Figures
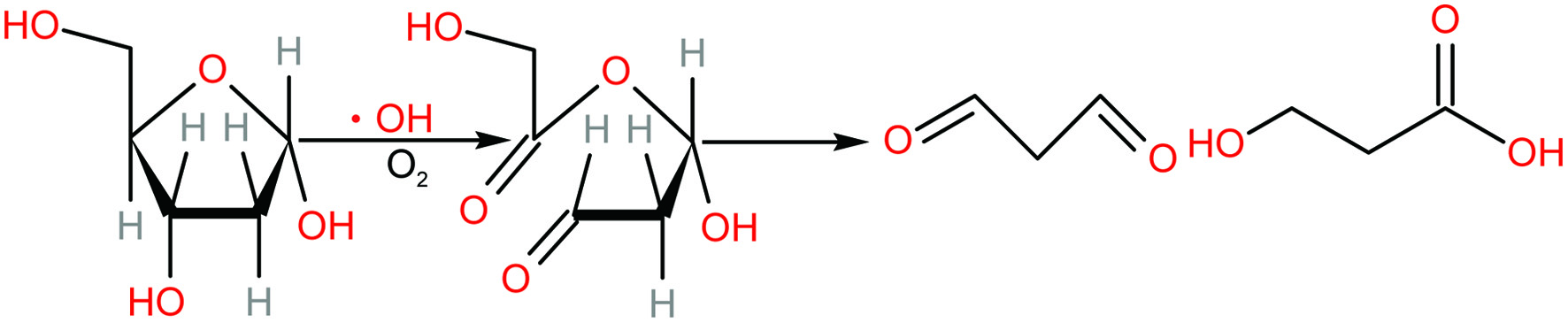
Figure 1. Proposed mechanism for the formation of malondialdehyde after 2-deoxyribose was attacked by hydroxyl radical (adapted from Cheeseman et al., 1988).
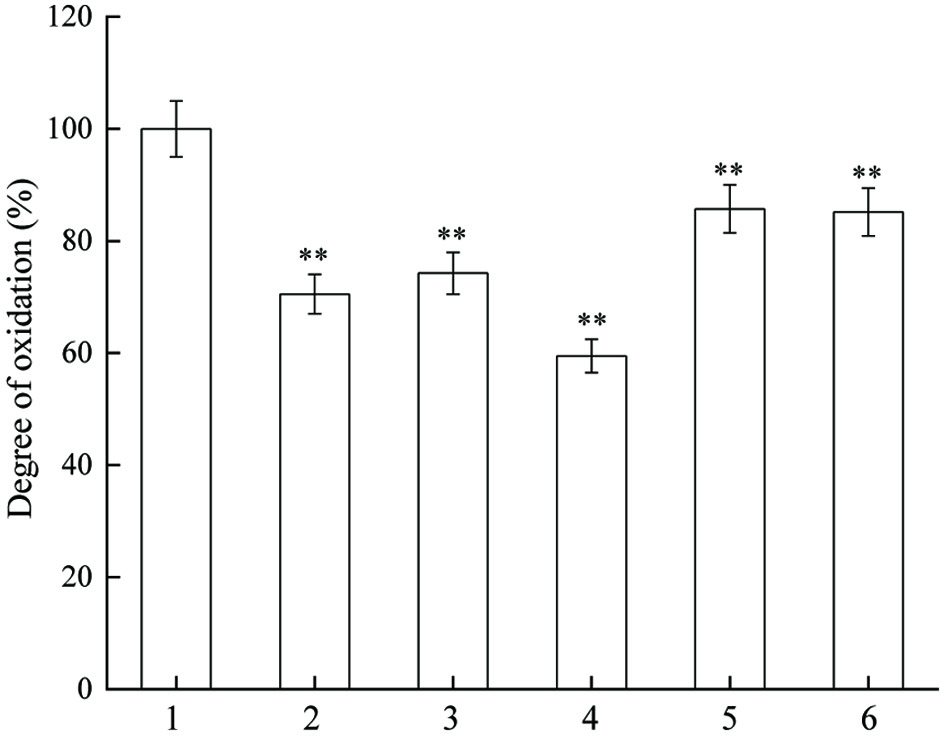
Figure 2. Inhibitory actvity of JAPS on linoleic acid oxidation in FeSO4/VC system. 1: FeSO4/VC + Linoleic acid, 2: FeSO4/VC + Linoleic acid+ 0.5 μg/mL of JAPS, 3: FeSO4/VC + Linoleic acid+ 2.5 μg/mL of JAPS, 4: FeSO4/VC + Linoleic acid+ 5.0 μg/mL of JAPS, 5: FeSO4/VC + Linoleic acid+ 25.0 μg/mL of JAPS, 6: FeSO4/VC + Linoleic acid+ 50.0 μg/mL of JAPS. **p < 0.01, group with JAPS vs. group without JAPS.
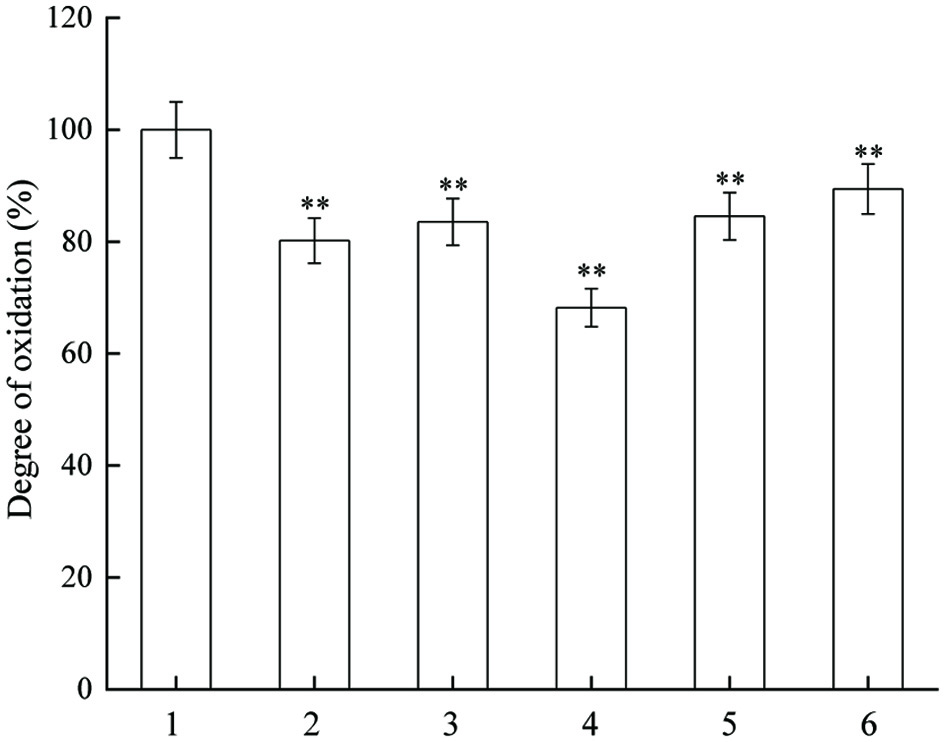
Figure 3. Inhibitory actvity of JAPS on linoleic acid oxidation in AAPH system. 1: AAPH + Linoleic acid, 2: AAPH + Linoleic acid+ 0.5 μg/mL of JAPS, 3: AAPH + Linoleic acid+ 2.5 μg/mL of JAPS, 4: AAPH + Linoleic acid+ 5.0 μg/mL of JAPS, 5: AAPH + Linoleic acid+ 25.0 μg/mL of JAPS, 6: AAPH + Linoleic acid+ 50.0 μg/mL of JAPS. **p < 0.01, group with JAPS vs. group without JAPS.
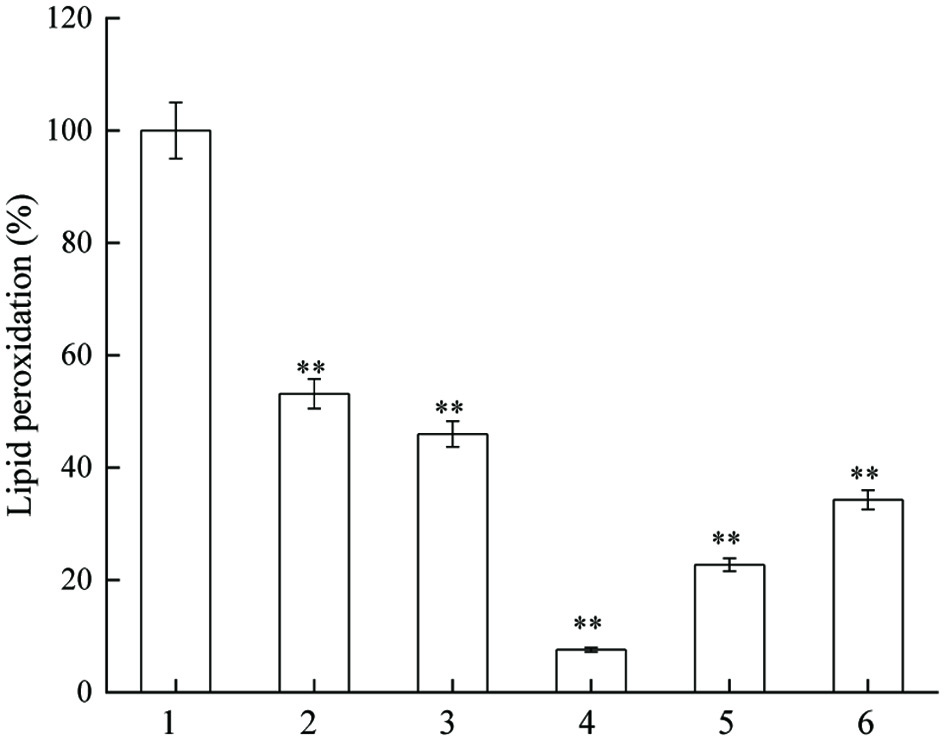
Figure 4. Inhibitory actvity of JAPS on lipid peroxidation. 1: Fe2+ + Lecithin, 2: Fe2+ + Lecithin + 0.5 μg/mL of JAPS, 3: Fe2+ + Lecithin + 2.5 μg/mL of JAPS, 4: Fe2+ + Lecithin + 5.0 μg/mL of JAPS, 5: Fe2+ + Lecithin + 25.0 μg/mL of JAPS, 6: Fe2+ + Lecithin + 50.0 μg/mL of JAPS. **p < 0.01, group with JAPS vs. group without JAPS.
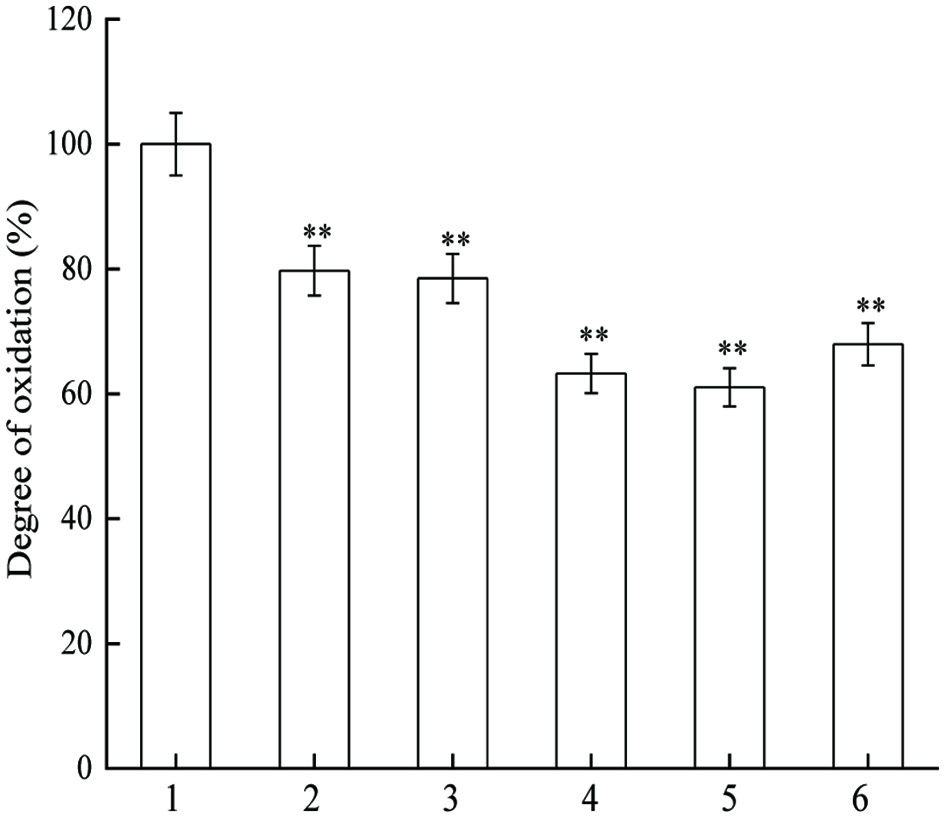
Figure 5. Inhibitory effect of JAPS on DNA oxidation in phen-CuSO4-Vc. 1: phen-CuSO4-Vc + DNA, 2: phen-CuSO4-Vc + DNA + 0.5 μg/mL of JAPS, 3: phen-CuSO4-Vc + DNA + 2.5 μg/mL of JAPS, 4: phen-CuSO4-Vc + DNA + 5.0 μg/mL of JAPS, 5: phen-CuSO4-Vc + DNA + 25.0 μg/mL of JAPS, 6: phen-CuSO4-Vc + DNA + 50.0 μg/mL of JAPS. **p < 0.01, group with JAPS vs. group without JAPS.
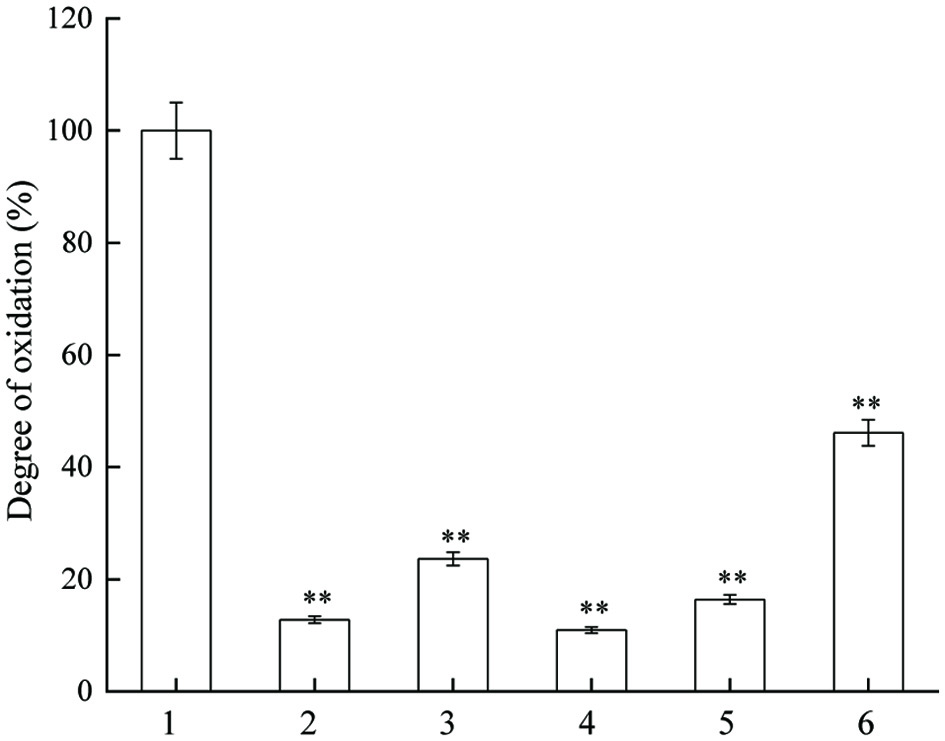
Figure 6. Inhibitory effect of JAPS on DNA oxidation in AAPH system. 1: AAPH + DNA, 2: AAPH + DNA + 0.5 μg/mL of JAPS, 3: AAPH + DNA + 2.5 μg/mL of JAPS, 4: AAPH + DNA + 5.0 μg/mL of JAPS, 5: AAPH + DNA + 25.0 μg/mL of JAPS, 6: AAPH + DNA + 50.0 μg/mL of JAPS. **p < 0.01, group with JAPS vs. group without JAPS.
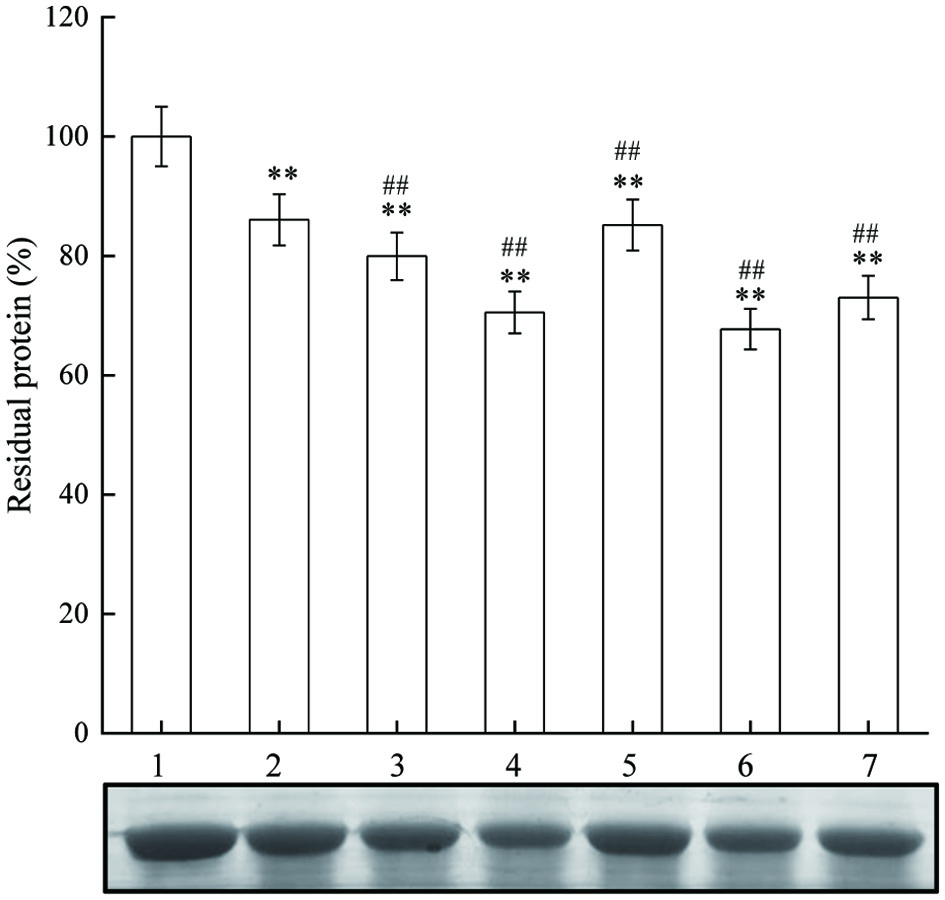
Figure 7. The effect of JAPS on BSA oxidation in Cu2+/H2O2 system. Lane 1: BSA, Lane 2: Cu2+/H2O2 + BSA, Lane 3: Cu2+/H2O2 + BSA + 0.5 μg/mL of JAPS, Lane 4: Cu2+/H2O2 + BSA + 2.5 μg/mL of JAPS, Lane 5: Cu2+/H2O2 + BSA + 5.0 μg/mL of JAPS, Lane 6: Cu2+/H2O2 + BSA + 25.0 μg/mL of JAPS, Lane 7: Cu2+/H2O2 + BSA + 50.0 μg/mL of JAPS. **p < 0.01 vs. Lane 1. ##p < 0.01 vs. Lane 2.
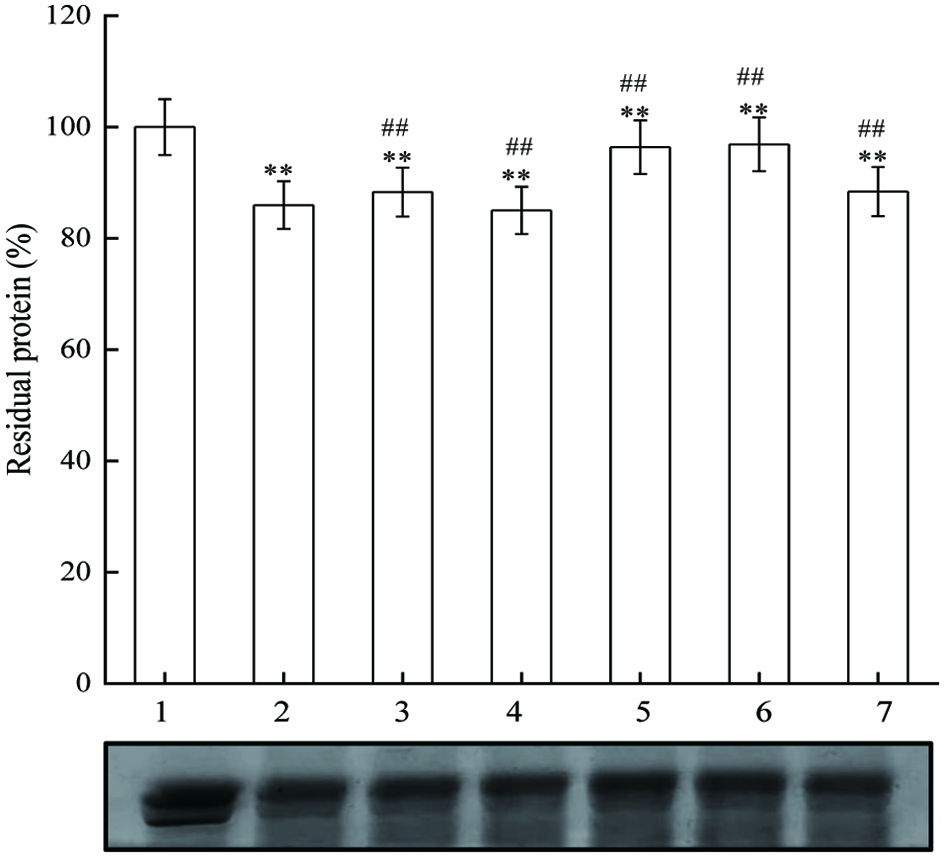
Figure 8. The effect of JAPS on BSA oxidation in AAPH system. Lane 1: BSA, Lane 2: AAPH + BSA, Lane 3: AAPH + BSA + 0.5 μg/mL of JAPS, Lane 4: AAPH + BSA + 2.5 μg/mL of JAPS, Lane 5: AAPH + BSA + 5.0 μg/mL of JAPS, Lane 6: AAPH + BSA + 25.0 μg/mL of JAPS, Lane 7: AAPH + BSA + 50.0 μg/mL of JAPS. **p < 0.01 vs. Lane 1. ##p < 0.01 vs. Lane 2.








