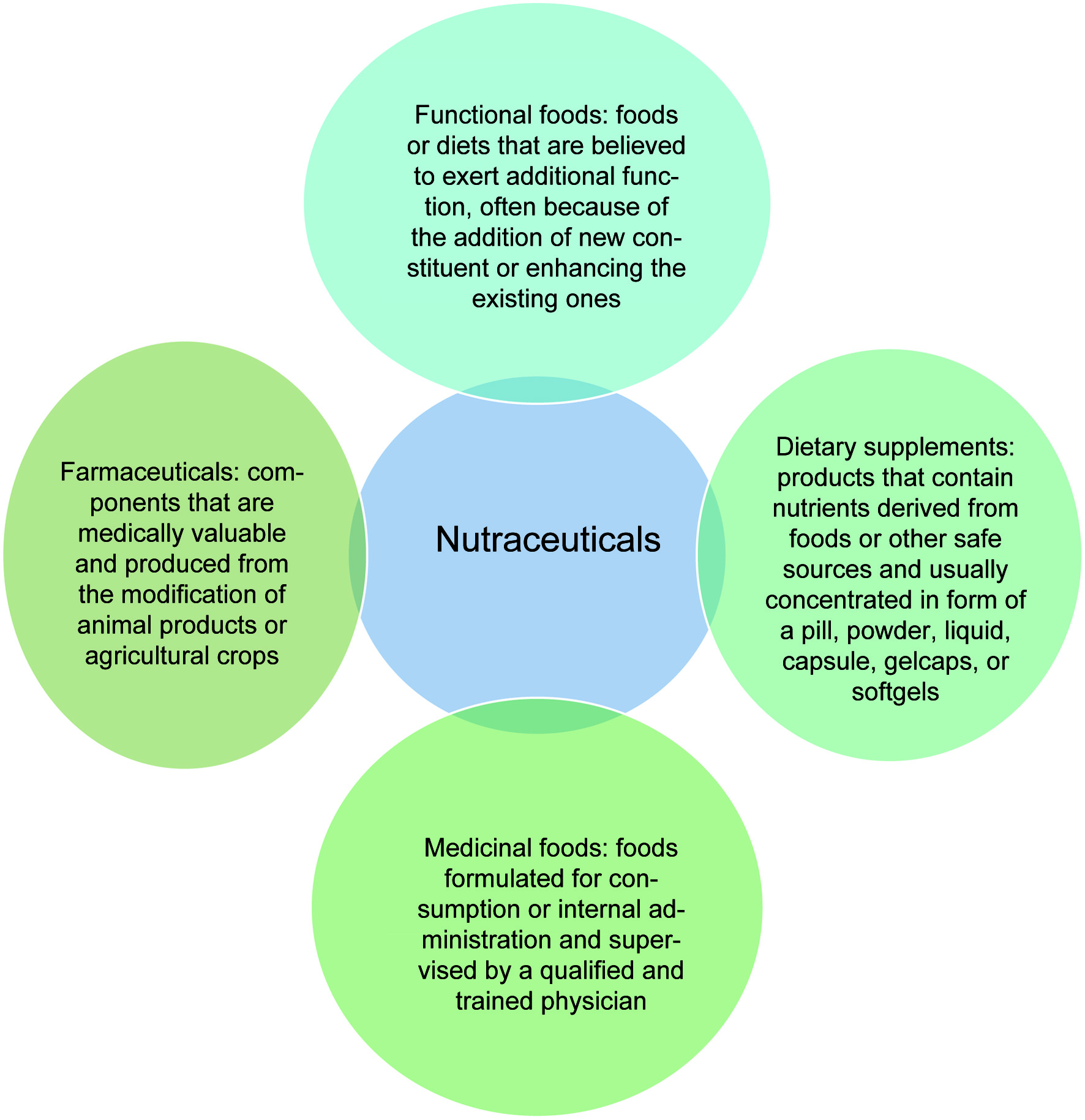
Figure 1. Classification of nutraceuticals.
| Journal of Food Bioactives, ISSN 2637-8752 print, 2637-8779 online |
| Journal website www.isnff-jfb.com |
Review
Volume 19, September 2022, pages 97-123
Natural nutraceuticals, especially functional foods, their major bioactive components, formulation, and health benefits for disease prevention: an overview
Figure

Tables
| Functional food classification | Examples | Major bioactive components | Nutraceutical/functional effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beverages (Nutraceutical beverages) | Tea, coffee, enhanced/mineral water, plant milks, fortified fruit drinks/juices, smart drinks, ready-to-drink teas, performance/sports drinks, dairy beverages, etc. Nutraceutical beverages are mostly obtained from fruits, vegetables, coffee, tea, soybean, milk, dairy products, etc. | Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, epicatechin gallate, caffeine, etc. | Nutraceutical beverages improve digestion, overall health, immunity, heart health, energy boost, etc. Tea is a popular nutraceutical beverage that have important bioactive compounds and nutrients with strong antioxidant, anticancer, antiinflammatory, immunomodulator, antihistamine, antimicrobial, antidepressant, cardioprotective, blood pressure lowering, nervous system protective, and health promoting properties. Several studies have shown that the consumption of coffee might reduce incidence of many chronic conditions, such as mental health, liver disease, suicidal risks, all-cause mortality, etc. | Saeed et al., 2019; Díaz et al., 2020; Bulman et al., 2021 |
| Fermented foods | Yoghurt, sauerkraut, soy products, tempeh, kefir, barley, kimchi, rice bran, kombucha, etc. | Polyphenols, dietary fiber, probiotics, prebiotics, conjugated linoleic acid, calcium, cobalamin, magnesium, fatty acids, etc. | Fermented foods have immune-modulatory, antioxidant, chemoprotective, anti-inflammatory, cardioprotective, immune boosting, and anticancer, and antidiabetic properties. The microorganisms mostly used for fermentation are yeasts and lactic acid bacteria, which can improve nutrients bioavailability and increase the bioactive compounds in the foods. fermentation favour in vitro antioxidant activities of fermented products. Citrus blended vinegars can be used as functional foods due to their anti-obesity, anti-aging, and antioxidant properties. Yogurt helps benefit digestive health, strengthen immune system, protect against osteoporosis, benefit heart health, promote weight management, etc. | Islam et al., 2019; Vasilean et al., 2021; Yun et al., 2021 |
| Fruits | Limes, strawberries, blackberries, blueberries, bananas, oranges, apples, peaches, pears, kiwi, avocado, bananas, pineapple, pomegranate, apples, grapefruit, oranges, lemons, etc. | Polyphenols (e.g., flavonoids), vitamins, minerals, dietary fiber, ellagitannins, prodelphinidins, gallocatechins, catechins, alkaloids, cardiac glycosides, pelargonidin glycosides, cyanidin, delphinidin, etc. | They have health-boosting antioxidant, cardioprotective, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, anti-depression, anticancer, immunomodulatory, nervous system enhancement, and antidiabetic properties, among others. Regular consumption of diets high in fruits can improve overall health and reduce one’s risk of developing diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases, inflammation, cancer, diabetes mellitus, obesity, etc. | Ellis, 2021; Lim et al., 2021 |
| Herbs and spices | Ginger, cinnamon, cayenne pepper, fenugreek, garlic, turmeric, red pepper, etc. | Curcumin, gingerol saponin, fiber, capsaicin, allicin, shogaols, piperine, etc. | The nutraceutical, anti-oxidant, anti-diabetic, nutritional, anti-hypercholesterolemic, cardioprotective, anti-microbial, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and anti-carcinogenic activities of spices have significant importance as nutraceuticals. Curcumin in turmeric, [6]-gingerol in ginger, saponin and fiber in fenugreek, capsaicin in red pepper, allicin in garlic have important nutraceutical properties due to their several physiological and medicinal effects. Spices and herbs have been shown to have the nutraceutical properties, including antioxidant, antimicrobial, antidiabetic, immune promoting, antihistamine, immunomodulatory, anticancer, cardioprotective, and blood pressure lowering properties, among others. | Ahmad et al., 2020; Pandey et al., 2022; Chopra et al., 2022 |
| Honey | Mostly honey bees and other bees | Organic acids (gluconic, succinic, palmitic, formic, capronic, valeric, propionic, acetic, pyroglutamic, malic, lactic, citric, and butyric acids, among others), royalisin (defensin-1), hydrogen peroxide, methylglyoxal, sugar, eugenol, naringin, luteolin, syringic acid, p-coumaric acid, kaempferol, galangin, apigenin, quercetin, chrysin, gallic acid, isorhamnetin, pinocembrin, pinobanksin, caffeic acid, ferulic acid, etc. | Bioactive compounds in honey help resist infections, tolerate cold, possibly live longer, heal wounds, and prevent some diseases. They also have antioxidant, anticancer, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, immune boosting, blood pressure lowering, antihistamine, antimicrobial, cognitive, cardioprotective, and nervous improving properties. Honey is topically used as antibiotic in herbal and traditional medicine. It is used for treating burns and skin injuries in traditional medicine. Honey usage is recommended as provisional intervention for suspected or known ingestions of button cell battery to decrease the severity and/or risk of esophagus injury induced by the battery before its removal. Honey might be beneficial for the control of side effects of chemotherapy or radiation therapy used in cancer treatment. | Anfang et al., 2018; Grüter, 2020; Berenbaum and Calla, 2021; Martinez-Armenta et al., 2021 |
| Legumes | Beans, lupins, peas, peanuts (groundnut), black beans, chickpeas, navy beans, lentils, soybean, etc. | Dietary fiber, protein, dietary minerals, isoflavones (genistein, daidzein, glycitein), phytosterols, peptides, saponins, resveratrol, etc. | Due to their nutritional and phytochemical compositions, legumes generally help to prevent or treat diseases, including cancer, obesity, cardiovascular diseases, overweight, diabetes mellitus, digestive diseases, nervous system disorders, etc. Regular consumption of soybean can ameliorate the menopause symptoms and reduce the risk of cancers, including breast and prostate cancers. Peanuts have been used to fight malnutrition for decades. | Barman et al., 2018; Carrera et al., 2021 |
| Nuts | Tree nuts, peanuts, almonds, macadamia nuts, cashews, pistachios, Brazil nuts, macadamias, pecans, cashews, walnuts, hazelnuts, pine nuts, etc. | α-linolenic acid, minerals, polyunsaturated fatty acids, L-arginine, dietary fiber, antioxidants (polyphenols, tocopherols, etc.), folate, etc. | The components in nuts synergistically and favorably influence vascular and metabolic physiology pathways, improve cardiovascular prognosis, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases. The consumption of nuts within a given population is associated with lower incidence of cancer and cancer related mortality, and decrease in all-cause mortality. The consumption of nuts also has moderate improvements on inflammation, endothelial function, blood pressure (BP), and glycaemic control. Nuts generally have preventive, protective, and ameliorative effects on cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, diabetes, cancer, brain health, overall mortality, lowering blood pressure, improving lipid profile, improving epithelial functions, antiinflammatory actions, obesity/overweight, etc. | Del Gobbo et al., 2015; ARS, 2019; Ros et al., 2021 |
| Seafood (fishes) | Salmon, trout, herring, sardines, anchovies, cod, mackerel, lobster, tilapia, perch, mollusks, sea slugs, bryozoans, shrimp, tunicates, tuna, sponges, etc. | Polyunsaturated fatty acids, linoleic acid, arachidonic acid precursor, thromboxanes, leukotrienes, α-linolenic acid, highly unsaturated fatty acids (HUFA) >C20, docosahexaenic acid (DHA), docosapentaenic acid (DPA), eicosapentaenic acid (EPA), gelatin, collagen, myosin, peptides, copper, zinc, calcium, essential amino acids, vitamin B12, sodium, iodine, selenium, potassium, β-carotene, astaxanthin, glycosaminoglycans, glucosamine, chitosan, chitin, etc. | Seafood generally have high levels of essential fatty acids, including omega-3 fatty acids, that reduce the risks of cardiovascular diseases (heart diseases) and can improve the health of infants when consumed by pregnant or breastfeeding women. The bioactive compounds in seafood exert several physiological functions, such as antioxidant, antimicrobial, anticoagulant, anti-obesity, antitumor, anti-allergic, neuroprotective, anti-atherosclerotic, antihypertensive, antioxidant, anticancer, anticoagulant, anti-inflammatory, anti-obesity, appetite-suppressing, muscle relaxant, cardioactive, antidiabetic, hypotensive, analgesic, antibiotic, and immunomodulatory properties, among other nutraceutical properties | Telessy, 2019; Ashraf et al., 2020; Ellis, 2021 |
| Seeds | Flaxseeds, chai seeds, Sesame seeds, avocado seeds, Black seeds, pumpkin seeds, hemp seeds, sunflower seeds, etc. | Fiber, essential oils, omega-3 fats, antioxidants, polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats, vitamins, minerals, lignans, caffeic acid, triterpenes, campesterol, ferulic acid, p-coumaric acid, neolinustatin, lariciresinol, pinoresinol, sesamin, sesamolin, linystatin, secoisolariciresinol diglucoside (SDG), sitosterol, stigmasterol, catechins, triterpenoid glycosides, ferulic acid, coumaric acid, etc. | The inclusion of seeds in regular diets can reduce blood pressure, control blood sugar, lower LDL cholesterol, reduce risk of cancer, reduce the risk cardiovascular diseases, fight microbial infections, etc. reduce the risk of heart disease and cholesterol levels. In addition to reducing the risk of heart disease and cancer, flaxseeds can reduce blood sugar level and risk of diabetes mellitus. Seeds contain many important polyphenols that have antioxidant, antiinflammatory, anticancer, immune promoting, and cardioprotective properties, among other health and medicinal benefits. | Kawakami et al., 2015; Khosravi-Boroujeni et al., 2017; Robertson, 2017; Suryapal et al., 2021 |
| Vegetables | Broccoli, cauliflower, zucchini, pumpkin, kale, spinach, scent leaves, carrot, tea leaves, etc., | Omega-3 fatty acids, dietary fiber, cryptoxanthin, vitamins, zinc, β-carotene, selenium, lycopene, isoflavones, flavonoids, carotenoids (carotenes and xantophylls), epigallocatechin-3-gallate, epicatechin, epigallocatechin, epicatechin-3-gallate, glucosinolates, phytosterols, thiols, etc. | Vegetables play an important role in human health, including the prevention and treatment of many diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, infections, etc. Regular inclusion of vegetables in the diets leads to a decrease in incidence of cardiovascular diseases, stroke, cancer, and other diseases. Carotenoids in vegetables such as the carotenes, e.g., beta carotene, and the xanthophylls, e.g., astazanthin, zeaxanthin, canthaxantin, cryotpxanthin, etc., have a wide range of nutraceutical and health benefits | Saiwal et al., 2019; Arya et al., 2019 |
| Whole grains | Wheat, barley, rice, rye, oats, corn/maize, millets, job’s tears, canary grass, fonio, sorghum, wild rice, triticale, teff, buckwheat, amaranth, quinoa, Tartary buckwheat | Dietary fiber, minerals, vitamins, polyphenols, inulin, β-glucan, carotenoids (lutein, zeaxanthin, β-cryptoxanthin, β-carotene), lignans, vitamin E compounds, folate, betaine, phytosterols, tocols, etc. | The inclusion of whole grains in breakfast cereals is associated with improvement in the intake of micronutrient and reduced risk of diseases such as gastrointestinal conditions, poor cognition, obesity, CVDs, type 2 diabetes mellitus, coronary heart disease, cancer, all-cause mortality, stroke, diverticulosis, etc. | Priebe and McMonagle, 2016; Kelly et al., 2017; Zabolotneva et al., 2022 |
| Plant species | Image display | Common cultivars | Parts commonly used |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beta vulgaris |  | Swiss chard, beetroot, sugar beet, sea beet | Leaves, roots |
| Vicia faba |  | Broad bean | Seeds, pods |
| Brassica oleracea |  | Broccoli, cabbage, collard greens, Savoy cabbage, red cabbage, kohlrabi, cauliflower, kale, Brussels sprouts, etc. | Flower heads, axillary buds, leaves, stems |
| Daucus carota |  | Carrot | Root, stems, leaves |
| Cucumis sativus |  | Cucumber | Fruits |
| Solanum melongena |  | Eggplant (aubergine) | Fruits |
| Allium ampeloprasum |  | Elephant garlic, leek | Leaf sheaths |
| Lactuca sativa |  | Celtuce, lettuce | Leaves, seed oil, stems |
| Brassica rapa |  | Napa cabbage, turnip, bok choy | Root, leaves |
| Allium cepa |  | Onion, shallot, scallion, spring onion | Bulbs, leaves |
| Cucurbita spp. |  | Pumpkin, gourd, zucchini (courgette), marrow, squash | Leaves, flowers, fruits |
| Raphanus sativus |  | Daikon, radish, seedpod varieties | Leaves, root, sprouting, seed oil, seed pods |
| Spinacia oleracea |  | Spinach | Leaves |
| Ipomoea batatas |  | sweet potato | Leaves, shoots, tubers |
| Solanum lycopersicum |  | Tomato | Fruits |
| Bioactive component | Examples | Nutraceutical effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dietary fiber | Mucilages, beta-glucan, pectin, cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin | Fiber binds to excess fat and glucose, moving them to large intestine for defecation via stool. Fiber also helps in body detoxification mechanisms and prevention of diverticulosis. Fiber helps prevent excess fats and sugar in the blood, thus, reducing the risks of CVDs, obesity, and T2DM. | He et al., 2010; Ambuja and Rajakumar, 2018 |
| Essential fatty acids | Alpha-linolenic acid, linoleic acid, docosahexaenoic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid, docosapentaenoic acid, etc. | Essential fatty acids perform many important functions in the body, including cardioprotective, immune boosting, antimicrobial, metabolic, heart promoting, anti-inflammatory, and health promoting functions. Adequate intake of essential fatty acids has many health and nutraceutical benefits, including improvement in brain health, reduced depression, reduced joint pain from rheumatoid arthritis, improved cognition, improved heart health, reduced risk of atherosclerosis, reduced risk of heart disease, reduction in triglycerides, reduced inflammation, improved blood pressure, etc. | Hengeveld et al., 2018; Herrera Vielma et al., 2021; Joshi et al., 2022 |
| Minerals | Calcium, sodium, potassium, magnesium, phosphorus, sulfur, chloride, iodine, zinc, iron, copper, cobalt, manganese, selenium, fluoride, etc. | Minerals play many biological and physiological roles and have many potentials in homeostasis and metabolism. See Table 4 for the nutraceutical roles of specific minerals | Gharibzahedi and Jafari, 2017 |
| Phytochemicals | Polyphenols, alkaloids, glycosides, terpenes and terpenoids, etc. | Many phytochemicals exert important impacts on human and animal health system and provide many medicinal benefits on health, including helping in preventing and/or treating physiological disorders and many diseases. Many phytochemicals have antioxidant, cardioprotective, immune boosting, antimicrobial, metabolic, heart promoting, anti-inflammatory, and health promoting properties, among others. | Howes et al., 2020; Yeh et al., 2022 |
| Prebiotics | Resistant starch, oligosaccharides (galacto-oligosaccharides, inulin, and fructo-oligosaccharides), guar gum, pectin | In the colon, they serve as substrates for many beneficial bacteria, resulting in improved colon-pH reduction and short-chain fatty acids production, and act as selective stimulants to their proliferation. The short-chain fatty acids also have antioxidant (ROS scavenger), antiproliferative (regulation of apoptosis, signal transduction, and gene expression), and anti-inflammatory (reduced PGE2 and pro-inflammatory cytokines) properties. | Kellow et al., 2014; Zaman et al., 2015 |
| Probiotics | Lactobacillus plantarum, Leuconostoc argentinum, Leuconostoc citreum, Lactobacillus brevis, Pediococcus pentosaceus, etc. | Probiotics have been associated with the prevention and/or treatment of many diseases and conditions, including diarrhea (antibiotic-induced diarrhea, travellers diarrhea, acute diarrhea), Crohn’s disease, lactose intolerance, Helicobacter pylori infection, pouchitis, ulcerative colitis, metabolic diseases (e.g., dyslipidemia, obesity, diabetes mellitus), impaired immunity (allergic conditions), respiratory tract infections, neurological and mental health conditions, acute otitis media, allergies (eczema, milk allergy, etc.), depression and anxiety, dermatitis (eczema), childhood asthma, bacterial vaginosis, high blood pressure, inflammatory bowel disease, etc. | Cuello-Garcia et al., 2015; Saez-Lara et al., 2015; Dolan et al., 2016; Parker et al., 2016; Williamson et al., 2017; Robles-Vera et al., 2017; Lin et al., 2018; Guo et al., 2019; Scott et al., 2019; Ansari et al., 2020; Collinson et al., 2020 |
| Vitamins | Vitamins A, E, D, etc. | Vitamins improve health and can prevent diseases such as heart disease, vision loss, cancer, osteoporosis, immune system suppression, osteoarthritis, T2DM, and CVDs, and improves survival and quality of life. Antioxidant vitamins, such as vitamins C and E, inhibit oxidation process in the body and prevent the actions of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and free radicals, thus ensuring overall health and the prevention of many acute and chronic diseases. | Öztürk, 2017; Xiao and Li, 2020 |
| Dietary element | High nutrient density dietary sources | Category | Excess | Deficiency | Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA)/ Adequate intake (AI) Male/Female [mg] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sources: Schlenker and Gilbert (2014); Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare, Japan (2015); Food and Nutrition Board (2020). | |||||
| Calcium | Milk, dairy products, eggs, green leafy vegetables, fish with bones (sardines, salmon, etc.), tofu, thyme, nuts, seeds, oregano, etc. | Builds bone; needed for healthy muscle, digestive system, and heart; helps in blood clotting; supports function and synthesis of blood cells | hypercalcaemia | hypocalcaemia | 1,000 |
| Chlorine | Table salt (NaCl) | Needed for hydrochloric acid production in the stomach, as well as in the functions of cellular pump | hyperchloremia | hypochloremia | 2,300 |
| Chromium | Broccoli, meat, grape juice, whole grains, etc. | Involved in the metabolism of glucose and lipid | Chromium toxicity | Chromium deficiency | 0.035/0.25 |
| Cobalt | Required in synthesizing vitamin B12, however, as bacteria are required for vitamin B12 synthesis, it is normally regarded as part of vitamin B12 that is obtained from consuming foods from animal sources (e.g., eggs) | Enzyme with cobalt as its essential cofactor takes part in translation regulation; also, cobalt may be an oxygen sensor constituent. | Cobalt poisoning | Cobalt deficiency | none |
| Copper | Liver, oysters, seeds, nuts, seafood, legumes, whole grains, etc. | Required cytochrome c oxidase co-factor. Along with iron, copper helps the body to form red blood cells (RBCs). Helps in maintaining healthy blood vessels, bones, iron absorption, nerves, and immune functions | Copper toxicity | Copper deficiency | 0.9 |
| Iodine | Iodized salt, seaweed (kombu, kelp), eggs, grains | Required for synthesizing thyroid hormones, which control many body functions such as growth, development, etc. | Hyperthyroidism, iodism | Goiter, iodine deficiency | 0.150 |
| Iron | Meat, nuts, seafood, dark chocolate, beans, etc. | Required for several proteins, including enzymes, especially hemoglobin for the prevention of anemia. Involves in synthesizing hemopglobin for new RBCs | iron overload disorder | iron deficiency | 8/18 |
| Magnesium | Spinach, whole grains, legumes, avocado, nuts, seeds, peanut butter, etc. | Required for bones and for ATP processing. Essential for muscle and nerve functions, and helps in maintaining carbohydrates metabolism, bone health, regulating blood sugar, etc. | hypermagnesemia | hypomagnesemia, magnesium deficiency | 420/320 |
| Manganese | Grains, nuts, leafy vegetables, coffee, legumes, seeds, tea, etc. | Required superoxide dismutase co-factor. Involves in metabolism of amino acids, glucose, cholesterol, and carbohydrates. Involves in bone formation, scavenging reactive oxygen species, immune response, and reproduction. Involves in blood clotting and hemostasis | manganism | manganese deficiency | 2.3/1.8 |
| Molybdenum | Legumes, nuts, whole grains, etc. | Required for proper xanthine oxidase, sulfite oxidase, and aldehyde oxidase functioning. Oxygen transfer reaction functions | Molybdenum toxicity | Molybdenum deficiency | 0.045 |
| Phosphorus | Red meat, poultry, fish, dairy foods, oats, bread, rice. Often occurs as phosphate | A constituent of bones, DNA, ATP, energy processing, cells, etc. Helps keep heartbeat steady, kidney filter wastes, energy storage, tissue repair and development, breakdown of macromolecules, etc. | hyperphosphatemia | hypophosphatemia | 700 |
| Potassium | Sweet potato, lentils, milk and dairy products, potato, carrot, beans, tomato, prune, orange, seafood, banana, etc. | Systemic electrolyte. Essential in ATP coregulating with sodium. Involves in regulating water balance, heart functions, muscle contractions, etc. | hyperkalemia | hypokalemia | 4,700 |
| Selenium | Brazil nuts, meats, grains, seafoods, milk and dairy products, organ meats, eggs, etc. | Essential to antioxidant enzymes activity, including glutathione peroxidase | selenosis | selenium deficiency | 0.055 |
| Sodium | Table salt (NaCl), milk, spinach, sea vegetables, etc. | Systemic electrolyte. Essential in ATP coregulating with potassium. Plays role in muscle and nerve functions | hypernatremia | hyponatremia | 1,500 |
| Zinc | Oysters, nuts, poultry, milk and dairy products, whole grains, red meat, etc. | Required for many enzymes, including matrix metalloproteinases, carbonic anhydrase, liver alcohol dehydrogenase, zinc finger proteins, etc. | zinc toxicity | zinc deficiency | 11/8 |