Figures
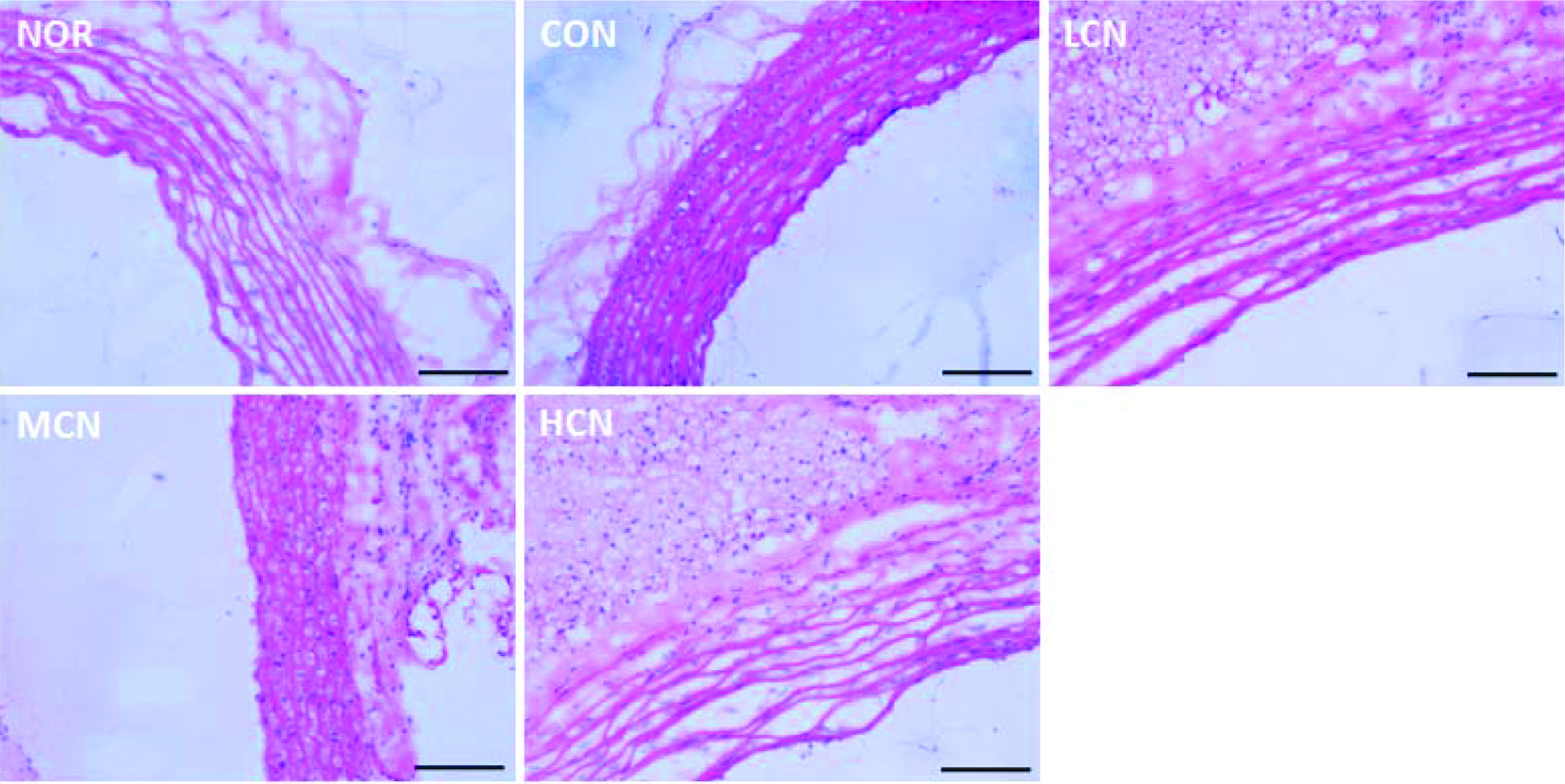
Figure 1. H&E staining results of cardiovascular tissue in rats of different treatment groups. (At the end of the experiment, the proximal aorta samples from five randomly selected rats in each group were harvested, then H&E staining was performed. The scale bar represents 200 μm)
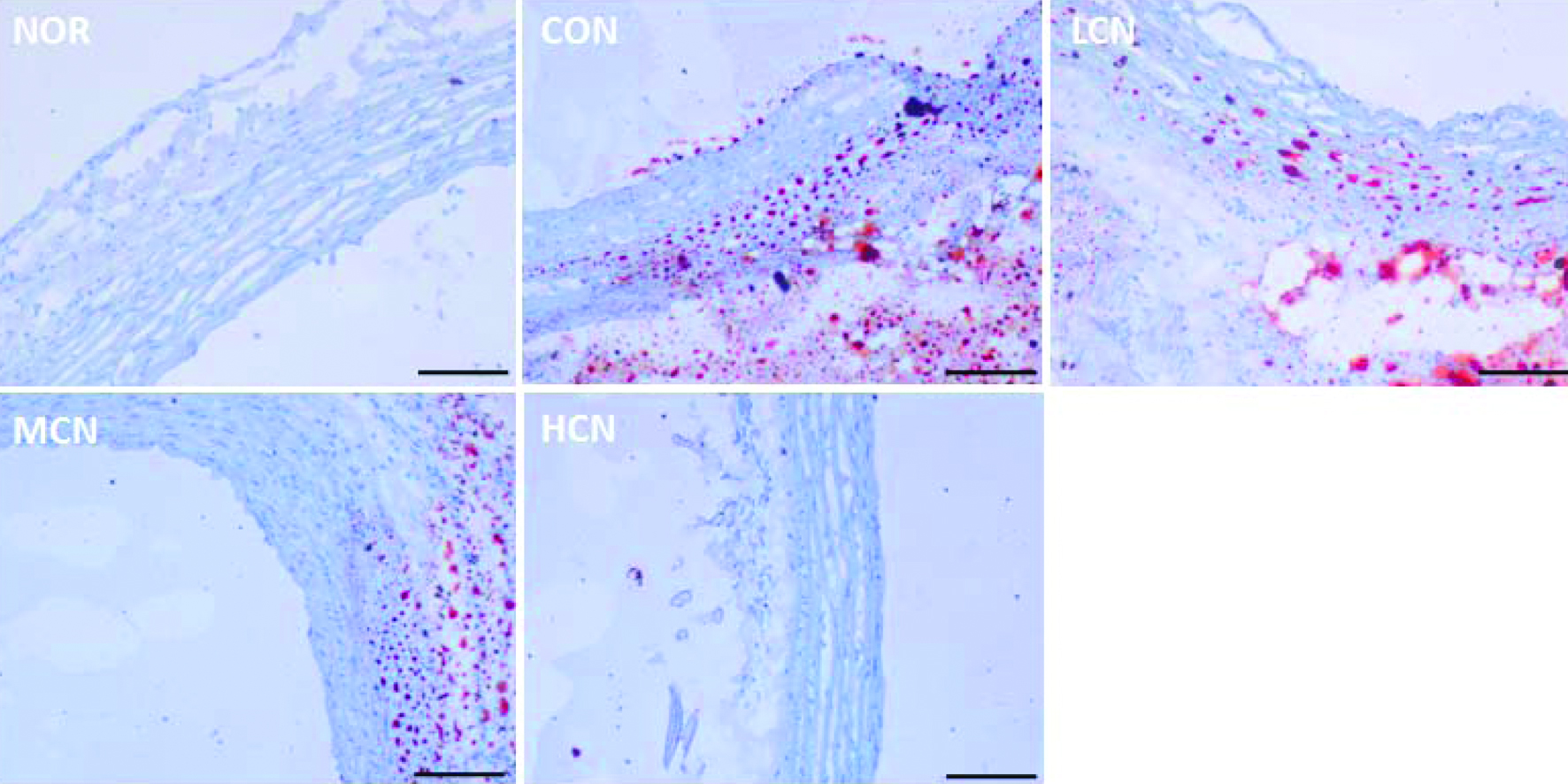
Figure 2. Oil red O staining results of cardiovascular tissue in rats of different treatment groups. (At the end of the experiment, the proximal aorta samples from five randomly selected rats in each group were harvested, then oil red O staining was performed. The scale bar represents 200 μm)
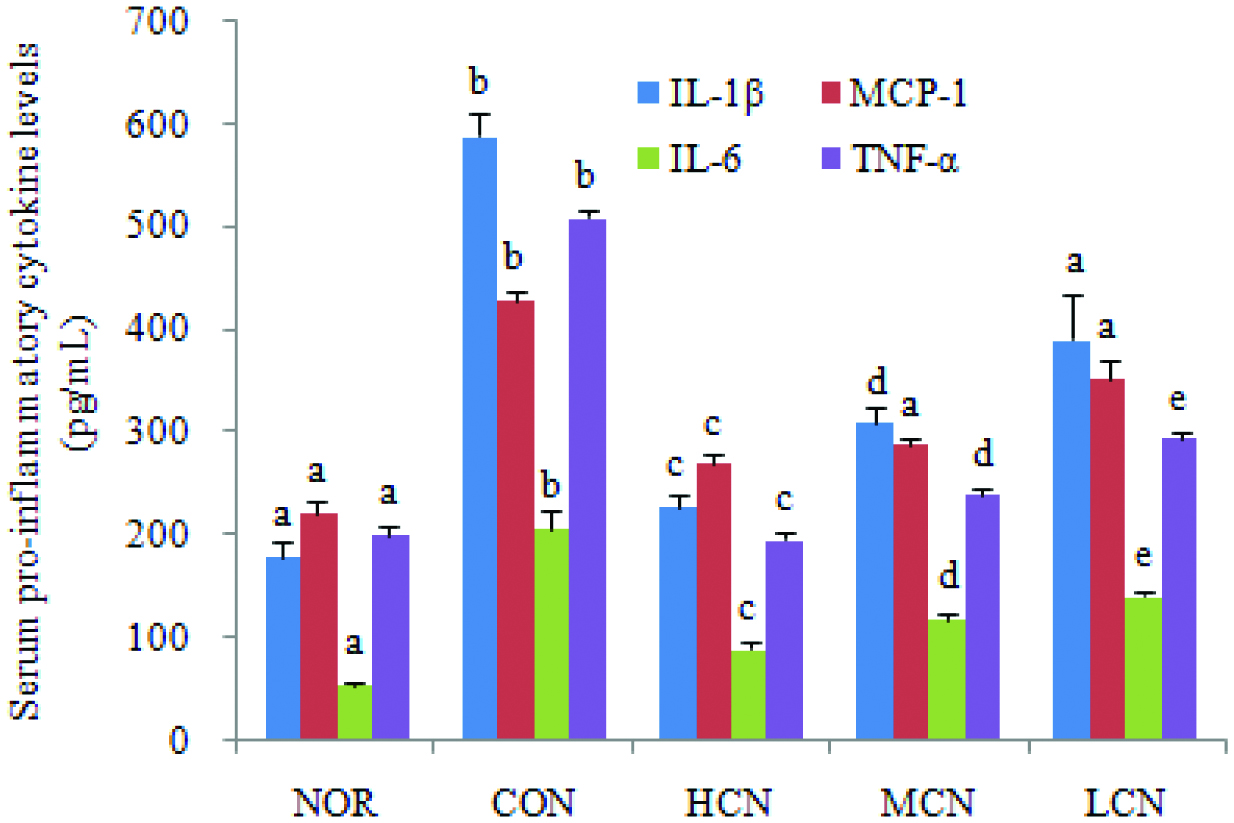
Figure 3. Effect of nobiletin on serum pro-inflammatory cytokines level in choline chloride-treated SD rats. The average content of serum pro-inflammatory cytokines of each group is expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 3 per group). Values not sharing the same superscript letters (a–e) of the same indexs are significantly different between the groups. p < 0.01.
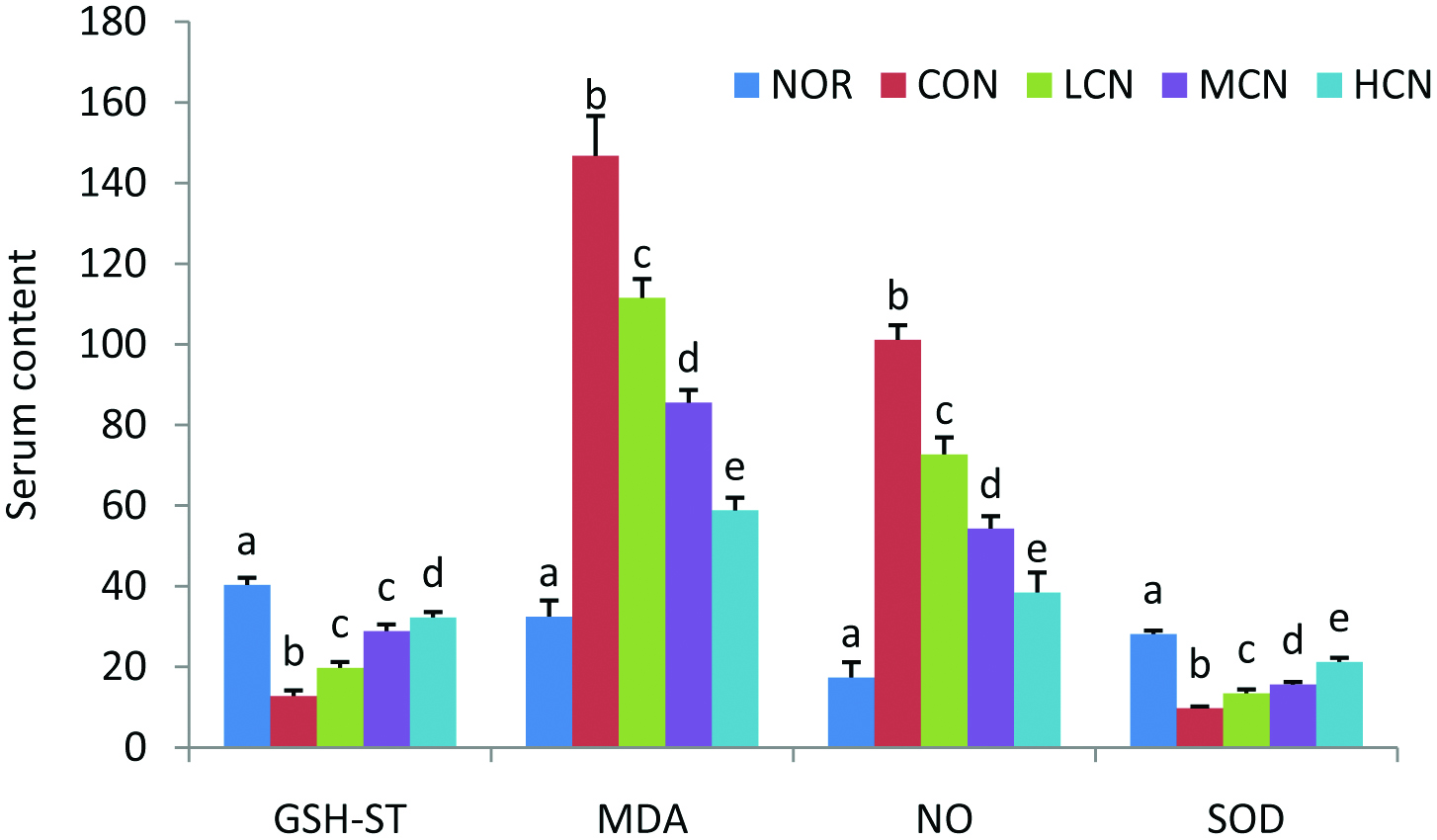
Figure 4. Effects of nobiletin on the content of liver function and oxidative metabolites in vivo. Serum levels of GSH-ST (U/L), MDA (nmol/mL), NO (nmol/mL) and SOD (U/mL). The average content of data in each group is expressed as the mean ± SD (A: n = 8 per group). The significant difference among each group was analyzed by one-way ANOVA and Duncan’s multiple range tests. Different letters of a–e represent significant differences of the same indexes when p < 0.01.



