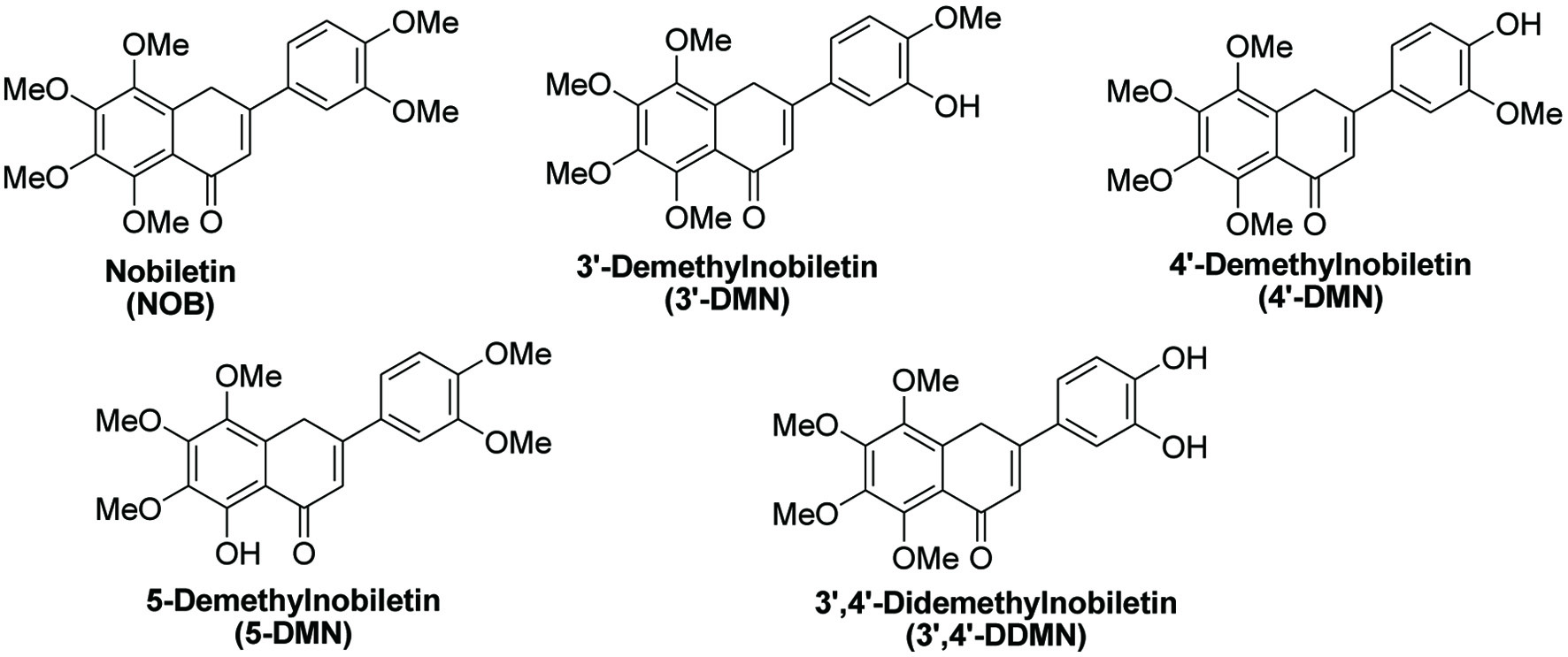
Figure 1. Structures of nobiletin and its in vivo metabolites.
| Journal of Food Bioactives, ISSN 2637-8752 print, 2637-8779 online |
| Journal website www.isnff-jfb.com |
Review
Volume 14, June 2021, pages 53-59
Recent study on the anticancer activity of nobiletin and its metabolites
Figures

Table
| Protective Effects | PMF Compounds | Cancer Types | Dosage | Results | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
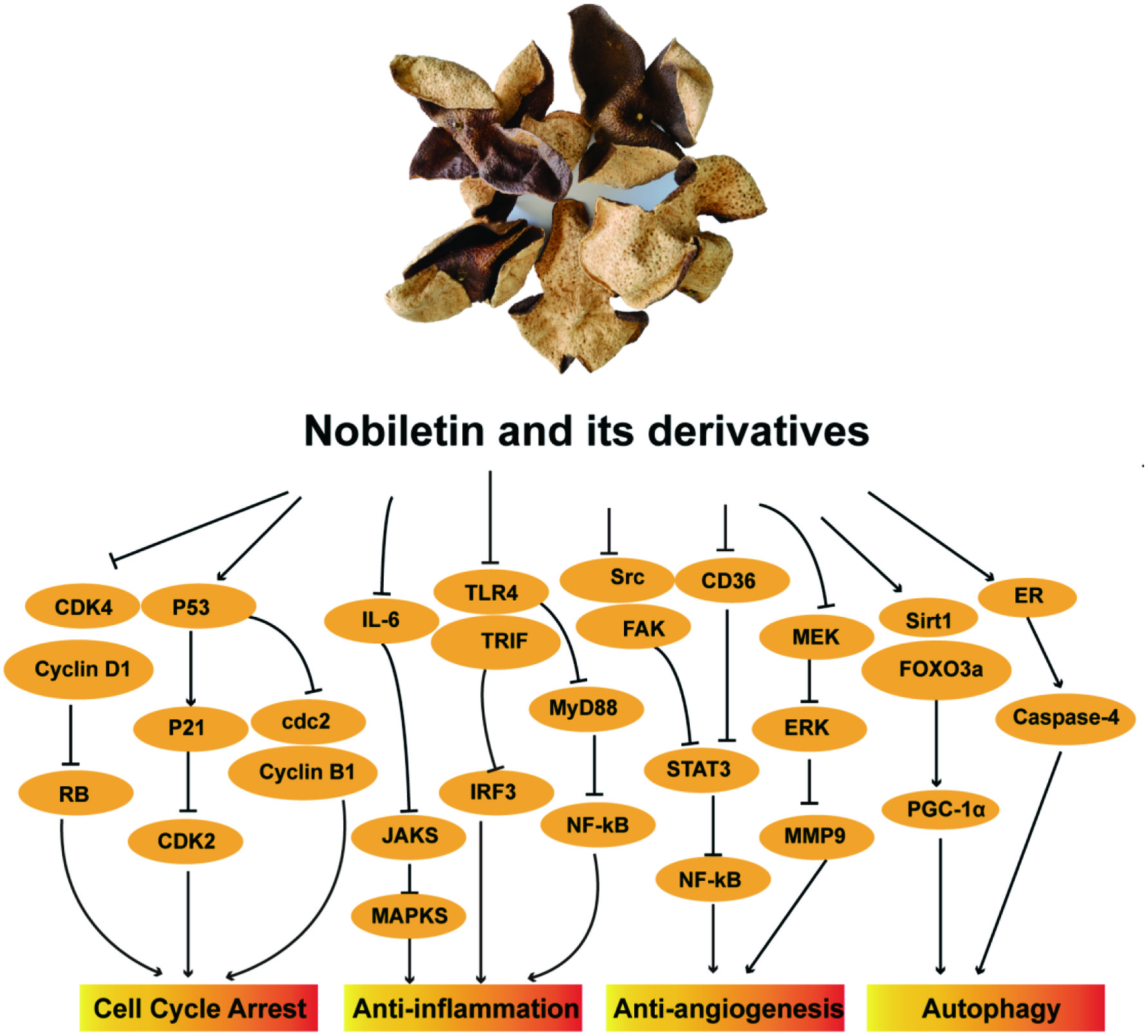
| Cell Cycle Arrest | Nobiletin | Pancreatic cancer | 6.12 µM | Inhibited the growth and metastasis. Induced autophagy, G0/G1 cell cycle arrest. Inhibited NF-kB signal pathway | Jiang et al., 2020 |
| Glioma | 100 μM | Inhibited glioma cell growth and migration. Arrested the cell cycle in the G0/G1 phase. Suppressed MAPK and Akt pathways | Lien et al., 2016 | ||
| 4′-DMN | Colon cancer | 0.05% (w/w, in diet) | Inhibited cell growth. Induced G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis | Wu et al., 2018 | |
| 3′,4′-DDMN | Colon cancer | 7.5 µM | Inhibited cell growth. Induced significant G2-M cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis | DiMarco-Crook et al., 2020 | |
| 5-DMN | Lung cancer | 12.5 µM | Inhibited cell growth. Induced G2/M cell cycle phase arrest. Induced autophagy. Activated JNK signaling pathway | Chen et al., 2015 | |
| 4′-DMN, | Lung cancer | 50 µM | Inhibited cell growth caused cell cycle arrest and cellular apoptosis. Modulated the expression of proteins related to cell proliferation and death | Song et al., 2016 | |
| 3′,4′-DDMN | 25 µM | ||||
| Anti-inflammation | Nobiletin | Prostate cancer | 80 µM | Inhibited cell growth. Suppressed TLR4/TRIF/IRF3, TLR9/IRF7 signal pathways. Inhibited the release of IFN-α and IFN-β | Ozkan et al., 2020 |
| Nobiletin and its metabolites | Colon cancer | 2.03 µM, NOB; 3.28 µM, 3′-DMN; 24.13 µM, 4′-DMN; 12.03 µM;,3′,4′-DDMN | Suppressed LPS-induced iNOS and COX-2 expression. Increased heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and NQO1 expression | Wu et al., 2017 | |
| 3′,4′-DDMN | Skin tumor | 1 or 3 µM | Inhibited TPA-induced iNOS, COX-2, VEGF, MMP-9 and ODC expression, nuclear translocation and phosphorylation of p65/RelA | Lai et al., 2008 | |
| Anti-angiogenesis | Nobiletin | Breast cancer | 200 µM | Inhibited cell growth. Inhibited VEGF-dependent angiogenesis. Inhibited EGFR activity and Src/FAK/STAT3 signaling | Sp et al., 2017 |
| Inhibited the expression of CD36 and its downstream target proteins. Inhibited CD36-mediated Angiogenesis. Inhibited CD36-dependent breast cancer cell migration and Invasion, inhibited tumorsphere formation and survival | Sp et al., 2018 | ||||
| Nobiletin | Colorectal cancer | 64 µM | Inhibited MEK activity and ERK phosphorylation | Miyata et al., 2008 | |
| Autophagy | Nobiletin | Hepatic Ischemia and reperfusion injury | 5 mg/kg | Alleviated oxidative damage, inflammation, and cell death caused by hepatic ischemia and reperfusion. Activated the SIRT-1/FOXO3a and PGC-1α pathways | Dusabimana et al., 2019 |
| Ovarian cancer | 40 μM | Selectively suppressed cell growth and proliferation. Induced G0/G1 phase arrest and reduced G2/M phase. Induced apoptosis. | Jiang et al., 2018 | ||
| Nobiletin | Gastric cancer | 50 μM | Increased the levels of ER-stress related proteins IRE1-α, ATF-4, C/EBP homology protein, GRP78 and caspase-4. Decreased cell viability. Increased the number of sub-G1 phase cells. Induced apoptosis | Moon and Cho, 2016 | |
| 5-DMN | Colon cancer | 50 or 100 mg/kg | Decreased the tumor size and tumor weight. Increased the ratio of cleaved-PARP and LC3 expression in tumor tissues. Induced p53-regulated cell death signaling pathway | Song et al., 2020 | |
| ROS | Nobiletin | Ovarian Cancer | 50 μM | Inhibited cell growth. Induced cell apoptosis and autophagy. Induced ROS generation contributing to pyroptosis | Zhang et al., 2020 |
| Oral cancer | 100 μM | Increased the expression of the apoptosis molecule PARP and caspase-3. Increased the level of ROS and the degree of DNA damage. Inhibited cell growth | Yang et al., 2020 | ||
| Gastric cancer | 50 μM | Reduced ROS levels. Inhibited p38, extracellular receptor kinase 1, and c-Jun amino-terminal expression. Inhibited cell growth | Ouyang, Li and Ling, 2020 |