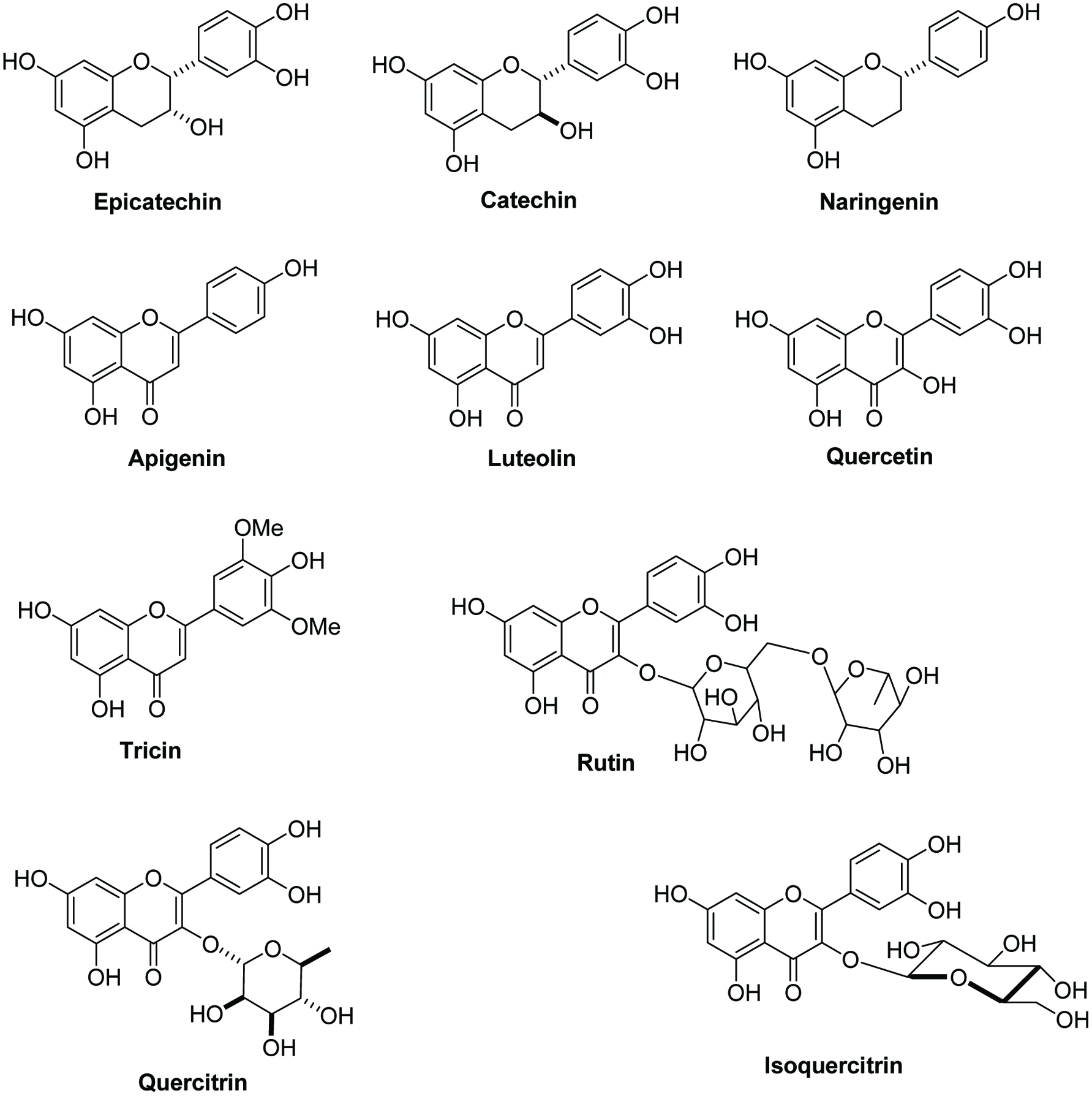
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of flavonoids from sugarcane rind.
| Journal of Food Bioactives, ISSN 2637-8752 print, 2637-8779 online |
| Journal website www.isnff-jfb.com |
Review
Volume 3, Number , September 2018, pages 1-7
Sugarcane rind: applications and health benefits: a review
Figures

Chemical structures of flavonoids from sugarcane rind.

Chemical structures of policosanol and 1-octacosanol.
Tables
| Compound | Gallic acid | Catechin | Sinapic acid | Ferulic acid | (−)-Epicatechin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aThe values are expressed as the mean ± SD of triplicate tests. | |||||
| Content (mg/g) | 0.50 ± 0.04 | 0.67 ± 0.45 | 1.66 ± 0.01 | 1.31 ± 0.09 | 27.24 ± 1.48 |
| Extraction methods | Conditions | 1-OC contents | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| aThe value is expressed as the mean ± SD of triplicate tests. | |||
| Supercritical CO2 extraction | Extracted for 4 h at 30 MPa and at 45 °C. | 53.14 mg/g of sugarcane skin on wet basis | (Yang et al., 2008) |
| Supercritical CO2 extraction | Extracted for 4 h at 350 bar and at 50 °C, with liquid CO2 flow rate of 40 g/min. | 1902.8 ± 242.3 μg/g of dry planta | (Attard et al., 2015) |
| Anhydrous ethanol extraction | Ethanol-sugarcane rind powder 8:1 ml/g, extracted for 4 h at 80 °C. | 31 mg/g of crude sugarcane waxes | (Feng et al., 2015c) |