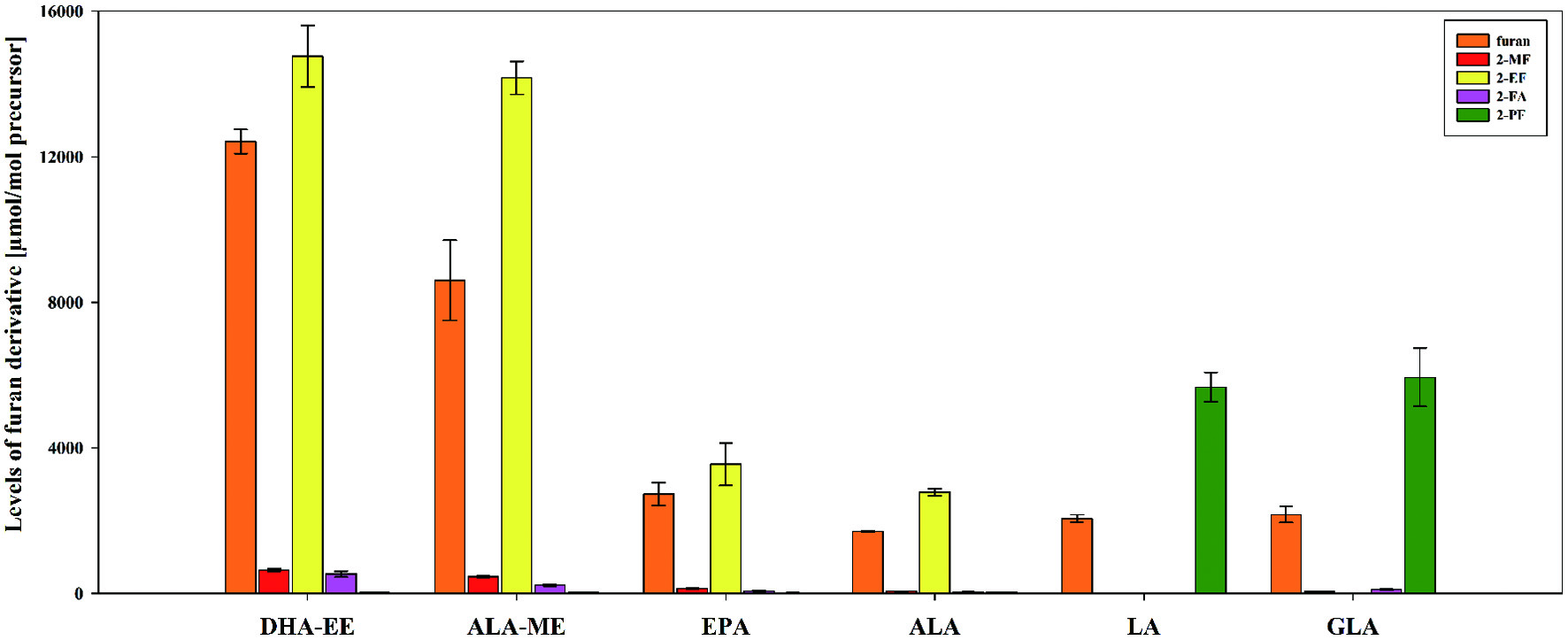
Figure 2. Levels [µmol/mol precursor] of furan, 2-methylfuran (2-MF), 3-methylfuran (3-MF), 2-ethylfuran (2-EF), furfural (2-FA), and 2-pentylfuran (2-PF) (mean ± SD, n = 3) obtained by heat treatment of the polyunsaturated fatty acids α-linolenic acid (ALA), α-linolenic acid methyl ester (ALA-ME), γ-linolenic acid (GLA), DHA ethyl ester (DHA-EE), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and linoleic acid (LA) in model A at pH 7.
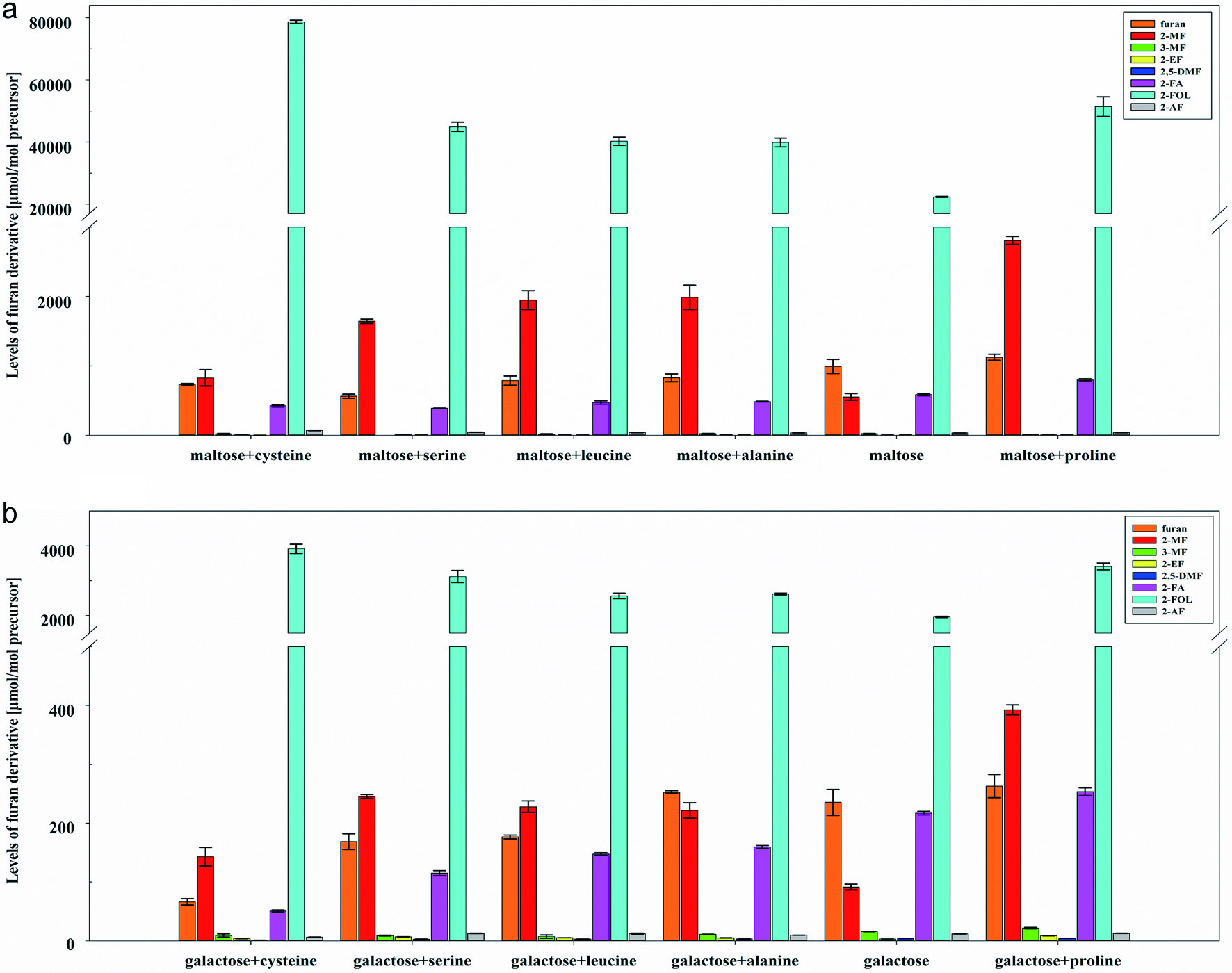
Figure 3. Levels [µmol/mol precursor] of furan, 2-methylfuran (2-MF), 3-methylfuran (3-MF), 2-ethylfuran (2-EF), 2,5-dimethylfuran (2,5-DMF), furfural (2-FA), furfuryl alcohol (2-FOL), and 2-acetylfuran (2-AF) (mean ± SD, n = 3) obtained by heat treatment of mixtures of (a) maltose and (b) galactose with alanine, cysteine, leucine, proline, and serine in model A at pH 7.
Tables
Table 1. Precursor and product ions of the GC–MS/MS method for furan, 2-methylfuran (2-MF), 3-methylfuran (3-MF), 2-ethylfuran (2-EF), 2,5-dimethylfuran (2,5-DMF), 3-furaldehyde (3-FA), furfural (2-FA), furfuryl alcohol (2-FOL), 3-furanmethanol (3-FOL), 2-acetylfuran (2-AF), and 2-pentylfuran (2-PF) and the corresponding stable isotopically substituted internal standards
| Compound | Retention time [min] | Precursor ion [m/z] | Product ion [m/z] | Collision energy [eV] |
|---|
| Furan-d4 | 5.8 | 72 | 42 | 22 |
| Furan | 5.8 | 68 | 39 | 22 |
| 2-MF-d6 | 9.7 | 88 | 42 | 22 |
| 2-MF | 9.8 | 82 | 39 | 18 |
| 3-MF-d3 | 10.3 | 85 | 41 | 19 |
| 3-MF | 10.4 | 82 | 39 | 18 |
| 2-EF-d5 | 14.8 | 101 | 83 | 12 |
| 2-EF | 15.0 | 96 | 81 | 12 |
| 2,5-DMF-d3 | 15.2 | 99 | 43 | 32 |
| 2,5-DMF | 15.4 | 96 | 43 | 31 |
| 3-FA | 22.5 | 96 | 95 | 9 |
| 2-FA-d3 | 23.3 | 99 | 98 | 12 |
| 2-FA | 23.3 | 96 | 95 | 12 |
| 2-FOL-d5 | 24.0 | 103 | 47 | 8 |
| FOL | 24.0 | 98 | 42 | 9 |
| 3-FOL | 24.4 | 98 | 42 | 8 |
| 2-AF | 25.2 | 110 | 95 | 8 |
| 2-PF | 25.8 | 138 | 81 | 18 |
| [13C2]-2-PF | 25.8 | 140 | 81 | 18 |
Table 2. Limits of detection (LOD), limits of quantification (LOQ), linearity, repeatability, and reproducibility for furan, 2-methylfuran (2-MF), 3-methylfuran (3-MF), 2-ethylfuran (2-EF), 2,5-dimethylfuran (2,5-DMF), 3-furaldehyde (3-FA), furfural (2-FA), furfuryl alcohol (2-FOL), 3-furanmethanol (3-FOL), 2-acetylfuran (2-AF), and 2-pentylfuran (2-PF)
| Compound | LODa [ng] | LOQb [ng] | R2c | RSD low conc. [%]d | RSD high conc. [%]e | Accuracy low conc. [%]f | Accuracy high conc. [%]g |
|---|
| aLimit of detection (LOD) based on signal-to-noise (S/N) of ≥3; bLimit of quantification (LOQ) based on S/N of ≥10; cLinearity expressed by correlation coefficient (R2) (n = 3); dPrecision at low concentration levels (spiked with 10 µL of standard solution) expressed by relative standard deviation (RSD) (n = 6); ePrecision at high concentration levels (spiked with 500 µL of standard solution) expressed by RSD (n = 6); fAccuracy at low concentration levels (spiked with 10 µL of standard solution) expressed by the coefficient of determined amount and spiked amount × 100 (n = 6); gAccuracy at high concentration levels (spiked with 500 µL of standard solution) expressed by coefficient of determined amount and spiked amount × 100 (n = 6). |
| Furan | 0.323 | 0.970 | ≥0.9999 | 6.45 | 5.98 | 97.12 ± 6.26 | 96.16 ± 5.76 |
| 2-MF | 0.090 | 0.270 | ≥0.9999 | 5.88 | 5.29 | 97.34 ± 4.72 | 98.70 ± 5.76 |
| 3-MF | 0.093 | 0.280 | ≥0.9999 | 4.84 | 5.84 | 97.34 ± 4.72 | 98.70 ± 5.76 |
| 2-EF | 0.019 | 0.056 | ≥0.9999 | 5.32 | 5.35 | 95.84 ± 5.10 | 97.61 ± 5.22 |
| 2,5-DMF | 0.074 | 0.223 | ≥0.9999 | 4.49 | 4.78 | 94.61 ± 4.25 | 98.57 ± 4.70 |
| 3-FA | 1.47 | 4.41 | ≥0.9995 | 3.21 | 2.95 | 97.99 ± 3.15 | 99.31 ± 2.92 |
| 2-FA | 1.77 | 5.30 | ≥0.9999 | 6.70 | 2.23 | 92.76 ± 6.22 | 99.98 ± 2.23 |
| 2-FOL | 88.0 | 264 | ≥0.9990 | 3.04 | 3.73 | 96.79 ± 2.95 | 101.16 ± 3.77 |
| 3-FOL | 108 | 325 | ≥0.9992 | 1.48 | 5.28 | 93.34 ± 1.49 | 101.00 ± 5.33 |
| 2-AF | 0.40 | 1.20 | ≥0.9991 | 3.05 | 2.76 | 94.24 ± 3.21 | 102.56 ± 2.83 |
| 2-PF | 0.030 | 0.090 | ≥0.9997 | 8.06 | 6.16 | 108.72 ± 8.76 | 94.94 ± 5.85 |
Table 3. Contents [mg/100 g sample] of furan, 2-methylfuran (2-MF), 3-methylfuran (3-MF), 2-ethylfuran (2-EF), furfural (2-FA), and 2-pentylfuran (2-PF) (mean ± SD, n = 3) obtained by heat treatment of different oils in model A at pH 7 and the corresponding fatty acid composition concerning the polyunsaturated fatty acids α-linolenic acid (ALA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), docosapentaenoic acid (DPA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and linoleic acid (LA)
| Contents of furanoic compounds [mg/100 g sample] | Data from literature |
|---|
| Furan | 2-MF | 3-MF | 2-EF | 2-FA | 2-PF | ALA [%] | LA [%] | DHA/EPA/DPA [mg/100 mL] |
|---|
| aSpecification of distributor; bnd = not detected (< limit of detection). Noticeable data in italic. |
| Linseed oil (Firestone, 2013) | 112.56 ± 11.76 | 5.80 ± 0.54 | 0.20 ± 0.02 | 216.32 ± 26.93 | 3.90 ± 0.34 | 37.94 ± 5.01 | 35–66 | 7–25 | – |
| Algea oil (74% algea oil, 23% olive oil, 2% sunflower oil)a | 58.76 ± 3.19 | 5.89 ± 0.20 | 0.83 ± 0.04 | 72.75 ± 3.88 | 4.72 ± 0.52 | 6.83 ± 1.10 | no specification | EPA: 609; DPA: 157; DHA: 1,158 |
| Fish oil (80% fish oil, 19% olive oil)a | 35.78 ± 10.14 | 4.22 ± 0.62 | 0.63 ± 0.06 | 50.84 ± 14.69 | 2.19 ± 0.50 | 5.24 ± 1.87 | no specification | EPA: 560; DPA: 64; DHA: 268 |
| Soybean oil (Firestone, 2013) | 4.02 ± 0.57 | 1.36 ± 0.08 | 0.28 ± 0.02 | 2.24 ± 0.31 | 0.27 ± 0.04 | 12.52 ± 2.26 | 5.5–11.0 | 46.2–57.1 | – |
| Safflower oil (Firestone, 2013) | 20.73 ± 1.88 | 1.11 ± 0.15 | 0.22 ± 0.03 | 1.16 ± 0.06 | 1.62 ± 0.24 | 75.34 ± 0.70 | 0–0.13 | 8.7–83.2 | – |
| Rapeseed oil (Firestone, 2013) | 0.88 ± 0.04 | 0.78 ± 0.08 | 0.16 ± 0.02 | 0.62 ± 0.01 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | ndb | 4–25 | 10–40 | – |
| Olive oil (Firestone, 2013) | 1.19 ± 0.15 | 1.51 ± 0.26 | 0.32 ± 0.06 | 0.53 ± 0.08 | 0.19 ± 0.04 | nd | 0–4 | 3.5–21.0 | – |
| Sunflower oil (Firestone, 2013) | 26.66 ± 9.36 | nd | nd | nd | 1.65 ± 0.62 | 97.10 ± 22.64 | 0–0.5 | 17–85 | – |
| Coconut oil (Firestone, 2013) | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | 0–0.2 | 0.8–2.1 | – |


