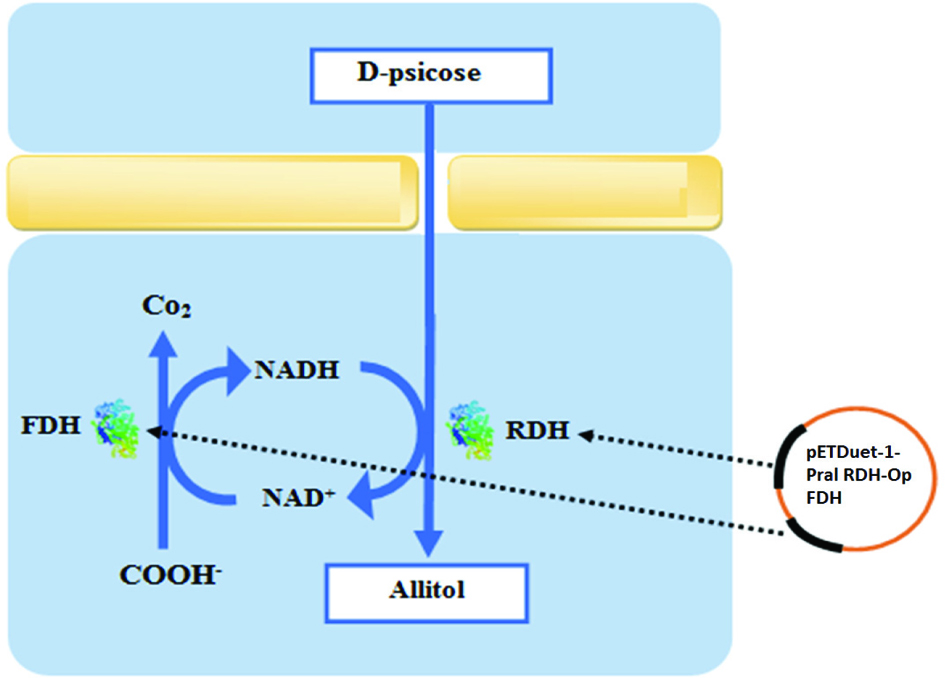
Allitol production pathway using engineered E. coli coexpressed with ribitol dehydrogenase (RDH) and formate dehydrogenase (FDH).
| Journal of Food Bioactives, ISSN 2637-8752 print, 2637-8779 online |
| Journal website www.isnff-jfb.com |
Original Research
Volume 4, Number , December 2018, pages 117-122
Facile synthesis of bioactive Allitol from D-psicose by coexpression of ribitol dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenase in Escherichia Coli
Figures

Allitol production pathway using engineered E. coli coexpressed with ribitol dehydrogenase (RDH) and formate dehydrogenase (FDH).
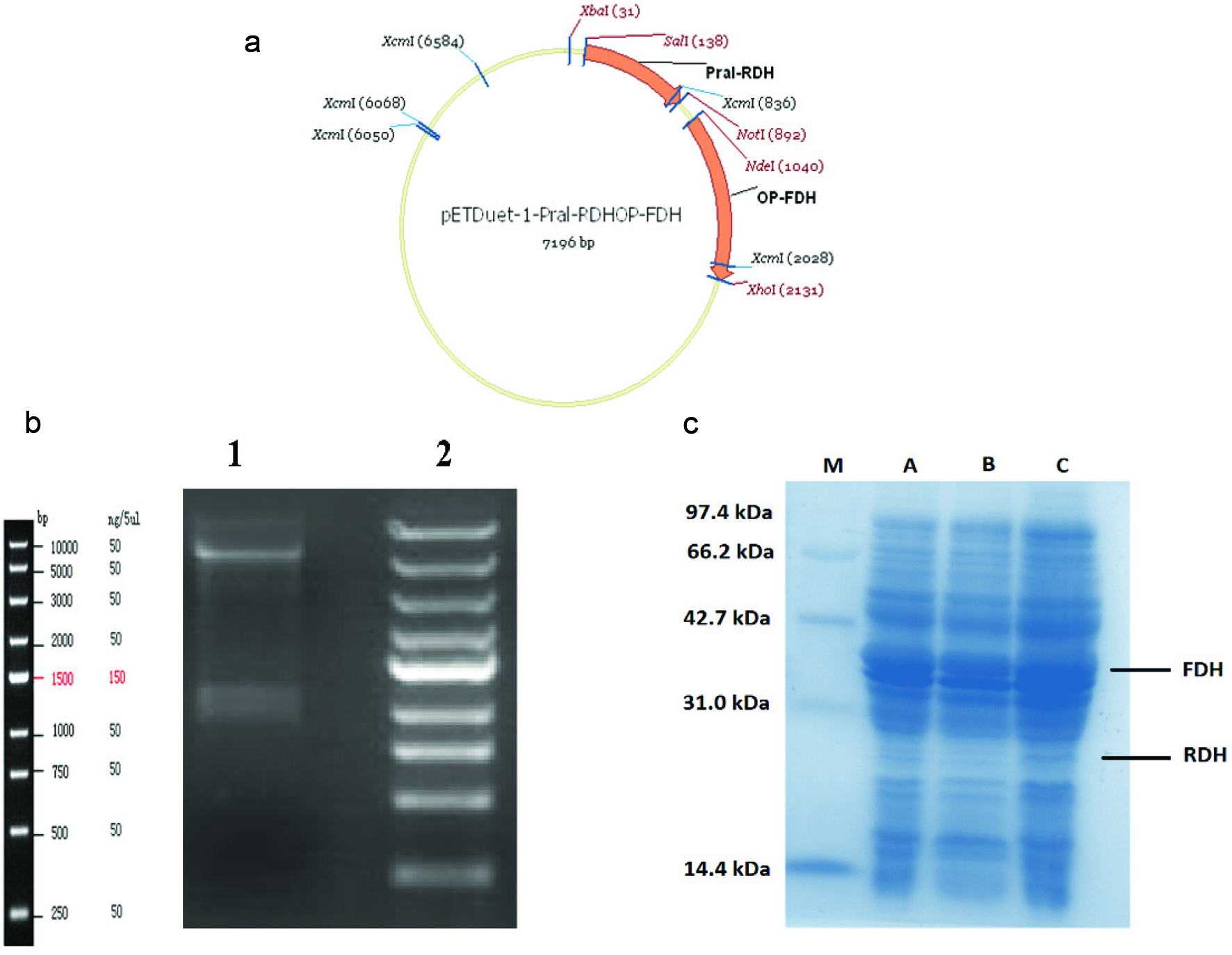
Plasmid construction (a) constructed vector map (pETDuet-RDH-FDH). (b)The result of extracts DNA from transformed E. coli with pETDuet-RDH-FDH (1) DNA ladder (2) The DNA digested with EcoRI/XhoI restriction enzymes. (c) SDS-PAGE analysis of the co-expression recombinant enzymes. (M) protein marker; (A) proteins in the supernatant of constructed E. coli induced with IPTG (6 hours), (B) proteins in the supernatant of constructed E. coli without IPTG; (C) proteins in the supernatant of constructed E. coli induced with IPTG (20 hours).
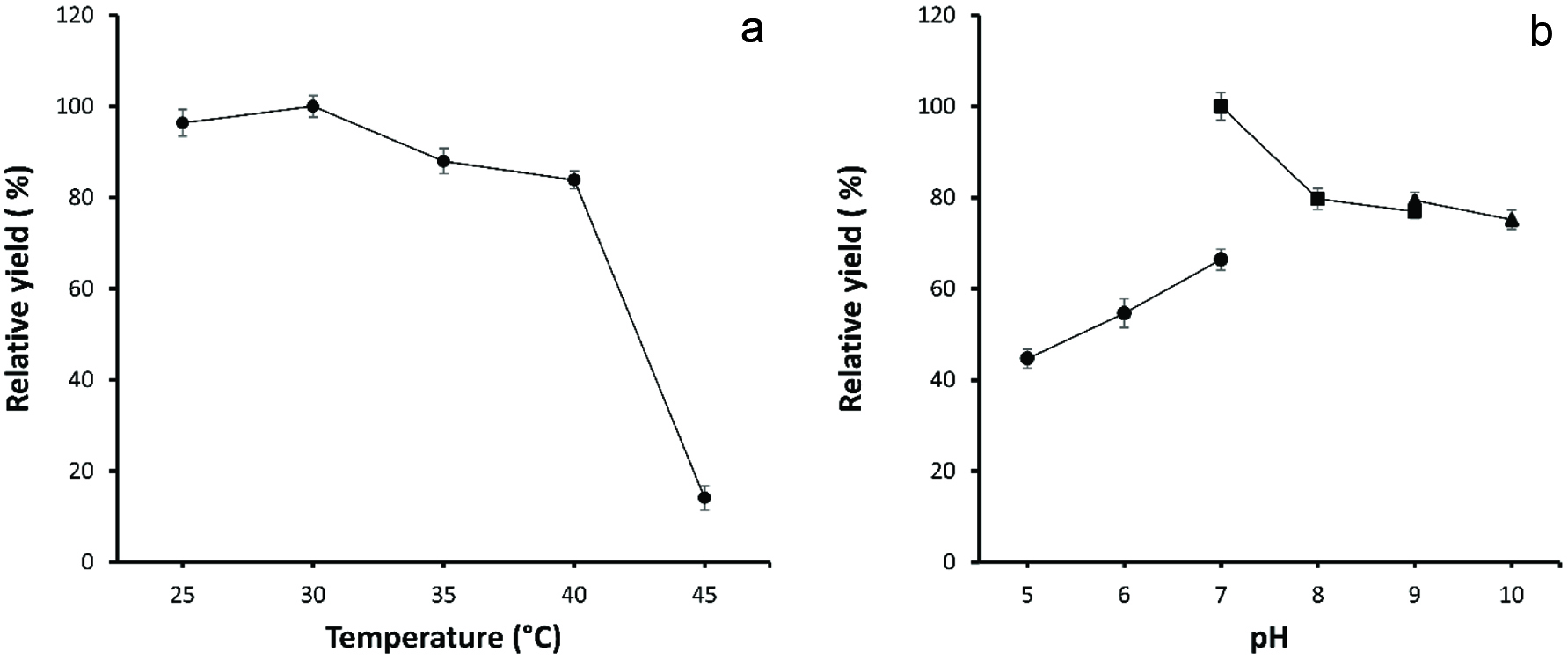
Effect of temperature (a) and pH (b) ((•) Phosphate buffers (■) Tris-HCl buffers (▲) Glycine-NaOH buffers) on the whole cell biotransformation.
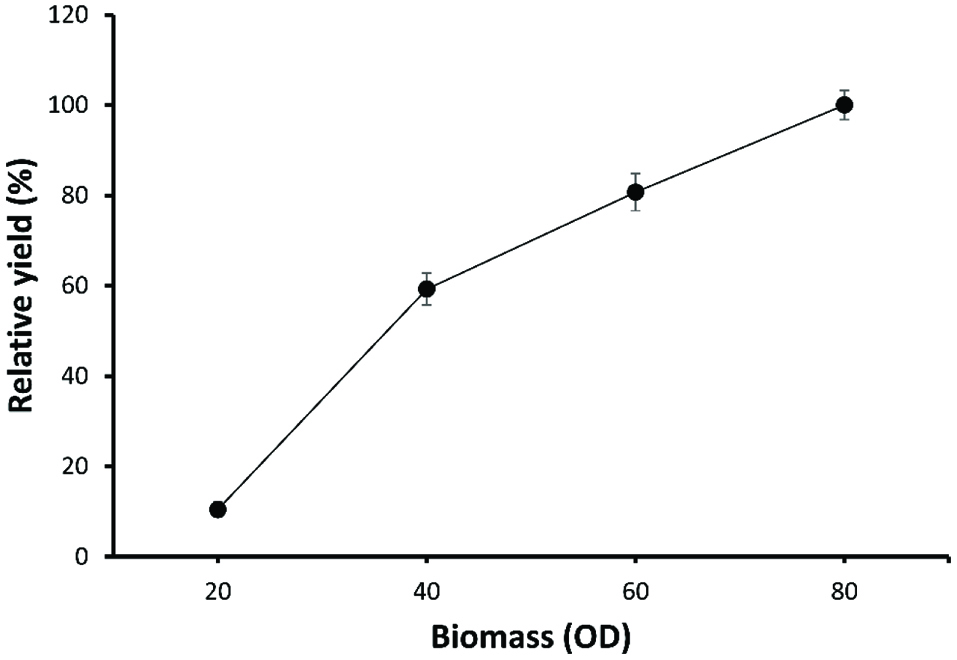
Effect of the cell biomass on the synthesis of allitol using whole cell biotransformation.
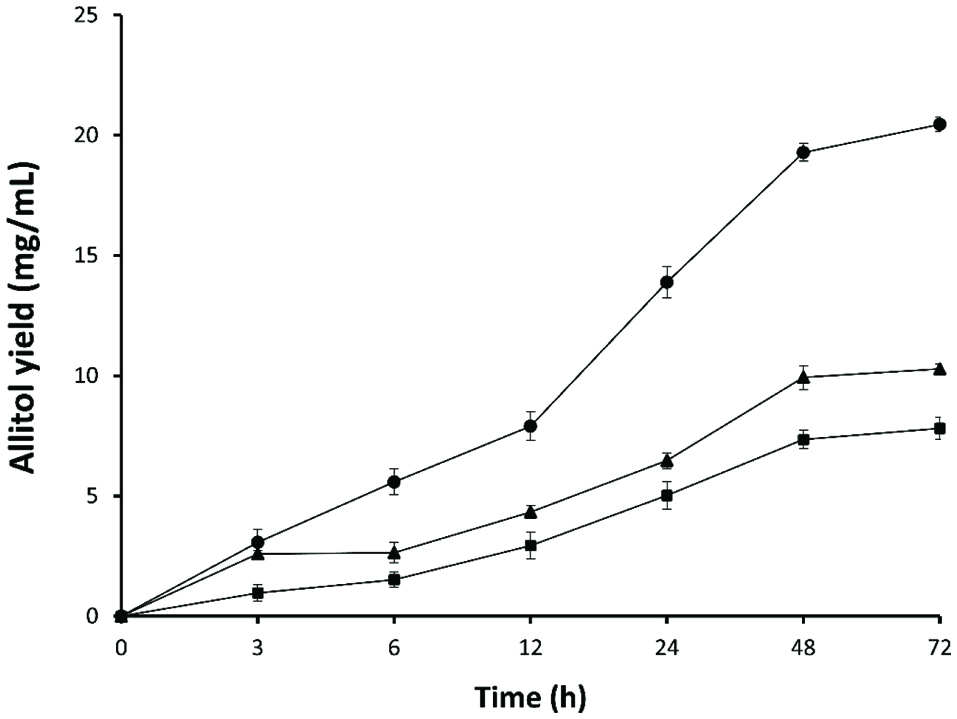
Effect of cell biomass on allitol synthesis. (■) 0.5% D-psicose. (▲) 1% D-psicose (•). 2% D-psicose.
Table
| Plasmids/Strains | Relevant Characteristics | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| pET-pral-RDH | amp; pET-21a(+) carrying gene for RDH | (Hassanin et al., 2016) |
| pET-Op-FDH | amp; pET-21a(+) carrying gene for FDH | (Yu et al., 2014) |
| pETDuet-1 | Generay | |
| pETDuet-RDH-FDH | amp; pCDFDuet™-1 carrying genes for FDH and RDH | This study |
| E. coli DH5 | endA1, supE44, recA1, gyrA96, relA1, deoR U169, Φ80dlacZΔM15, mcrA Δ(mrr-hsdRMS-mcrBC) | Invitrogen |
| E. coli BL21 Star (DE3) | For gene expression | Invitrogen |
| Engineered E. Coli | BL21 Star (DE3) pETDuet-RDH-FDH | This study |