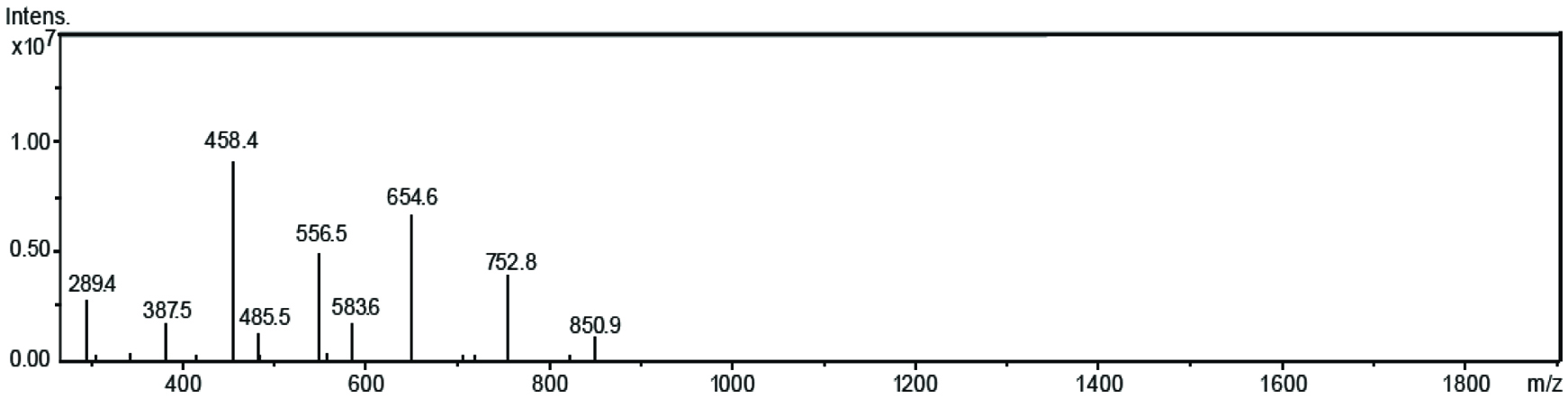
Mass spectrum of EGCG tetracaproylate.
| Journal of Food Bioactives, ISSN 2637-8752 print, 2637-8779 online |
| Journal website www.isnff-jfb.com |
Original Research
Volume 1, March 2018, pages 124-133
Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) esters with different chain lengths fatty acids and their antioxidant activity in food and biological systems
Figures

Mass spectrum of EGCG tetracaproylate.
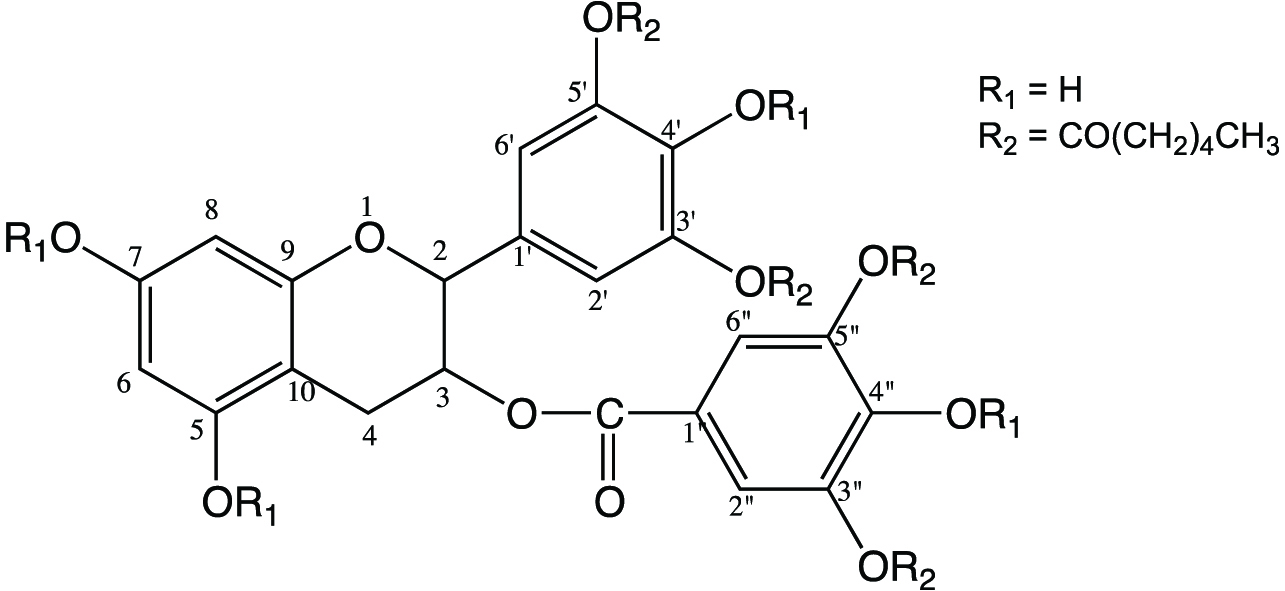
Chemical structures of EGCG-3′,5′,3″,5″-O- tetracaproylate.
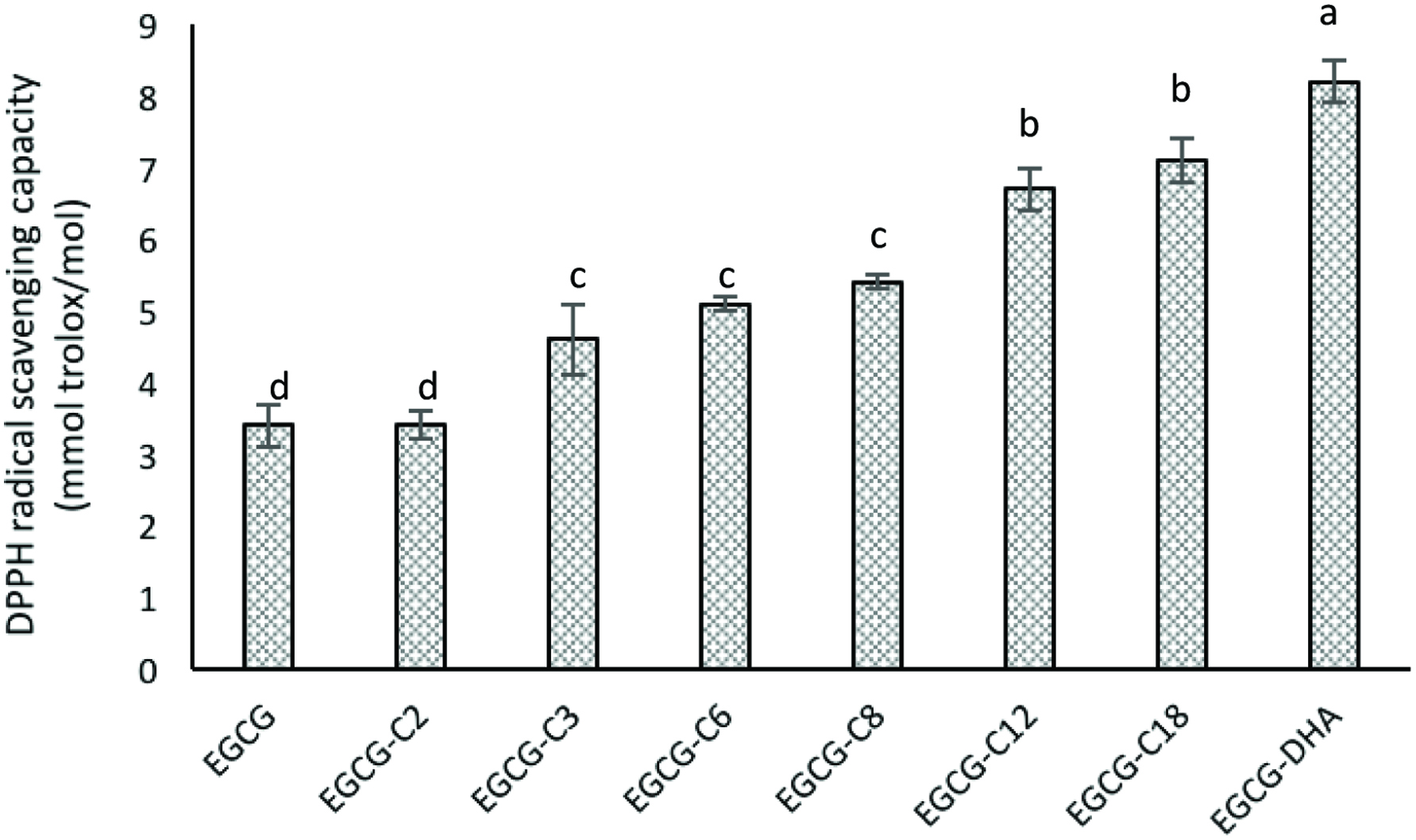
DPPH radical scavenging activities of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) and its esters. [(2) EGCG-C2, EGCG tetraacetate; (3) EGCG-C3, EGCG tetrapropionate; (4) EGCG-C6, EGCG tetracaproylate; (5) EGCG-C8, EGCG tetracapryloylate; (6) EGCG-C12, EGCG tetralauroylate; (7) EGCG-C18, EGCG tetrastearoylate; and (8) EGCG-DHA, EGCG tetradecosahexaenoate].
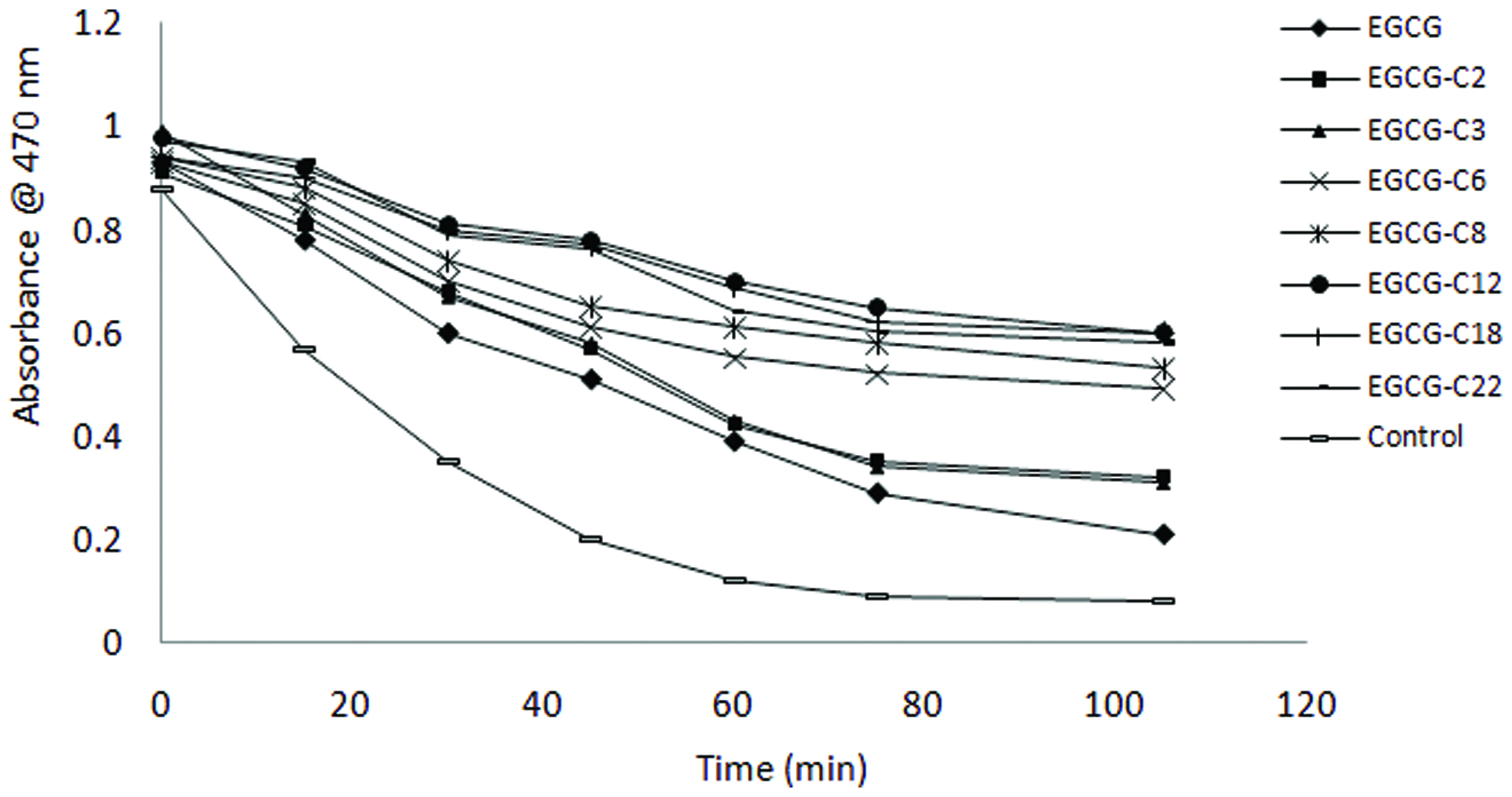
β-carotene bleaching as affected by epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) and its derivatives. [(2) EGCG-C2, EGCG tetraacetate; (3) EGCG-C3, EGCG tetrapropionate; (4) EGCG-C6, EGCG tetracaproylate; (5) EGCG-C8, EGCG tetracapryloylate; (6) EGCG-C12, EGCG tetralauroylate; (7) EGCG-C18, EGCG tetrastearoylate; and (8) EGCG-DHA, EGCG tetradecosahexaenoate].
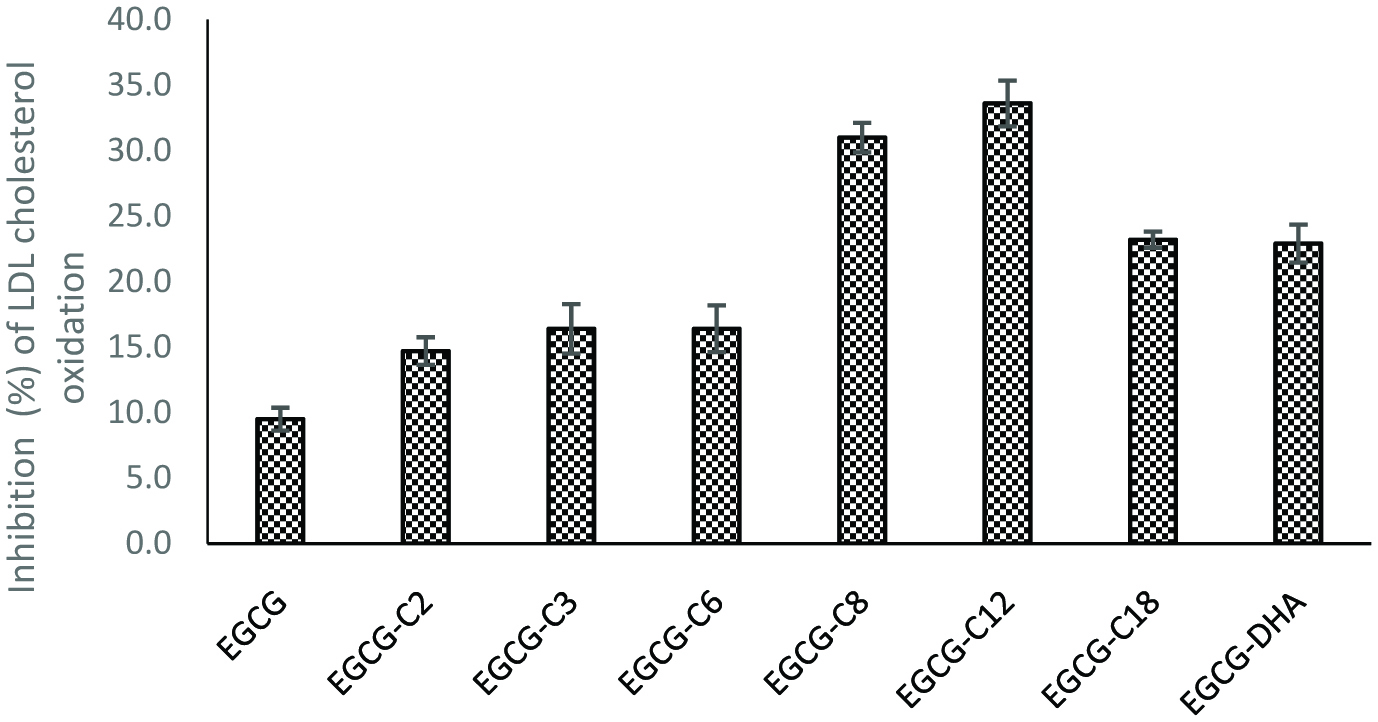
Inhibition of LDL choleterol peroxidation by EGC and its derivatives. [(2) EGCG-C2, EGCG tetraacetate; (3) EGCG-C3, EGCG tetrapropionate; (4) EGCG-C6, EGCG tetracaproylate; (5) EGCG-C8, EGCG tetracapryloylate; (6) EGCG-C12, EGCG tetralauroylate; (7) EGCG-C18, EGCG tetrastearoylate; and (8) EGCG-DHA, EGCG tetradecosahexaenoate].
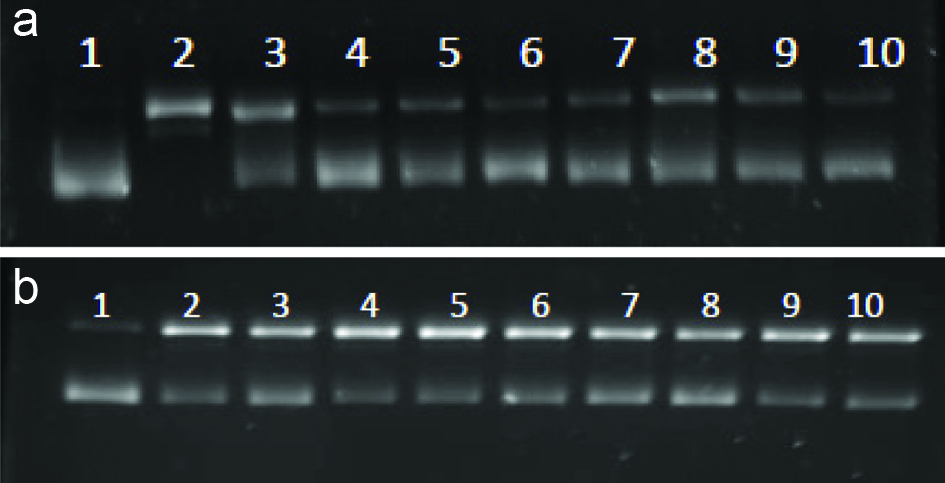
Inhibition of hydroxyl (A) and peroxyl (B) radicals induceed DNA scissionby EGC and its derivatives. Lanes 1-Blank (DNA only); 2-Control; 3-EGCG; 4-EGCG-C2; 5-EGCG-C3; 6-EGCG-C6; 7-EGCG-C8; 8-EGCG-C12; 9-EGCG-C18; 10-EGCG-DHA. [(2) EGCG-C2, EGCG tetraacetate; (3) EGCG-C3, EGCG tetrapropionate; (4) EGCG-C6, EGCG tetracaproylate; (5) EGCG-C8, EGCG tetracapryloylate; (6) EGCG-C12, EGCG tetralauroylate; (7) EGCG-C18, EGCG tetrastearoylate; and (8) EGCG-DHA, EGCG tetradecosahexaenoate].
Tables
| EGCG | EGCG-C6 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C/H position | 13C | 1H | 13C | 1H |
| 2 | 77.66 | 4.96 | 77.59 | 4.97 |
| 3 | 69.14 | 5.36 | 69.18 | 5.39 |
| 4 | 26.86 | 2.65 | 26.81 | 2.67 |
| 2.93 | 2.96 | |||
| 5 | 156.8 | 156.77 | ||
| 6 | 95.46 | 5.83 | 95.45 | 5.83 |
| 7 | 158.62 | 158.64 | ||
| 8 | 96.68 | 5.93 | 96.71 | 5.94 |
| 9 | 157.61 | 157.63 | ||
| 10 | 98.5 | 98.47 | ||
| 1′ | 129.71 | 129.61 | ||
| 2′ | 106.61 | 6.39 | 106.65 | 6.48 |
| 3′ | 146.52 | 150.72 | ||
| 4′ | 133.47 | 131.77 | ||
| 5′ | 146.52 | 150.72 | ||
| 6′ | 106.61 | 6.39 | 106.61 | 6.48 |
| 1″ | 120.42 | 120.44 | ||
| 2″ | 109.81 | 6.82 | 109.41 | 6.86 |
| 3″ | 146.76 | 151.26 | ||
| 4″ | 139.64 | 137.14 | ||
| 5″ | 146.76 | 151.26 | ||
| 6″ | 109.78 | 6.77 | 106.54 | 6.86 |
| COO | 166.38 | 166.36 | ||
| # | Compound* | Lipophilicity (Octanol-water partition coefficient, P) | Protection factor** |
|---|---|---|---|
| Values (mean ± SD of three replicates) with different letters were significantly different at P < 0.05. | |||
| *[(2) EGCG-C2, EGCG tetraacetate; (3) EGCG-C3, EGCG tetrapropionate; (4) EGCG-C6, EGCG tetracaproylate; (5) EGCG-C8, EGCG tetracapryloylate; (6) EGCG-C12, EGCG tetralauroylate; (7) EGCG-C18, EGCG tetrastearoylate; and (8) EGCG-DHA, EGCG tetradecosahexaenoate]. | |||
| **In stripped corn oil at 0.5 µmol/g of oil. | |||
| 1 | EGCG | 0.38 ± 0.06d | 1.51±0.30 c |
| 2 | EGCG-C2 | 0.43 ± 0.04 a | 1.12±0.45 e |
| 3 | EGCG-C3 | 0.45 ± 0.06 a | 1.08±0.68 e |
| 4 | EGCG-C6 | 0.55 ± 0.38 a | 1.85±0.05 b |
| 5 | EGCG-C8 | 0.70 ± 0.38 b | 2.26±0.75 a |
| 6 | EGCG-C12 | 0.77 ± 0.38 b | 2.38±0.40 a |
| 7 | EGCG-C18 | 1.07 ± 0.38 c | 2.23±0.35 a |
| 8 | EGCG-DHA | 1.38 ± 0.30 c | 1.94±0.25 b |
| # | Compound* | Inhibition (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| β-carotene bleaching | TBARS formation in cooked pork | ||
| Values (mean ± SD of three replicates) with different letters were significantly different at P < 0.05. | |||
| 1Inhibition (%) calculated at the end of the incubation period (105 min). | |||
| 2Inhibition (%) calculated at the end of storage period (day 14). | |||
| *[(2) EGCG-C2, EGCG tetraacetate; (3) EGCG-C3, EGCG tetrapropionate; (4) EGCG-C6, EGCG tetracaproylate; (5) EGCG-C8, EGCG tetracapryloylate; (6) EGCG-C12, EGCG tetralauroylate; (7) EGCG-C18, EGCG tetrastearoylate; and (8) EGCG-DHA, EGCG tetradecosahexaenoate]. | |||
| 1 | EGCG | 13.27 ±0.75e | 64.45±1.65 d |
| 2 | EGCG-C2 | 20.53 ±0.50d | 66.77±0.78 d |
| 3 | EGCG-C3 | 22.24 ±0.45d | 65.43±0.65 d |
| 4 | EGCG-C6 | 40.63 ±0.21c | 88.78±0.45 a |
| 5 | EGCG-C8 | 48.25 ±0.34b | 89.65±1.23 a |
| 6 | EGCG-C12 | 54.49 ±0.75a | 90.75±0.43a |
| 7 | EGCG-C18 | 47.26 ±0.24b | 87.45±2.45 b |
| 8 | EGCG-DHA | 46.66 ±0.22b | 84.22±1.38 b |
| BHA | – | 82.76±1.56 c | |
| # | Compound* | DNA retention (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydroxyl radical | Peroxyl radical | ||
| Values (mean ± SD of three replicates) in the same column with different letters were significantly different at P < 0.05. | |||
| *[(2) EGCG-C2, EGCG tetraacetate; (3) EGCG-C3, EGCG tetrapropionate; (4) EGCG-C6, EGCG tetracaproylate; (5) EGCG-C8, EGCG tetracapryloylate; (6) EGCG-C12, EGCG tetralauroylate; (7) EGCG-C18, EGCG tetrastearoylate; and (8) EGCG-DHA, EGCG tetradecosahexaenoate]. | |||
| Control | 27.87 ±0.45e | 23.27 ±0.75f | |
| 1 | EGCG | 43.27 ±1.75c | 81.45±1.65a |
| 2 | EGCG-C2 | 29.53 ±0.50e | 56.77±0.78e |
| 3 | EGCG-C3 | 30.28 ±0.95e | 55.43±0.65e |
| 4 | EGCG-C6 | 34.43 ±0.21d | 68.78±0.45c |
| 5 | EGCG-C8 | 48.27 ±0.34b | 69.65±1.23c |
| 6 | EGCG-C12 | 55.49 ±0.85a | 70.75±0.43c |
| 7 | EGCG-C18 | 40.26 ±1.24c | 78.45±2.45b |
| 8 | EGCG-DHA | 36.65 ±0.22d | 64.22±1.38d |