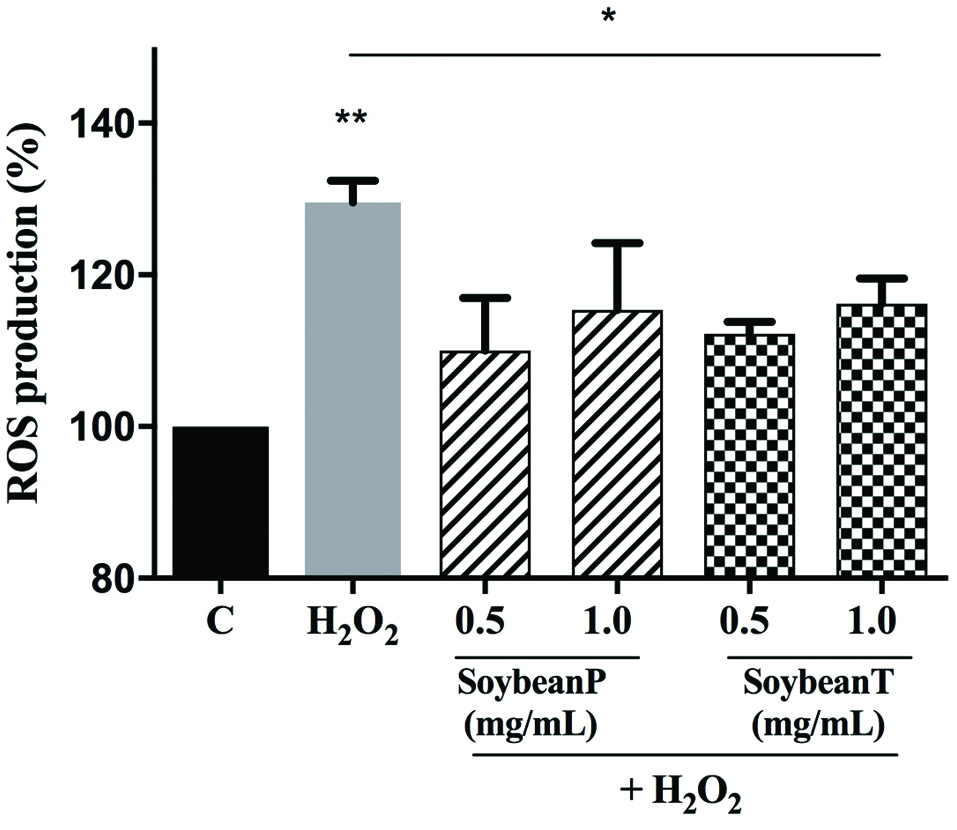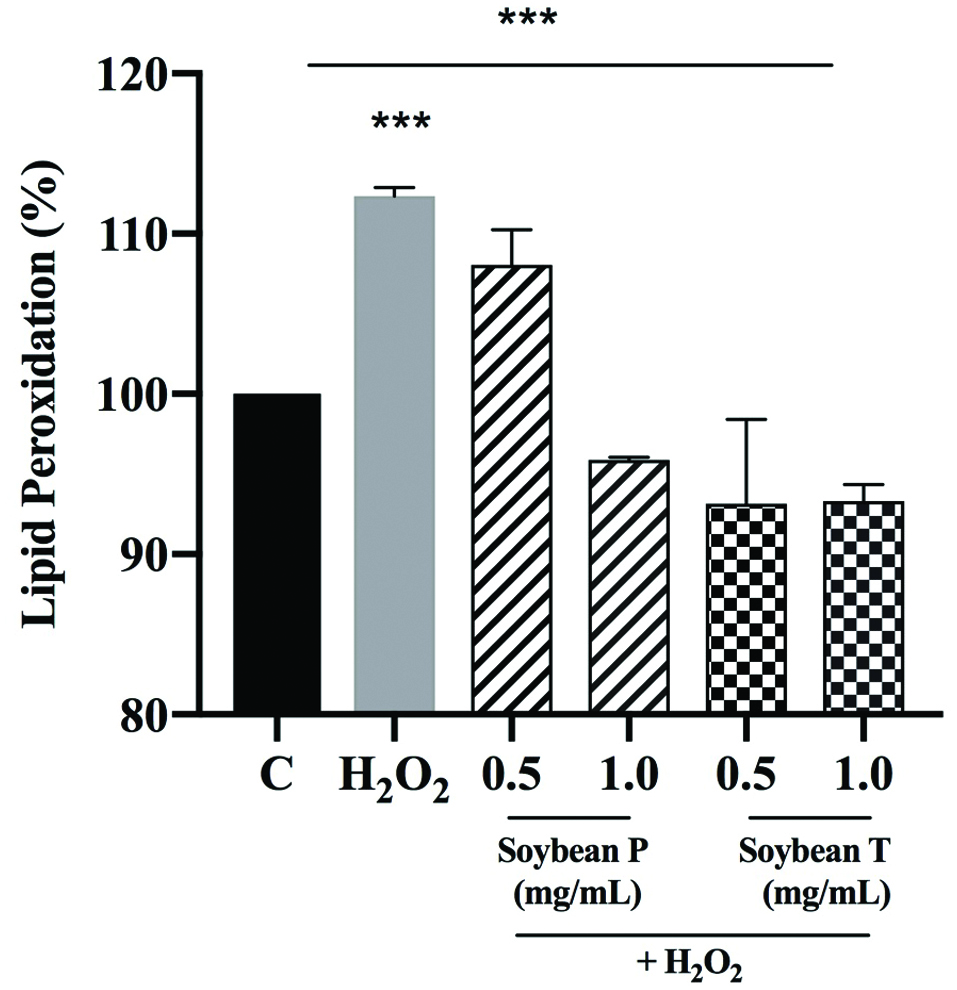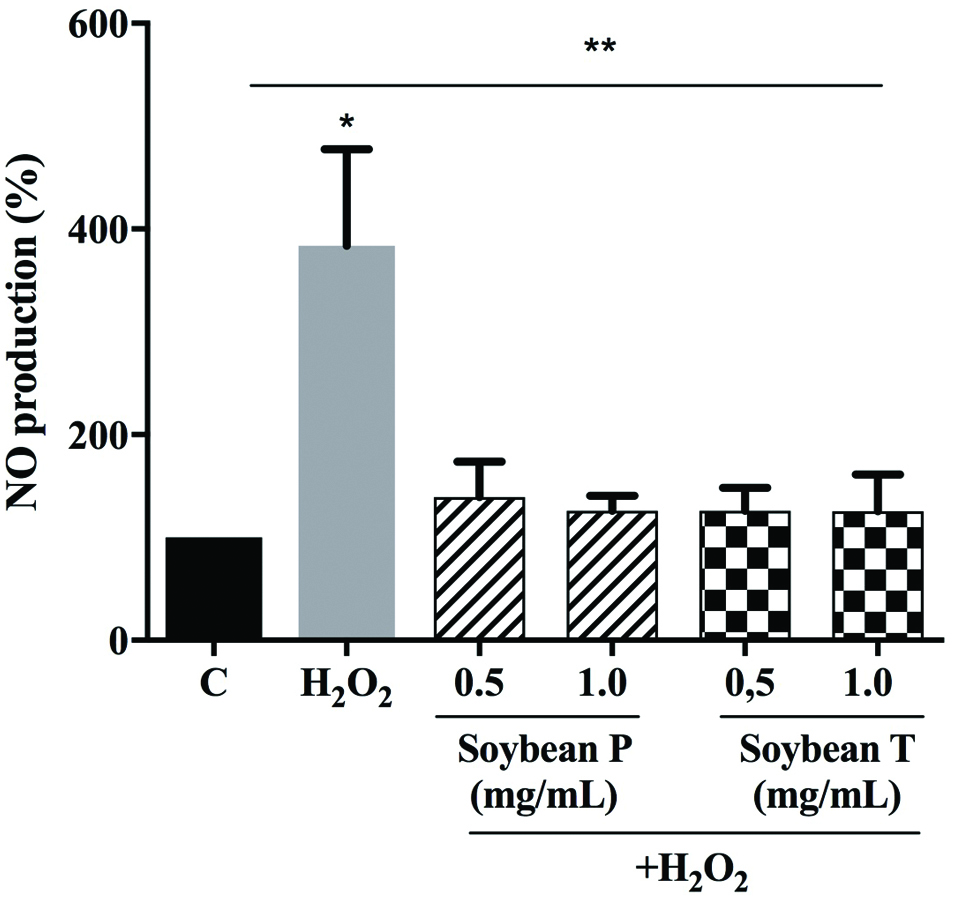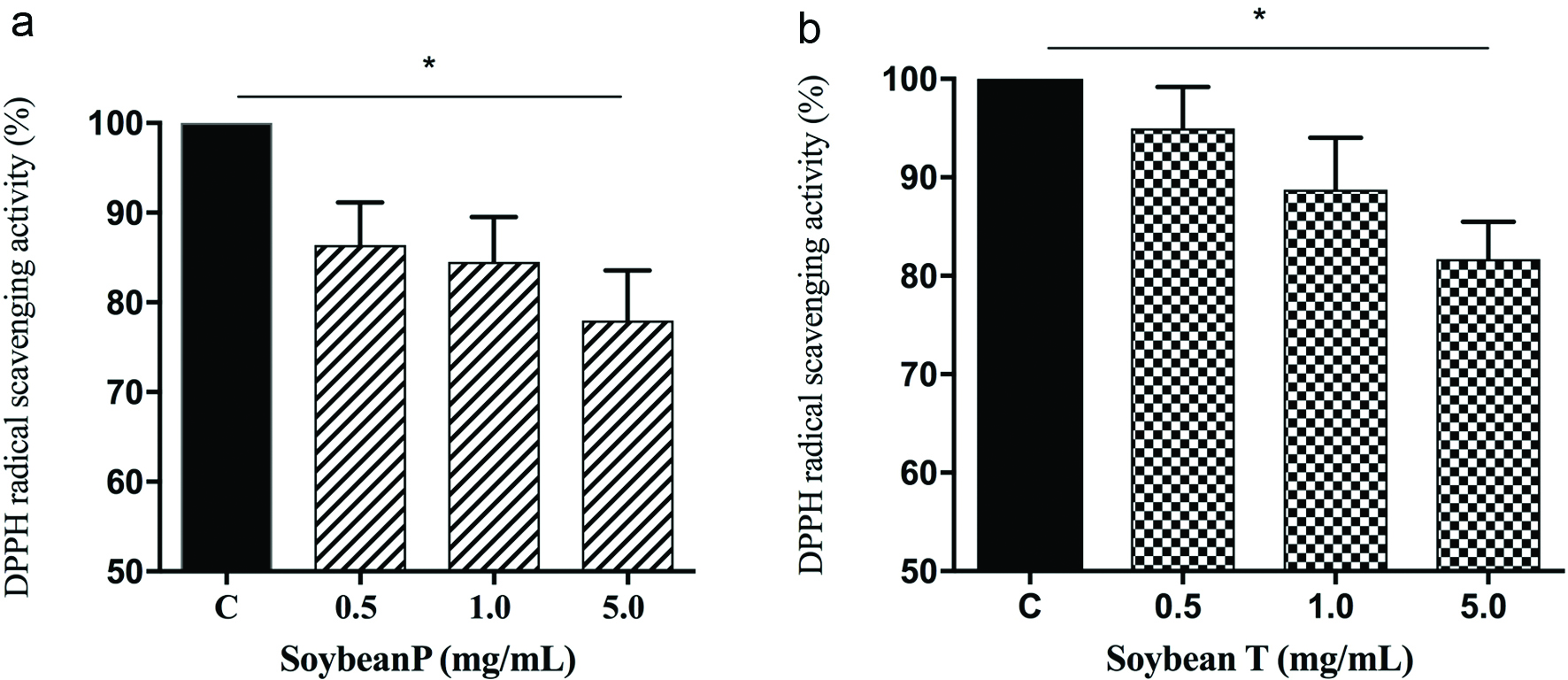
Figure 1. In vitro evaluation of the DPPH radical scavenger activity of Soybean P (a) and Soybean T (b) hydrolysates. The data points represent the averages ± sd of four independent experiments in duplicate. (*) p < 0.05. C: control sample.
| Journal of Food Bioactives, ISSN 2637-8752 print, 2637-8779 online |
| Journal website www.isnff-jfb.com |
Original Research
Volume 7, September 2019, pages 43-47
Antioxidant activity of soybean peptides on human hepatic HepG2 cells
Figures