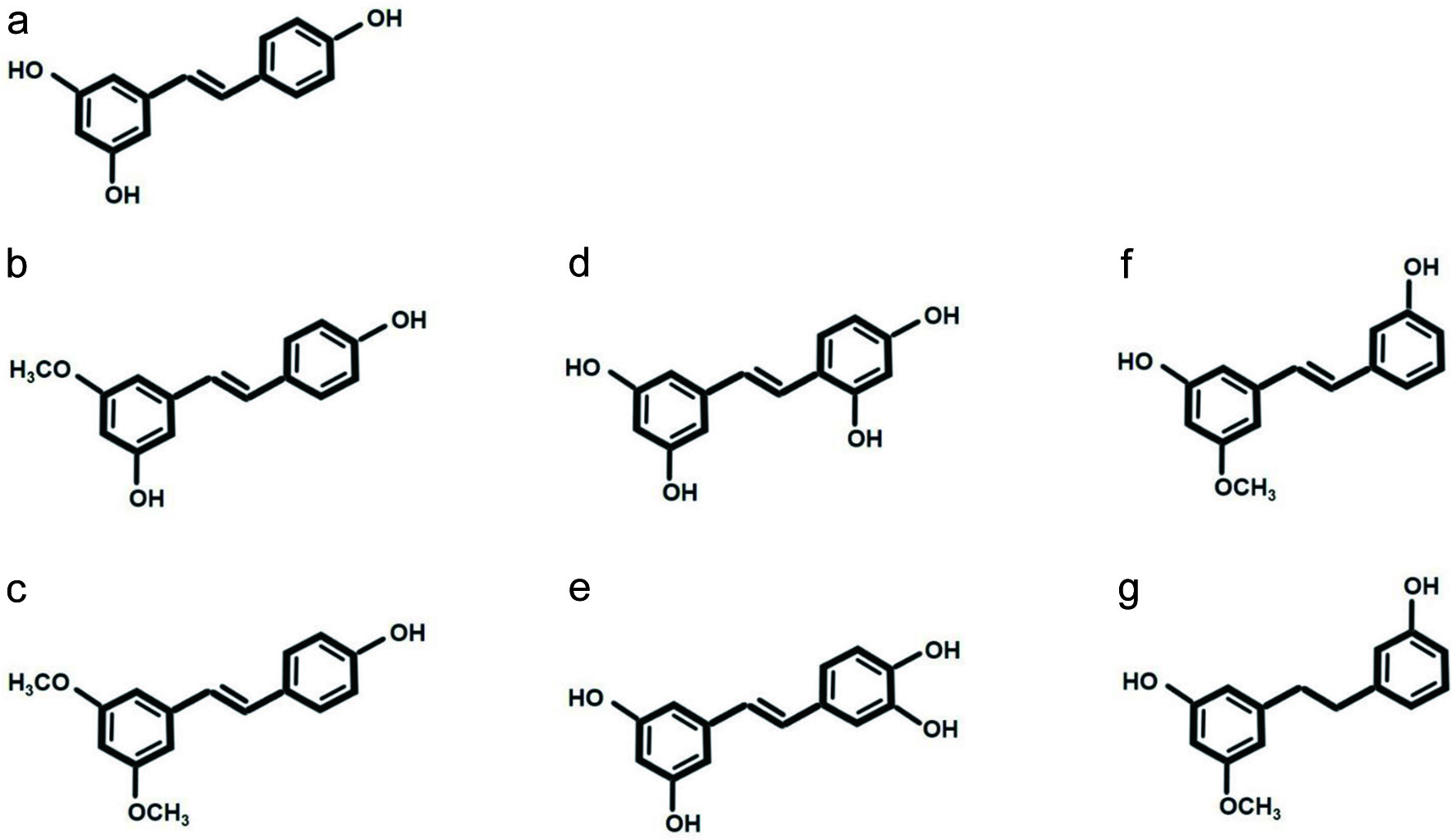
Figure 1. Resveratrol and its analogues found naturally in plants. (a) Resveratrol, (b) pinostilbene, (c) pterostilbene, (d) oxyresveratrol, (e) piceatannol, (f) thunalbene, and (g) batatasin III.
| Journal of Food Bioactives, ISSN 2637-8752 print, 2637-8779 online |
| Journal website www.isnff-jfb.com |
Review
Volume 12, December 2020, pages 97-105
A review: potential of resveratrol and its analogues to mitigate diseases via gut microbial modulation
Figures

Tables
| Supplementation | Model/inducer | Phylum | Class/Order | Family | Genus/Species | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resveratrol (50 mg/kg B.W.) | HFD-induced rat | – | – | Ruminococcaceae ↑ Lachnospiraceae ↑ | Akkermansia muciniphila ↑ Desulfovibrio ↑ | Chen et al., 2020 |
| Extract containing resveratrol | Feces of female human volunteer | – | Bacteroidales ↓ | Enterobacteriaceae ↑ | – | Giuliani et al., 2016 |
| Resveratrol (400 mg/kg B.W.) | HFD-induced rat | F/B ratio ↑ | – | Peptostreptococcaceae ↓ S24-7 ↓ | unclassified Peptostreptococcaceae ↑ unclassified Ruminococcaceae ↑ Anaerotruncus ↑ Bilophila ↑ Blautia ↑ Dorea ↑ Sutterella ↑ | Yang et al., 2019 |
| Resveratrol (400 mg/kg B.W.) + sinapic acid (200 mg/kg B.W.) | HFD-induced rat | Tenericutes ↓ Actinobacteria ↓ | – | Lachnospiraceae ↑ Peptostreptococcaceae ↑ | Roseburia ↑ | Yang et al., 2019 |
| Resveratrol (60 mg/kg B.W.) | HFD-induced mice | – | – | Ruminococcaceae ↑ Rikenellaceae ↑ Peptostreptococcaceae ↓ S24-7 ↑ | Alistipes ↓ Anaerotruncus ↑ Clostridium XI ↓ | Sreng et al., 2019 |
| Resveratrol (25–100 mg/kg B.W.) | Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) | Firmicutes ↑ Proteobacteria ↑ Cyanobacteria ↑ | – | Acetobacteraceae ↑ Methylobacteriaceae ↑ Streptococcaceae ↓ | – | Zheng et al., 2018 |
| Resveratrol (300 mg/kg B.W.) | HFD-induced mice | – | – | – | Desulfovibrio ↓ Lachnospiraceae_NK4A316_group ↓ Alistipes ↓ Allobaculum ↑ Bacteroides ↑ Blautia ↑ | Wang et al., 2020 |
| Resveratrol (0.4% in diet) | HFD-induced mice | Bacteriodetes ↑ Firmicutes ↓ F/B ratio ↓ | – | – | – | Yin et al., 2020 |
| Resveratrol (0.4% in diet) | HFD/high sucrose-induced mice | – | – | Turicibacteraceae ↓ Lachnospiraceae ↓ | Akkermansia ↓ Moryella ↓ Bacteroides ↑ Parabacteroides ↑ | Sung et al., 2017 |
| Resveratrol (50 mg/L drinking water) | HFD exposure during maternal and postnatal stage (offspring) | F/B ratio ↓ Bacteriodetes ↑ Cyanobacteria ↑ Tenericutes ↓ | – | – | Akkermansia ↓ | Huang et al., 2020 |
| Resveratrol (50 mg/L drinking water) | L-NAME treatment + HFD exposure | F/B ratio ↓ | – | – | Akkermansia ↑ | Chen et al., 2019 |
| Resveratrol (40–80 mg/kg B.W.) | CFA-induced TMJ inflammation in mice | Bacteroidetes ↑ | – | Lachnospiraceae ↑ | – | Ma et al., 2020 |
| Resveratrol (100 mg/kg B.W.) | TNBS-induced colitis in mice | – | – | – | Bacteroides acidifciens ↓ Ruminococcus gnavus ↑ Akkermansia mucinphilia ↑ | Alrafas et al., 2019 |
| Pterostilbene (15 mg/kg B.W.) | Zucker rats | Firmicutes ↓ Verrucomicrobia ↑ | – | – | Akkermansia muciniphila ↑ Odoribacter splanchnicus ↑ | Usune Etxeberria et al., 2017 |
| Resveratrol (0.4%in diet) | Choline or TMA drinking mice | – | – | Peptococcaceae ↓ Ruminococcaceae ↓ | Lactobacillus ↑ Bifidobacterium ↑ Akkermansia ↑ Bacteroides ↑ Prevotella ↓ Anaerotruncus ↓ Alistipes ↓ Helicobacter ↓ | Chen et al., 2016 |
| Pterostilbene (0.05% in diet) | Carnitine-drinking mice (1.3%) | – | – | Erysipelotrichia ↓ | Turicibacter ↓ Bacteroides ↓ | Koh et al., 2019; Simó and García-Cañas, 2020 |
| Piceatannol (0.1–0.25% in diet) | HFD-induced mice | Firmicutes ↑ Bacteroidetes ↓ | – | – | Lactobacillus ↓ | (Tung et al., 2016) |
| Piceatannol (15–45 mg/kg B.W.) | Zucker rats | Deferribacteres ↓ Planctomycetes ↓ Verrumicrobia ↓ | – | – | Bacteroides dorei ↑ Clostidium aerotolerans ↑ Clostidium viride ↑ Faecalibacterium prausnitzii ↑ Lactobacillus animalis ↓ Lactobacillus oris ↓ Bacteroides acidifaciens ↓ Clostidium hathewayi ↓ | Hijona et al., 2016 |
| Supplementation | Model | Potential outcomes | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resveratrol (50 mg/kg B.W.) | HFD-induced rat | Maintained intestinal barrier integrity by colonic CB1 Inhibited intestinal inflammation by CB2 | Chen et al., 2020 |
| Resveratrol (400 mg/kg B.W.) | HFD-induced rat | Blood glucose control Increased HDL-c level | Yang et al., 2019 |
| Resveratrol (400 mg/kg B.W.) + sinapic acid (200 mg/kg B.W.) | HFD-induced rat | Suppressed oxidative stress Mitigated intestinal dysbiosis induced by HFD | Yang et al., 2019 |
| Resveratrol (60 mg/kg B.W.) | HFD-induced mice | Efficacy of resveratrol on glycemic control was correlated with gut microbiota Curcumin could eliminate effect of resveratrol | Sreng et al., 2019 |
| Resveratrol (25–100 mg/kg B.W.) | Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) | Proportion of beneficial microbial taxa increased Proportion of harmful microbial taxa decreased | Zheng et al., 2018 |
| Resveratrol (300 mg/kg B.W.) | HFD-induced mice | Improved gut intestinal barrier integrity Increased abundance of SCFA-producing bacteria Ameliorated weight gained, hepatic lipid metabolism Prevented low-grade inflammation and liver steatosis | Wang et al., 2020 |
| Resveratrol (0.4% in diet) | HFD-induced mice | Lipogenesis-related genes and proteins (SREBP-1, FAS, ACC) were influenced by resveratrol modulated gut microbiota Hepatic steatosis was prevented | Yin et al., 2020 |
| Resveratrol (0.4% in diet) | HFD/high sucrose-induced mice | Glucose homeostasis of obese mice could be improved by resveratrol modulated gut microbiota | Sung et al., 2017 |
| Resveratrol (50 mg/L drinking water) | HFD exposure during maternal and postnatal stage (offspring) | Increased plasma propionate level Altered metabolic dysregulation and dysbiosis induced by maternal/postnatal HFD exposure | Huang et al., 2020 |
| Resveratrol (50 mg/L drinking water) | L-NAME treatment + HFD exposure | Prevented inhibition of AMPK/PGC-1α pathway induced by L-NAME and HFD exposure Prevented hypertension by gut microbiota modification | Chen et al., 2019 |
| Resveratrol (40–80 mg/kg B.W.) | CFA-induced TMJ inflammation in mice | Restored BBB integrity Reduced proinflammatory cytokine TMJ inflammatory pain could be prevented by resveratrol modulated gut microbiota | Ma et al., 2020 |
| Resveratrol (100 mg/kg B.W.) | TNBS-induced colitis in mice | Increased production of butyric acid Resveratrol modulated microbiota was more resistant to TNBS colitis Protected against colonic inflammation by inducing Tregs and suppression Th1/Th17 cells | Alrafas et al., 2019 |
| Pterostilbene (15 mg/kg B.W.) | Zucker rats | Re-composited gut microbiota Enrichment of mucin-degrading bacteria, Akkermansia and Odoribacter might be associated with anti-obesity effect of resveratrol | Usune Etxeberria et al., 2017 |
| Resveratrol (0.4%in diet) | Choline or TMA drinking mice | Enhanced bile acid deconjugation via increased Lactobacillus and Bidifobacterium Decreased TMAO level and increased hepatic bile acid neosynthesis via gut microbiota remodeling and enterohepatic FXR-FGF15 axis | Chen et al., 2016 |
| Pterostilbene (0.05% in diet) | Carnitine-drinking mice (1.3%) | Decreased hepatic flavin monooxygenase 3 (FMO3) mRNA level Decreased vascular inflammatory markers Decreased conversion of carnitine into TMA by gut microbiota | Koh et al., 2019 |
| Piceatannol (0.1–0.25% in diet) | HFD-induced mice | Preventing adipogenesis | Tung et al., 2016 |
| Piceatannol (15-45 mg/kg B.W.) | Zucker rats | Reduced plasma LPS level Decreased circulating non-esterified fatty acid, LDL-c and lactate Increased cardiac ephrin-B1 | Hijona et al., 2016 |