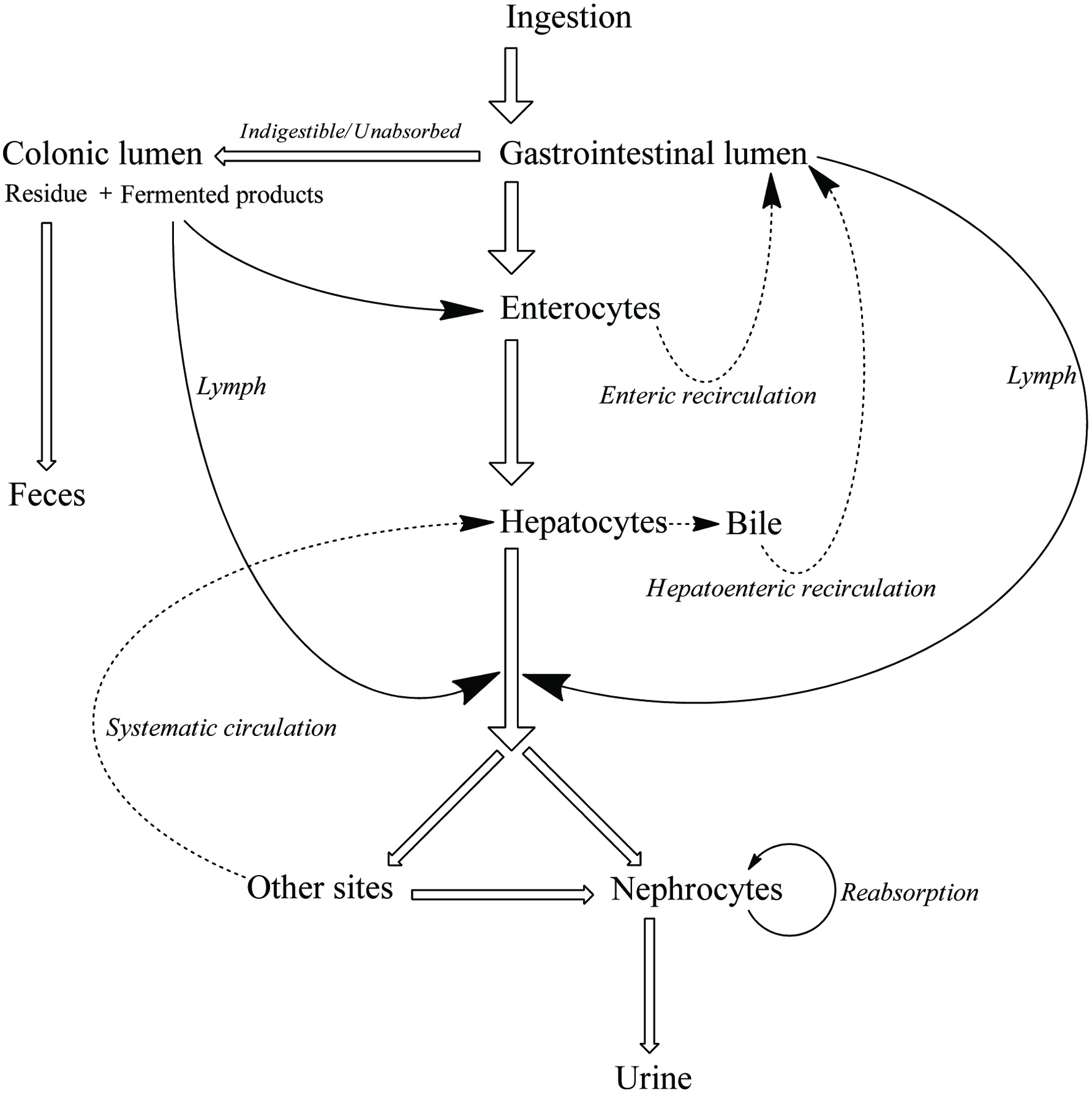
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of phenolic bioavailability.
| Journal of Food Bioactives, ISSN 2637-8752 print, 2637-8779 online |
| Journal website www.isnff-jfb.com |
Review
Volume 4, Number , December 2018, pages 11-68
Bioaccessibility and bioavailability of phenolic compounds
Figures

Schematic representation of phenolic bioavailability.
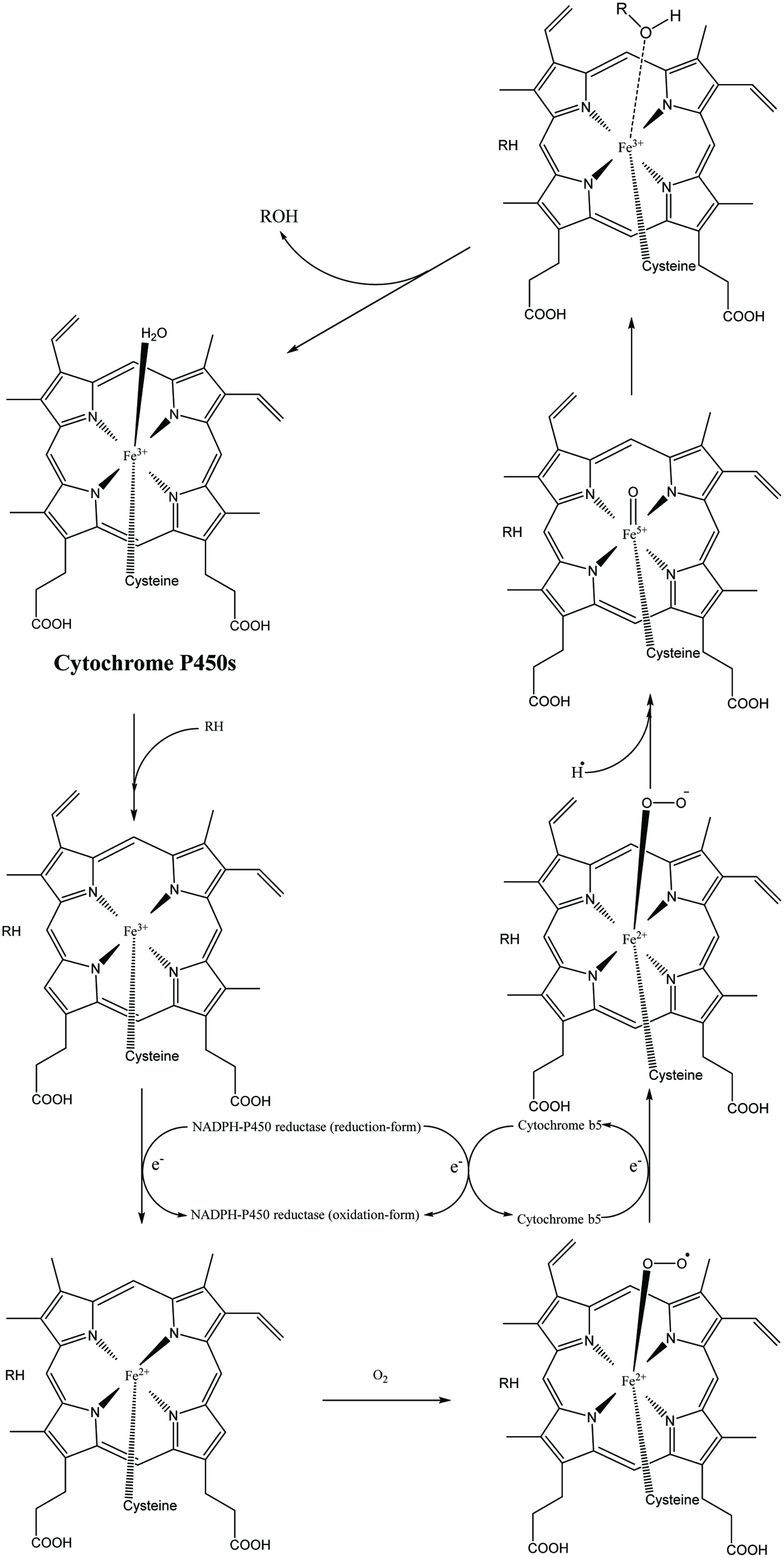
Cytochrome P450 catalytic process.
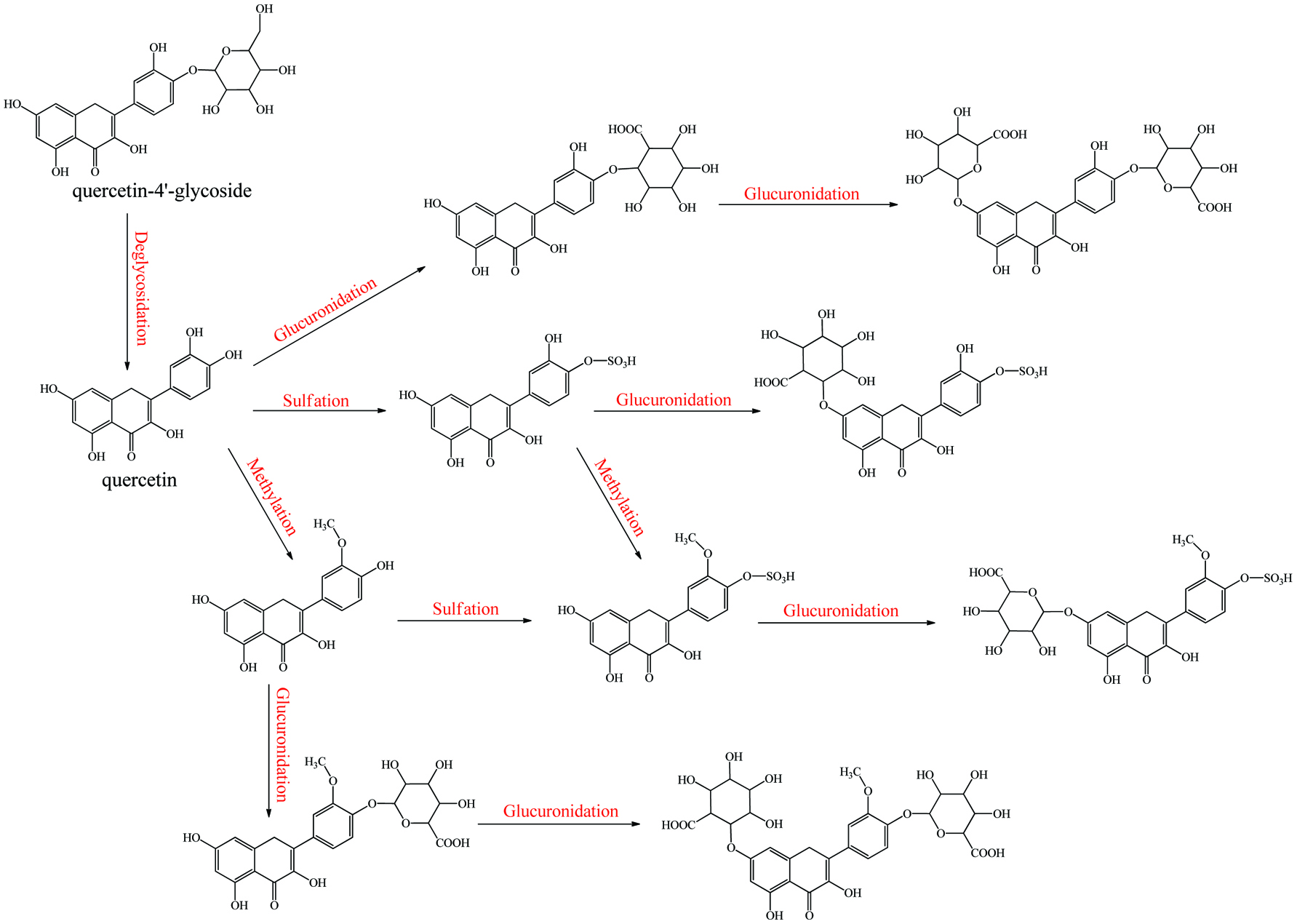
Metabolism of quecetin monoglycoside.
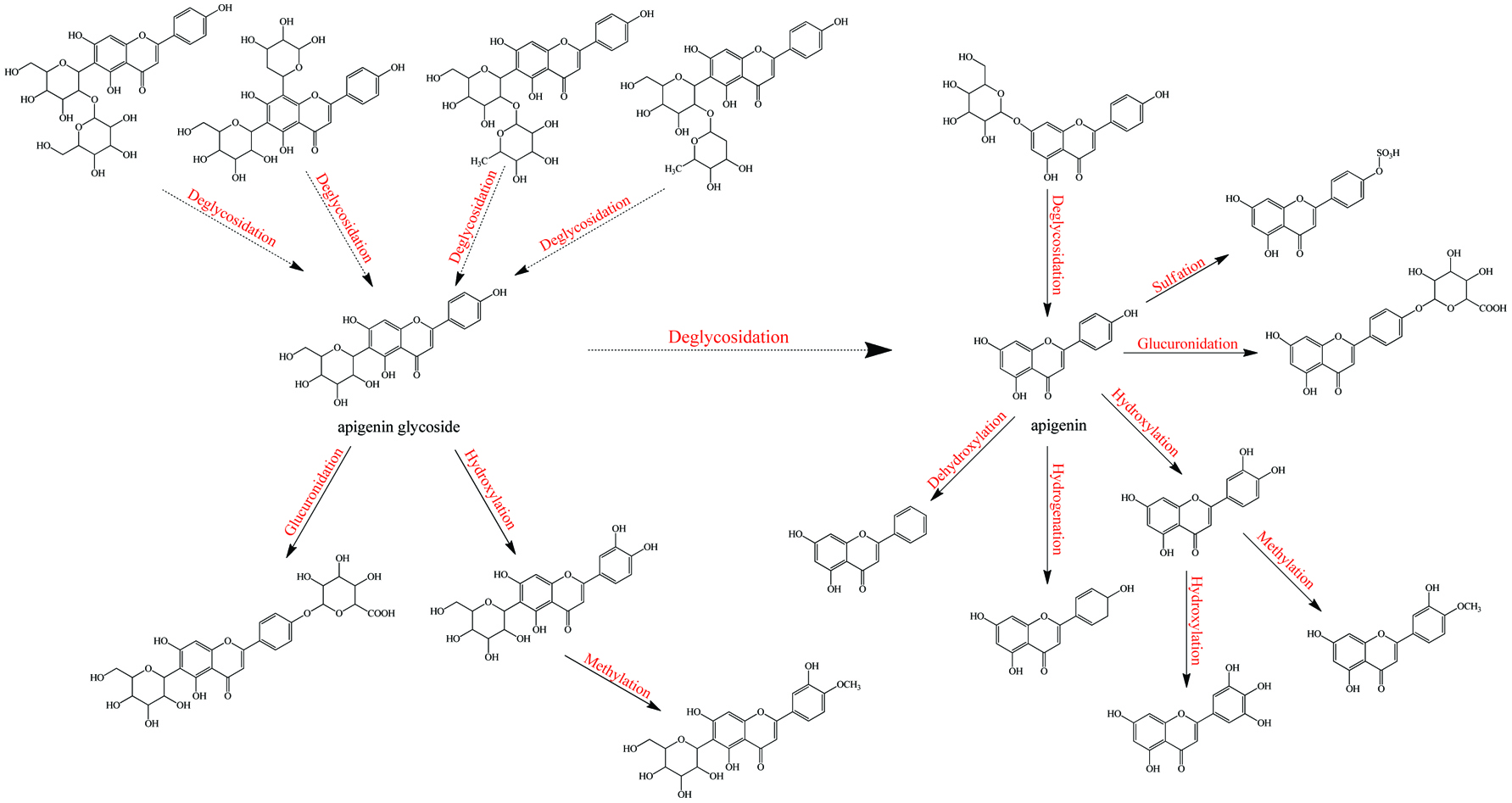
Metabolism of apigenin-C/O-glycosides.
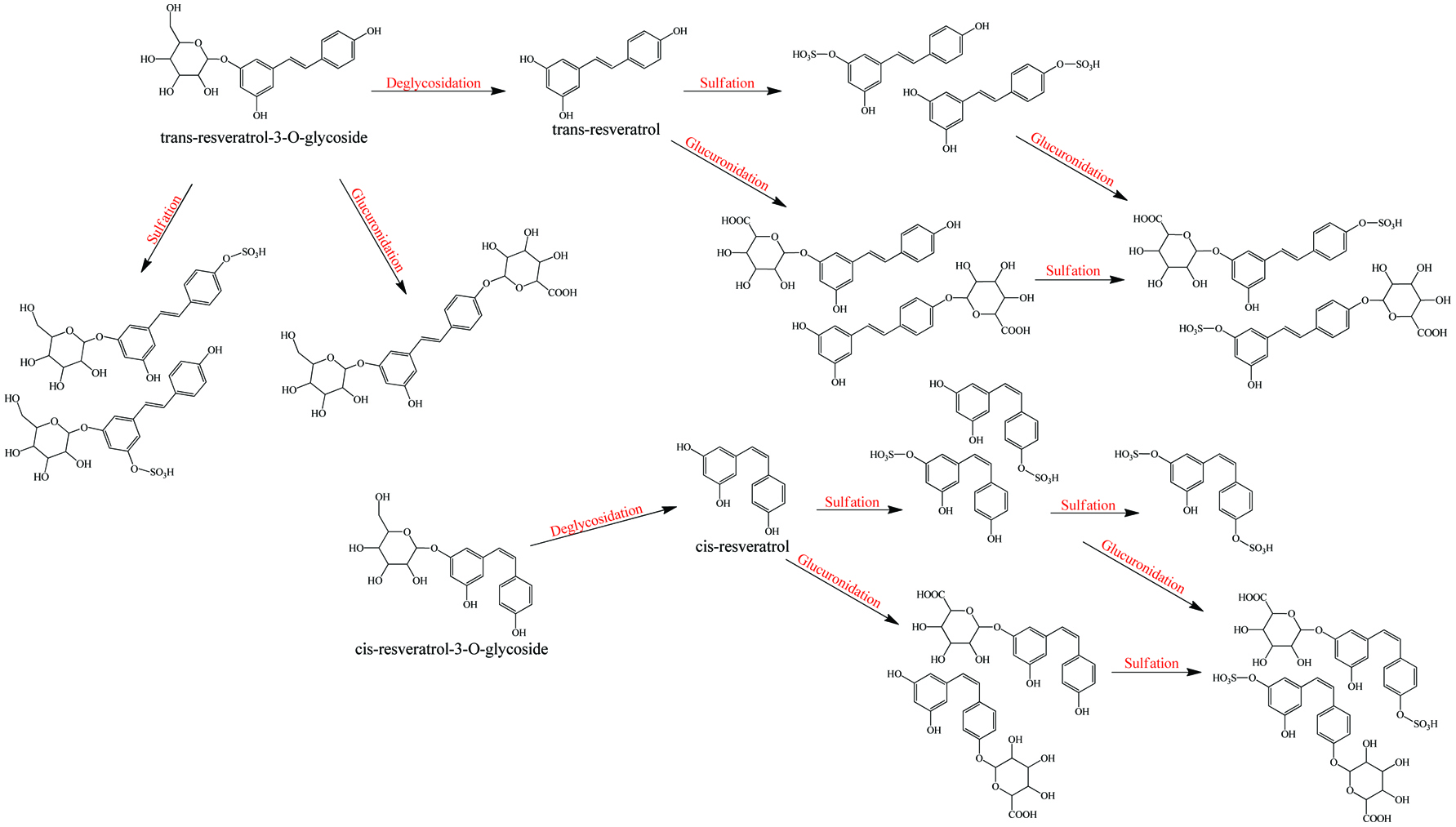
Metabolism of resveratrol and resveratrol glycoside.
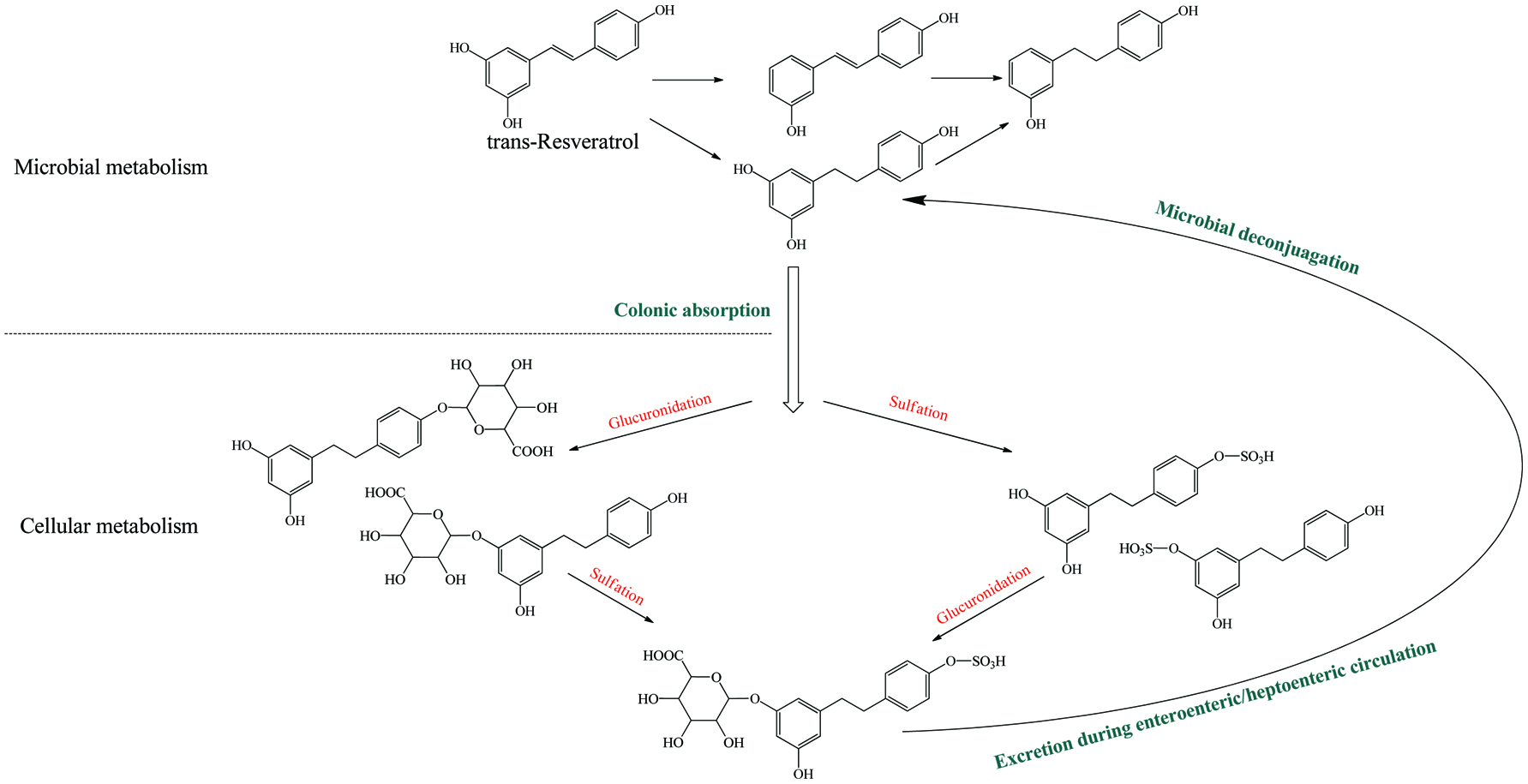
Microbial metablism of resveratrol and corresponding enterohepatic/enteroenteric circulation.
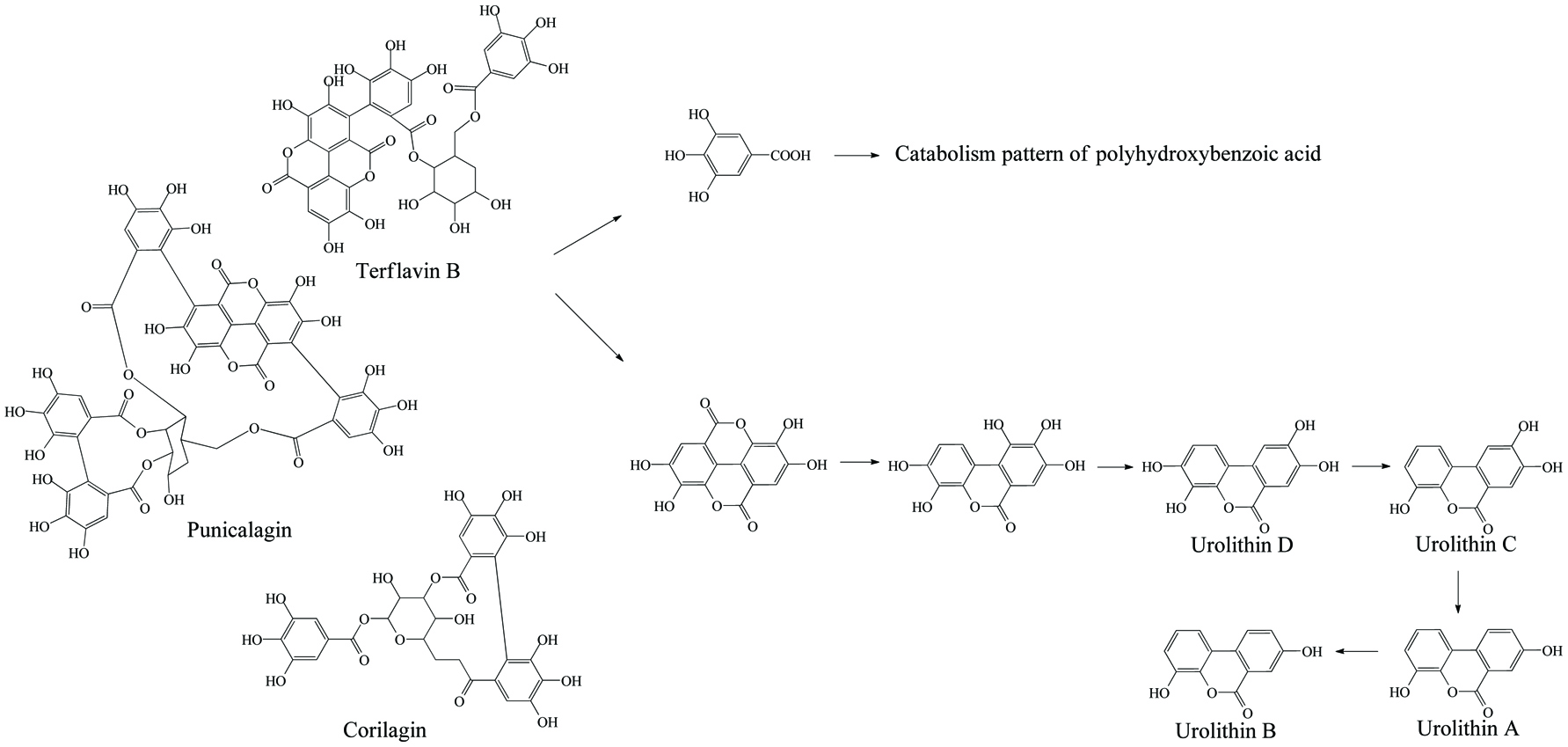
Microbial metabolism of ellagitannin.
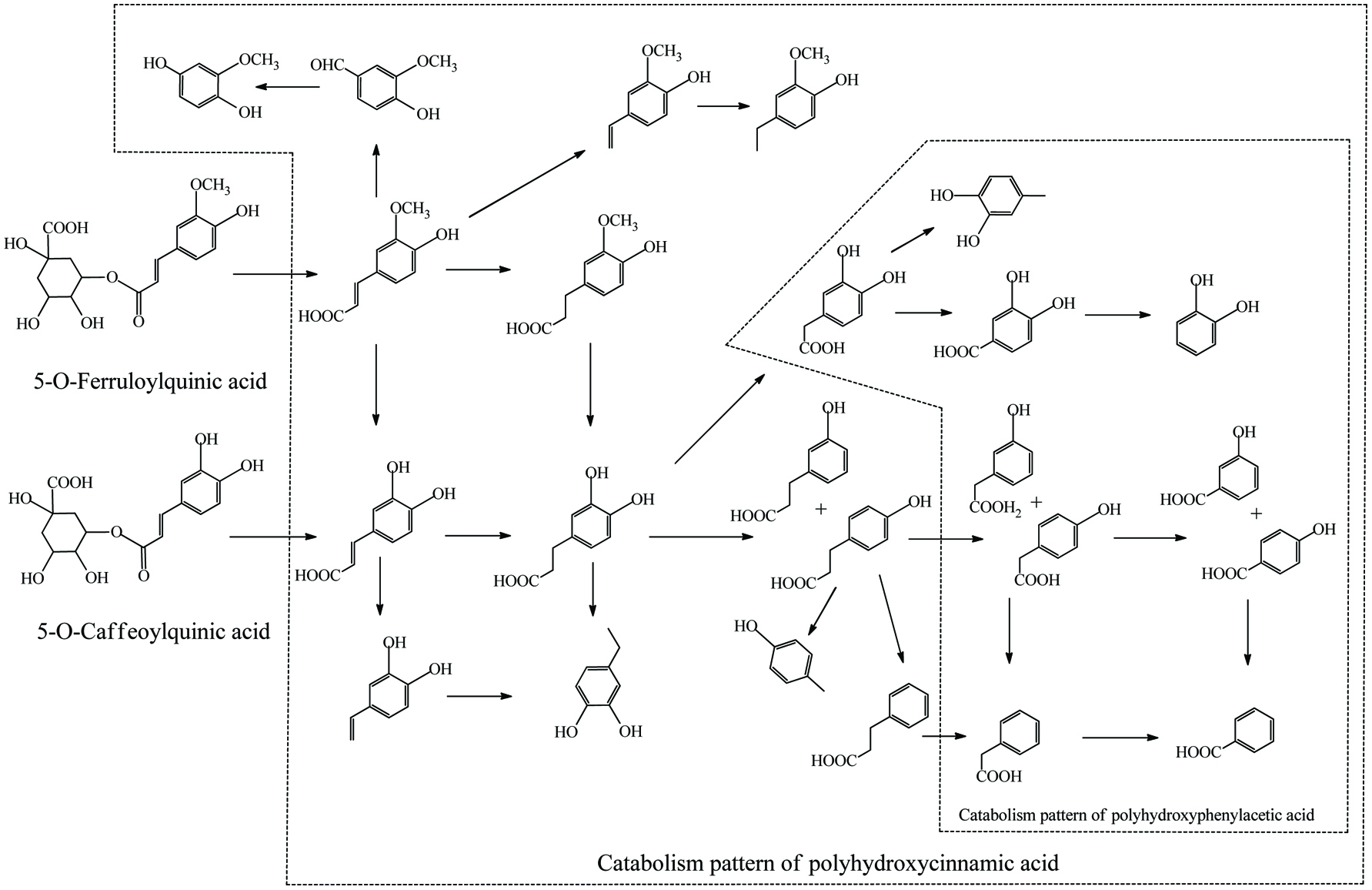
Microbial metablism of cinnamic acid esters.
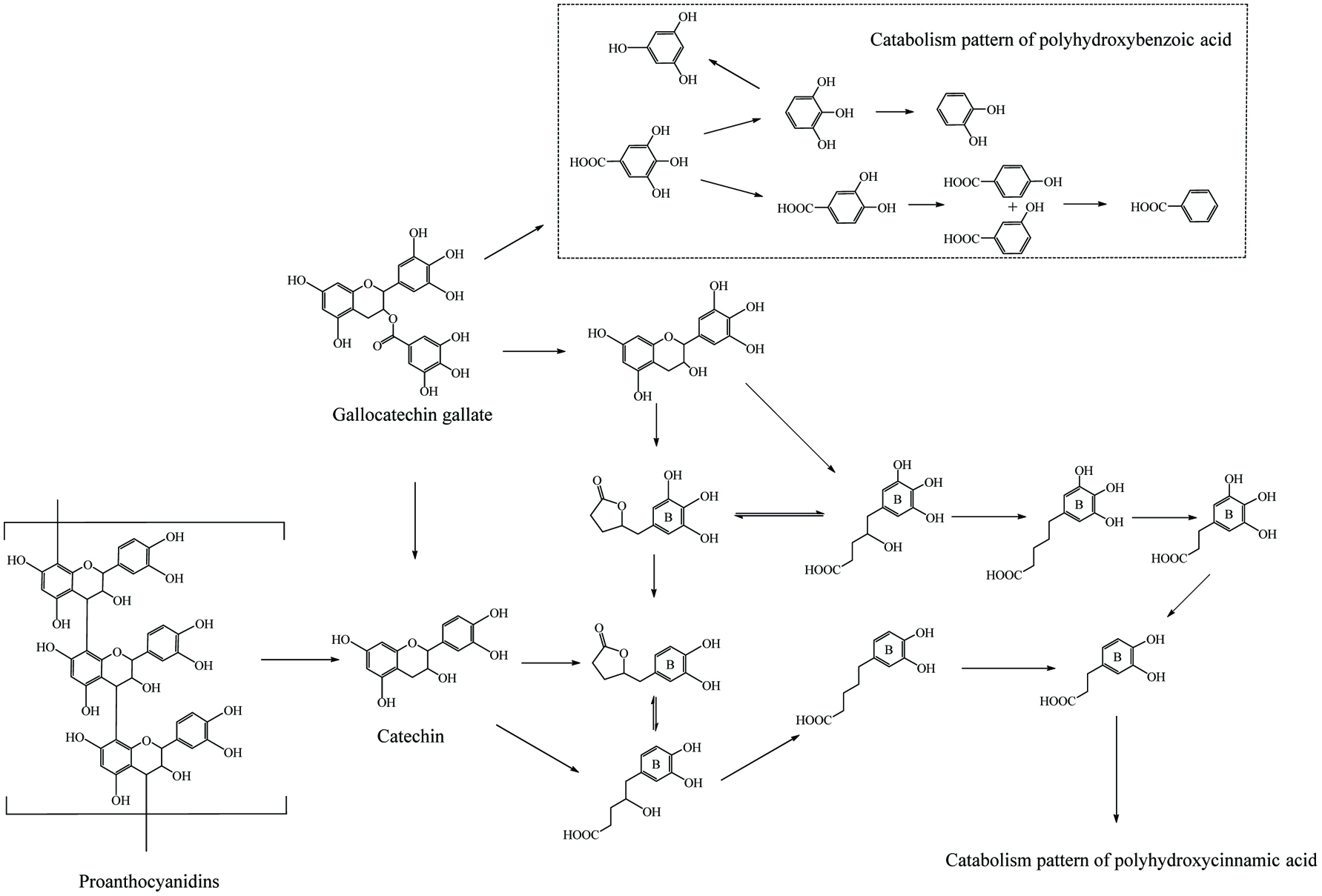
Microbial metablism of proanthocyanin.
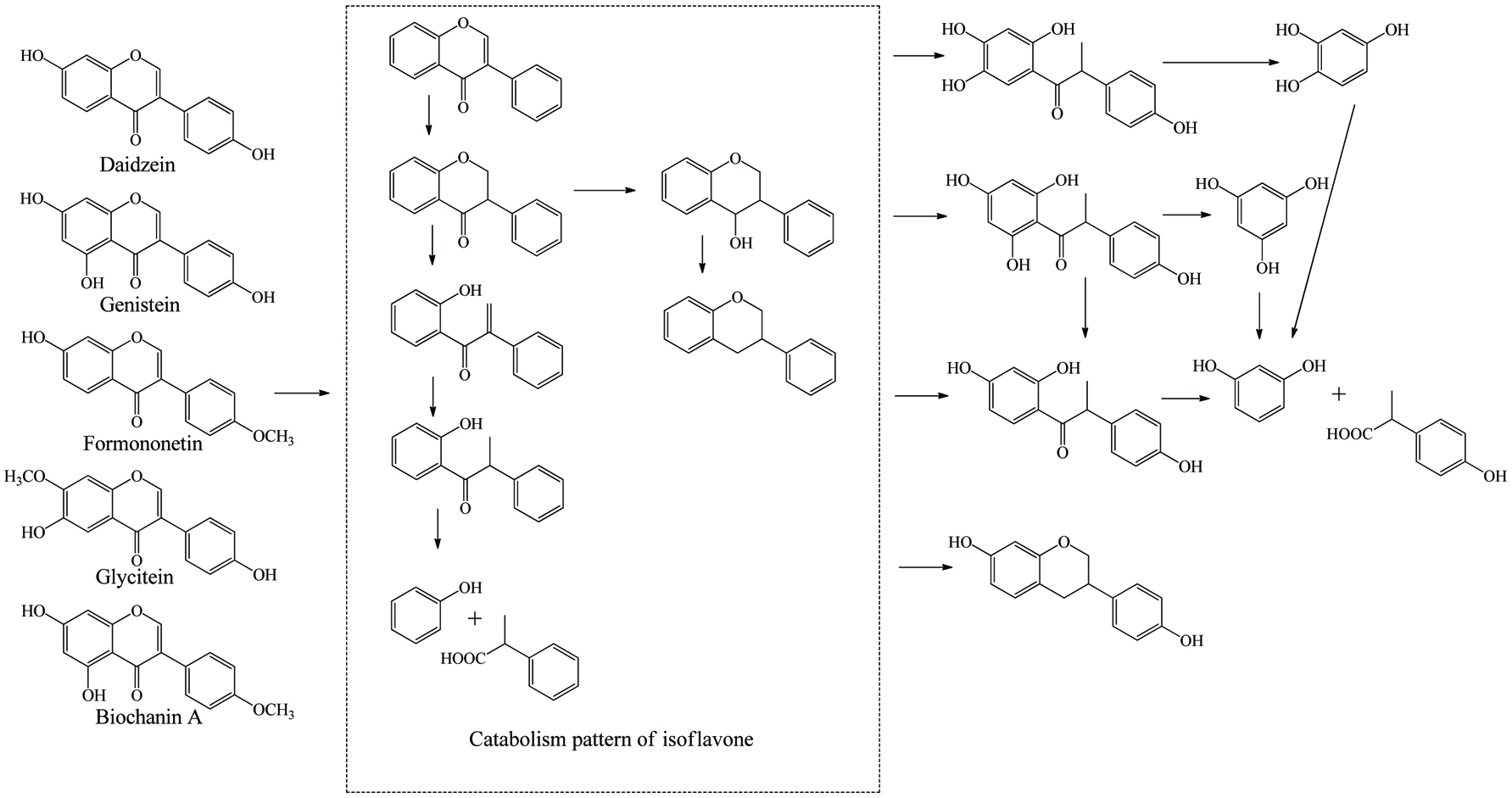
Microbial metablism of isoflavones.
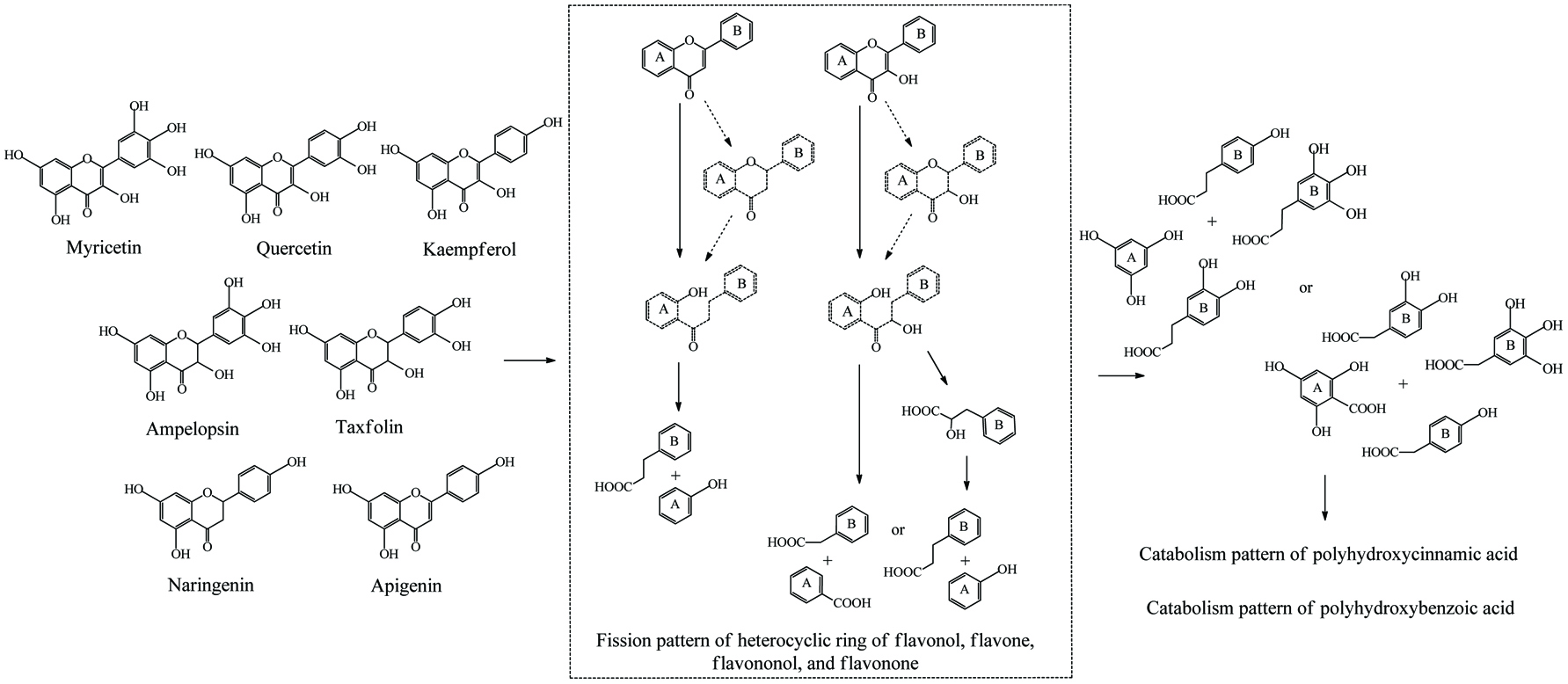
Microbial metablism of flavone, flavonol, flavanone and flavanonol.
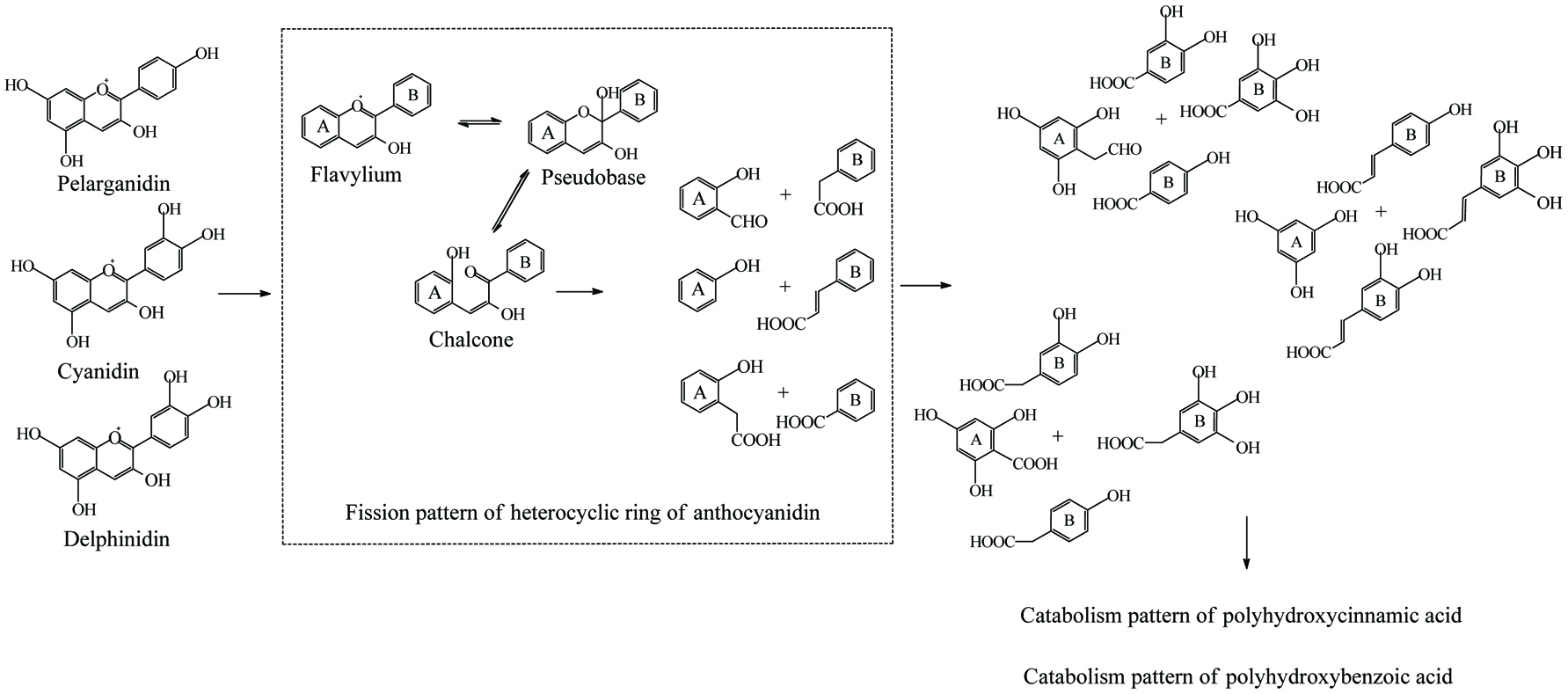
Microbial metablism of anthocyanidin.
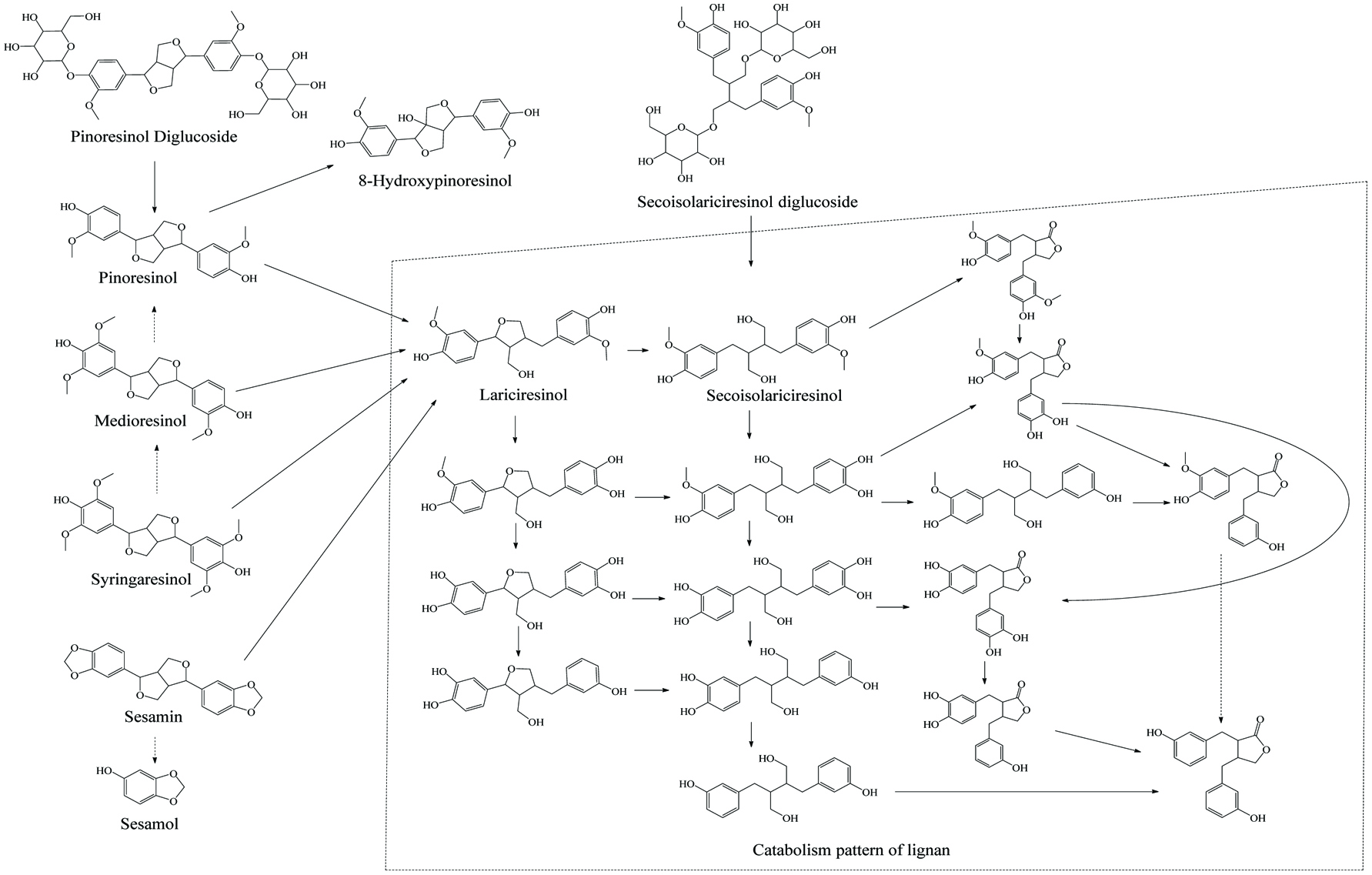
Microbial metablism of lignan.
Tables
| Materials | Oral condition | Gastric condition | Small intestine condition | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A Standardized Condition | ||||
| Food Sample | 1:1 (v/v) ∼ Oral fluid (amylase-75 U/mL): Sample, pH 7.0, 2 min, 37 °C | 1:1 (v/v) ∼ Gastric fluid (pepsin-2,000 U/mL): Oral fluid, pH 3.0, 2 h, 37 °C | 1:1 (v/v) ∼ Intestinal fuild (pancreatin based on trypsin activity at 100 U/mL, bile salts-10 mM): Gatric fraction, pH 7.5, 6 h, 37 °C | Minekus et al. (2014) |
| Phenolics and Other phytochemicals | ||||
| Tea beverage (phenolics) | Pepsin, pH 2.0, 1 h, 37 °C | Pancreatin, Bile salts (glycodeoxycholate, taurodeoxycholate, taurocholate), pH 7.4 (transition pH 5.3), 2.5 h, 37 °C | Chen et al. (2013) | |
| Grape seed extract (flavonoids) | Human saliva α-Amylase in water with weak acid, pH 6.9, 10 min, 37 °C | Pepsin, pH 2.0, 1 h, 37 °C | Pancreatin, Bile salts, pH 7.0 (transition pH 6.0), 2 h, 37 °C | Laurent et al. (2007) |
| Wheat bread (flavonoids) | Human saliva in buffer (Na2HPO4, KH2PO4, and NaCl), pH 7.0, 10 min, 37 °C | Pepsin, pH 1.2, 2 h, 37 °C | Pancreatin, Bile salts, NaCl, KCl, pH 7.0 (transition pH 6.0), 1 h, 37 °C | Gawlik-Dziki et al. (2009) |
| Soy bread (isoflavones) | Human saliva in saline, pH 7.0, 5 min, 37 °C | Pepsin, pH 2.0, 1 h, 37 °C | Pancreatin, pH 6.9, 2 h, 37 °C | Walsh et al. (2003) |
| Millet grain (phenolics) | Porcine α-amylase in phosphate buffer, pH 6.9, 5 min, 37 °C | Pepsin, pH 2.5, 2 h, 37 °C | Pancreatin, Mucin, Bile salts, pH 7.0, 3 h, 37 °C | Chandrasekara et al. (2012) |
| Raspberry (anthocyanins) | Pepsin in water, pH 1.7, 2 h, 37 °C | Pancreatin, Bile salts, pH 7.0, 2 h, 37 °C | McDougall et al. (2005) | |
| Blueberry (phenolics) | Pepsin in water, pH 2.0, 2 h, 37 °C | Pancreatin, Bile salts, pH 7.5, 2 h, 37 °C | Correa-Betanzo et al. (2014) | |
| Gooseberry (phenolics) | Pepsin in water, pH 1.7–2.0, 2 h, 37 °C | Pancreatin, Bile salts (glycodeoxycholate, taurodeoxycholate, taurocholate), pH 8.0, overnight, 37 °C | Chiang et al. (2013) | |
| Various baby food (carotenoids) | Pepsin in water, pH 2.0, 1 h, 37 °C | Pancreatin, Bile salts, pH 7.5 (transition pH 5.3), 2 h, 37 °C | Garrett et al. (1999) | |
| Various food (carotenoids and tocopherol) | Pepsin in saline, Pyrogallol, pH 4.0, 1 h, 37 °C | Pancreatin, Bile salts, pH 6.0, 0.5 h, 37 °C | Reboul et al. (2006) | |
| Various food (tocopherol and retinol) | Pepsin in HBSS, lipase, pH 4, 1 h, 37 °C | Pancreatin, Bile salt (glycodeoxycholate, taurocholate, and taurodeoxycholate), pH 7.8 (transit pH 5.4), 2 h, 37 °C | O’Callaghan et al. (2010) | |
| Broccoli (phenolics, glucosinolates, ascorbic acid) | Porcine pepsin in water, pH 2, 2 h, 37 °C | Pancreatin, Lipase, Bile salts, pH 7, 2 h, 37 °C | Vallejo et al. (2004) | |
| Hemi-purified glucoraphanin | α-Amylase in water, pH 7.0, 3 min, 37 °C | Pepsin, pH 2, 2 h, 37 °C | Pancreatin, Bile salts, pH 7.5, 2 h, 37 °C | Lai et al. (2010) |
| Soy flour (saponins) | α-Amylase in PBS, pH 7.0, 10 min, 37 °C | Pepsin, pH 2.5, 2 h, 37 °C | Pancreatin, Lipase, Bile salt (glycodeoxycholate, taurocholate, and taurodeoxycholate), pH 6.5, 2 h, 37 °C | Serventi et al. (2013) |
| Milk-based fruit beverage (phytosterol) | α-Amylase, Mucin, pH 6.5, 5 min, 37 °C | Pepsin, BSA, pH 1.07, 1 h, 37 °C | Pancreatic lipase, Cholesterol esterase, Phospholipase A2, Colipase, Taurocholate, pH 7.0, 2 h, 37 °C | Alvarez-Sala et al. (2016) |
| Other Ingredients | ||||
| Triacylglycerol (cod liver oil) | Lipase, Pepsin, pH 2.0 (transition pH 4.0 for another 30 min), 0.5 h, 37 °C | Pancreatin, Bile salts (glycocholate, glycochenodeoxycholate, glycodeoxycholate, taurocholate, taurochenodeoxycholate, taurodeoxycholate, taurolithocholate) | Larsson et al. (2012) | |
| Starch (variously modified starch and unmodified starch) | Pepsin, pH 2.0, 0.5 h, 37 °C | Pancreatin, α-Amylase, Amyloglucosidase, Acetate buffer, pH 5.0, 37 °C | Wolf et al. (1999) | |
| Proteins (spelt products) | Pepsin, pH 1.9, 0.5 h, 37 °C | Pancreatin in Phosphate buffer, pH 7.5, 6 h, 37 °C | Abdel-Aal (2008) | |
| Polysaccharides (seeds of Plantago asiatica L.) | Human saliva in water, pH 7.0, 4 h, 37 °C | Pepsin, Lipase, Gastric Electrolytes (NaCl, KCl, CaCl2·2H2O, NaHCO3), pH 3.0, 6 h, 37 °C | Pancreatin, Trypsin, Bile salts, Small intestinal electrolytes (NaCl, CaCl2·2H2O), pH 7.0, 6 h, 37 °C | Hu et al. (2013) |
| Iron (rye bread with FeCl3) | Pepsin in saline, L-lactic acid, Inositol phosphates, pH 2.0, 1 h, 37 °C | Pancreatin, Saline, pH 7.5, 6 h, 37 °C | Bering et al. (2006) | |
| Sample | Oral phase | Release percentage of phenolics (%) | Release standard | Total phenolics extraction | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gastric phase | Intestinal phase | ||||||
| Apple homogenate | Phenolics (68) Flavonoids (65) Anthocyanins (91) | Phenolics (74) Flavonoids (72) Anthocyanins (0) | Solubility | Pure methanol Ultrasonication | (Bouayed et al., 2011) | ||
| Phenolics (54) Flavonoids (39) Anthocyanins (0) | Dialyzability | ||||||
| Orange juice | Flavanones (51) Vicenin-2 (117) | Flavanones (51) Vicenin-2 (111) | Solubility | Direct determination | Gil-Izquierdo et al. (2001) | ||
| Flavonones (6) Vincenin-2 (22) | Dialyzability | ||||||
| Pumpkin flour | Phenolics (29–37) | Solubility | Free: HCl, water, and methanol (1:80:10); Bound: H2SO4 and methanol (1:10) | Aydin and Gocmen. (2015) | |||
| Grape | 50% phenolics 27% flavonoids 19% anthocyanins | Phenolics (61) Flavonoids (43) Anthocyanins (36) | Phenolics (62) Flavonoids (56) Anthocyanins (8) | Solubility | Free: acidified water Bound: acidified methanol | Tagliazucchi et al. (2010) | |
| Green lentil | Phenolics (21) Flavonoids (29) | Phenolics (50) Flavonoids (71) | Solubility | Acidified 70% methanol | Zhang et al. (2017) | ||
| Grape pomace | Phenolics (102) | Phenolics (67) | Solubility | Acidified pure methanol; 70% acetone | Wang et al. (2017) | ||
| Globe artichoke | 27% caffeoylquinic acid and dicaffeoylquinic acid | Caffeoylquinic acid and dicaffeoylquinic acid (36) | Caffeoylquinic acid and dicaffeoylquinic acid (55.8) | Solubility | 100% Water | D’Antuono et al. (2015) | |
| Pili pomace | Phenolics (12) Flavonoids (0.7) Tannins (3.2) Anthocyanins (200) | Phenolics (6) Flavonoids (0.2) Tannins (1.2) Anthocyanins (10) | Solubility | Acidified 50% ethanol | Arenas and Trinidad (2017) | ||
| Black bean coat | Phenolics (24) Flavonoids (82) Tannins (6) | Solubility | Acidified pure water Acidified pure methanol | Sancho et al. (2015) | |||
| Small red bean coat | Phenolics (49) Flavonoids (95) Tannins (7) | ||||||
| Kale | Phenolics (69) | Solubility | Hexane; Acetone; Methanol, water and formic acid (80:19:1) | Yang et al. (2018) | |||
| Sample (mg/g, dw) | Released anthocyanin (%) | Total phenolics extraction | References | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gastric phase | Intestinal phase | |||||
| aC3G: cyaniding-3-O-glucoside equivalent. | ||||||
| Cyanidin-3-xylosyl-glucosyl-galactoside | 5 (C3G)a | 40.0 | 32.0 | 70% methanol with 0.1% formic acid; Ultrasonication | Kamiloglu et al. (2017) | |
| 12 (C3G) | 75.0 | 41.7 | ||||
| 20 (C3G) | 55.0 | 30.0 | ||||
| Cyanidin-3-xylosyl-galactoside | 19 (C3G) | 62.9 | 11.6 | |||
| 52 (C3G) | 38.5 | 21.2 | ||||
| 75 (C3G) | 30.7 | 18.7 | ||||
| Cyanidin-3-xylosyl-sinapoyl-glucosyl-galactoside | 11 (C3G) | 27.3 | 45.5 | |||
| 27 (C3G) | 48.1 | 44.4 | ||||
| 48 (C3G) | 39.6 | 31.2 | ||||
| Cyanidin-3-xylosyl-feruloyl-glucosyl-galactoside | 32 (C3G) | 29.2 | 40.6 | |||
| 77 (C3G) | 57.1 | 42.9 | ||||
| 111 (C3G) | 49.5 | 46.8 | ||||
| Cyanidin-3-xylosyl-coumaroyl-glucosyl-galactoside | 5 (C3G) | 20.0 | 40.0 | |||
| 13 (C3G) | 46.2 | 30.8 | ||||
| 13 (C3G) | 61.5 | 61.5 | ||||
| Digested material | Phenolics loss (%) | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gastric phase | Intestinal phase | |||
| aOne stage overall process only. | ||||
| Phenolic standards | ||||
| Gallic acid (35.0 μg/mL) | 4.6a | 43.3 | Tagliazucchi et al. (2010) | |
| Caffeic acid (8.0 μg/mL) | 0.1a | 24.9 | ||
| Catechin (40.0 μg/mL) | 0.7a | 7.2 | ||
| Quercetin (60.0 μg/mL) | 0.9 | 5.8 | ||
| Resveratrol (3.0 μg/mL) | −2.3 | 69.5 | ||
| Cyanidin 3-rutinoside (52.8 μg/mL) | 0 | 9.1 | Bermúdez-Soto et al. (2007) | |
| Quercetin-3-rutinoside (160.6 μg/mL) | 0 | 3.1 | ||
| (+)-Catechin (320.0 μg/mL) | 3.1 | 58.0 | ||
| Chlorogenic acid (90.0 μg/mL) | 0 | 5.1 | ||
| Chlorogenic acid (100.0 μg/mL) | 48.1 | D’Antuono et al. (2015) | ||
| 1,5-O-Dicaffeoylquinic acid (100.0 μg/mL) | 49.6 | |||
| 3,5-O-Dicaffeoylquinic acid (100.0 μg/mL) | 25.8 | |||
| Chlorogenic acid (67.5 μg/mL) | 58.1 | 95.7 | Siracusa et al. (2011) | |
| Rutin (45.0 μg/mL) | 88.1 | total | ||
| Quercetin 3-O-glucoside (30.0 μg/mL) | total | total | ||
| Quercetin (15.0 μg/mL) | total | total | ||
| Pelargonidin-3-glucoside | 1.0 | 19.0 | Woodward et al. (2011) | |
| Cyanidin-3-glucoside | 2.0 | 67.0 | ||
| Pelargonidin | 8.0 | 36.0 | ||
| Cyanidin | 10.0 | 34.0 | ||
| Phenolic extracts | ||||
| Mulberry phenolic extracts | Anthocyanins | 1.6 | 95.1 | Liang et al. (2012) |
| Phenolics | 39.6 | 38.0 | ||
| Rose phenolic extracts | Phenolics | 6.2 | 15.7 | Zhang et al. (2016) |
| Caper phenolic extracts | Chlorogenic acid (3.3 μg/mL) | 5.8 | 33.0 | Siracusa et al. (2011) |
| 4-Caffeoylquinic acid (1.8 μg/mL) | 1.5 | 26.4 | ||
| 5-Coumaroylquinic acid (0.5 μg/mL) | 3.9 | 25.7 | ||
| 4-Feruloylquinic acid (0.7 μg/mL) | 2.5 | 19.8 | ||
| Rutin (10.2 μg/mL ) | 1.7 | total | ||
| Quercetin 3-O-glucoside (0.2 μg/mL ) | 3.8 | total | ||
| Kaempferol 3-O-rutinoside (2.3 μg/mL ) | 5.0 | total | ||
| Isorhamnetin 3-O-rutinoside (0.8 μg/mL ) | 2.3 | total | ||
| Kaempferol 3-O-glucoside (0.6 μg/mL ) | 6.6 | total | ||
| Sea Fennel phenolic extracts | 3-Caffeoylquinic acid (12.0 μg/mL ) | total | total | |
| Chlorogenic acid (198.6 μg/mL ) | 66.0 | 81.7 | ||
| 1-Caffeoylquinic acid (24.3 μg/mL ) | 67.4 | 78.1 | ||
| 5-p-Coumaroylquinic acid (16.6 μg/mL ) | total | total | ||
| 5-Feruloylquinic acid (25.0 μg/mL ) | total | total | ||
| 3,4-Dicaffeoylquinic acid (15.6 μg/mL ) | total | total | ||
| 3,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid (57.1 μg/mL ) | total | total | ||
| 4,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid (29.6 μg/mL ) | total | total | ||
| Grape pomace phenolic extracts | Galloylshikimic acid (3.4 mg/g) | total | Corrêa et al. (2017) | |
| Proanthocyanidine B dimer (25.4 mg/g) | 91.4 | |||
| Digalloylquinic acid (2.3 mg/g) | 95.2 | |||
| (-)-Epicatechin (7.3 mg/g) | 76.3 | |||
| (+)-Catechin (7.3 mg/g) | 75.7 | |||
| Digalloylshikimic acid (1.9 mg/g) | Total | |||
| Proanthocyanidine B trimer (8.5 mg/g) | 93.4 | |||
| Proanthocyanidine B tretramer (6.2 mg/g) | 93.9 | |||
| Myricetin-O-hexoside(1.4 mg/g) | 19.7 | |||
| Quercetin-3-O-glucuronide(0.6 mg/g) | Total | |||
| Quercetin-3-O-glucoside(0.5 mg/g) | 55.8 | |||
| Laricitrin-O-hexoside(0.4 mg/g) | total | |||
| Quercetin-O-pentoside(0.4 mg/g) | total | |||
| Quercetin-O-rhamnoside(0.4 mg/g) | 36.8 | |||
| Isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside(0.5 mg/g) | total | |||
| Methylisorhamnetin derivative(0.3 mg/g) | total | |||
| Total non-anthocyanin compounds(66.6 mg/g) | 87.5 | |||
| Petunidin-3-O-glucoside (0.6 mg/g) | 68.9 | |||
| Peonidin-3-O-glucoside (1.6 mg/g) | 85.4 | |||
| Malvidin-3-O-glucoside (3.4 mg/g) | 90.0 | |||
| Peonidin-3-O-acetylglucoside (0.7 mg/g) | 74.1 | |||
| Malvidin-3-O-acetylglucoside (0.7 mg/g) | 73.9 | |||
| Total anthocyanin compounds (7.0 mg/g) | 84.0 | |||
| Food matrix | ||||
| Chokeberry juice concentrates | Cyanidin 3-galactoside (362 μg/mL) | −3.3 | 39.2 | Bermúdez-Soto et al. (2007) |
| Cyanidin 3-glucoside (41.6 μg/mL) | −3.8 | 43.3 | ||
| Cyanidin 3-arabinoside (240 μg/mL) | −2.3 | 44.9 | ||
| Cyanidin 3-xyloside (29 μg/mL) | −4.1 | 50.8 | ||
| Cyanidin (7.2 μg/mL) | −350 | total | ||
| Quercetin hexoside pentoxide (22.4 μg/mL) | 4.5 | 28.6 | ||
| Quercetin 3-galactoside (27 μg/mL) | 2.2 | 15.5 | ||
| Quercetin 3-glucoside (37.2 μg/mL) | 7.0 | 19.1 | ||
| Quercetin 3-rutinoside (88.8 μg/mL) | 5.9 | 29.6 | ||
| Quercetin (3.6 μg/mL) | −5.6 | Total | ||
| Neochlorogenic acid (318 μg/mL) | 3.8 | 28.0 | ||
| Chlorogenic aid (296 μg/mL) | 3.4 | −23.9 | ||
| Other flavan-3-ols (710 μg/mL) | 14.9 | 19.3 | ||
| Strawberry yoghurt | (+)-Catechin (534.8 μg/g) | 10.9 | 47.0 | Oliveira and Pintado (2015) |
| Quercetin-3-rutinoside (11.0 μg/g) | 18.2 | 40.0 | ||
| Ellagic acid (8.6 μg/g) | 7.0 | 3.5 | ||
| Cyanidin-3-glucoside (6.5 μg/g) | −3.1 | 46.2 | ||
| Pelargonidin-3-glucoside (70.6 μg/g) | −11.6 | 65.3 | ||
| Pelargonidin-3-rutinoside (6.7 μg/g) | −26.7 | 58.2 | ||
| Peach yoghurt | (+)-Catechin (35.5 μg/g) | 20.6 | 80.0 | |
| Neochlorogenic acid (50.4 μg/g) | −8.5 | 45.0 | ||
| Chlorogenic acid (46.4 μg/g) | −9.9 | 38.6 | ||
| Quercetin-3-rutinoside (7.7 μg/g) | −7.8 | 31.2 | ||
| Sample | Dialyzed rate (%) | Absorption medium | Method Source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apple | Phenolics | 55 | 10 kDa dialysis membrane | Bouayed et al. (2011) |
| Flavonoids | 38 | |||
| Orange juice | Flavanone | 12–36 | 12 kDa dialysis membrane | Gil-Izquierdo et al. (2001) |
| Narirutin | 11–31 | |||
| Hesperidin | 16–37 | |||
| Vicenin-2 | 19–30 | |||
| Orange juice | Flavanone | 12–20 | 12 kDa dialysis membrane | Gil-Izquierdo et al. (2002) |
| Narirutin | 12–21 | |||
| Hesperetin | 12–21 | |||
| Vicenin-2 | 13–22 | |||
| Strawberry | Cyaniding-3-glucoside | 0–6 | ||
| Pelargonidin-3-glucoside | 1–13 | |||
| Pelargonidin rutinoside | 1–12 | |||
| Ellagic acid arabinoside | 5–21 | |||
| Ellagic acid | 6–173 | |||
| Quercetin-3-glucoside | 4–28 | |||
| Kaemferol-3-glucoside | 19–27 | |||
| Strawberry jam | Cyaniding-3-glucoside | 0–2 | ||
| Pelargonidin-3-glucoside | 1–4 | |||
| Pelargonidin rutinoside | 1–4 | |||
| Ellagic acid arabinoside | 6 | |||
| Ellagic acid | 6–10 | |||
| Quercetin-3-glucoside | 5–6 | |||
| Kaemferol-3-glucoside | 12–27 | |||
| White or Whole-meal Bread | Ferulic acid | 61–77 | Unknown dialysis membrane | Anson et al. (2009) |
| p-Coumaric acid | 63–78 | |||
| Sinapic acid | 89–92 | |||
| Whole-meal Bread | Ferulic acid | 2.5–5.1 | 5–8 kDa dialysis membrane | Hemery et al. (2010) |
| p-Coumaric acid | 5.9–15 | |||
| Sinapic acid | 20–60 | |||
| Soymilk | Flavonoids | 15 | 12 kDa dialysis membrane | Rodríguez-Roque et al. (2013a) |
| Phenolics | 20 | |||
| Hesperidin | 14 | |||
| Naringenin | 21 | |||
| Quercetin | 17 | |||
| Catechin | 28 | |||
| Rutin | 0 | |||
| Gallic acid | ||||
| p-Hydroxybenzoic acid | ||||
| p-Coumaric acid | ||||
| Ferulic acid | ||||
| Sinapic acid | ||||
| Mixed fruit juice | Phenolics | 12 | 12 kDa dialysis membrane | Rodríguez-Roque et al. (2013b) |
| Caffeic acid | 0 | |||
| Chlorogenic acid | 11 | |||
| p-Coumaric acid | 17 | |||
| Ferulic acid | 26 | |||
| Sinapic acid | 18 | |||
| Hesperidin | 18 | |||
| Naringenin | 19 | |||
| Rutin | 22 | |||
| Quercetin | 29 | |||
| Catechin | 23 | |||
| Durum Wheat Bran | Ferulic acid | 32 | 12 kDa dialysis membrane | Zaupa et al. (2014) |
| p-Coumaric acid | 100 | |||
| Sinapic acid | 79 | |||
| Caffeic acid | 52 | |||
| p-Hydroxybenzoic acid | 98 | |||
| Cooked finger Millet | Phenolics | 16–37 | 10 kDa dialysis membrane | Hithamani and Srinivasan (2014) |
| Flavonoids | 15–50 | |||
| Cooked pearl Millet | Phenolics | 73–96 | ||
| Flavonoids | 6–52 | |||
| Raspberry | Phenolics | 10 | 12 kDa dialysis membrane | McDougall et al. (2005) |
| Anthocyanins | 5 | |||
| Maqui berry | Rutin | 2.2 | 12–14 kDa dialysis membrane | Lucas-Gonzalez et al. (2016) |
| Ellagic acid | 0.3 | |||
| Quercetin-3-O-galactoside | 4.9 | |||
| Dimethoxy-quercetin | 0.04 | |||
| Delphinidin-3-sambubioside-5-glucoside | 0 | |||
| Delphinidin-3,5-diglucoside | ||||
| Delphinidin-3-glucoside | ||||
| Cyanidin-3,5-diglucoside | ||||
| Delphinidin-3-sambubioside | ||||
| Cyanidin-3-glucoside | ||||
| Cyanidin-3-sambubioside | ||||
| Cyanidin-3-sambubioside-5-glucoside | ||||
| Myricetin-3-galactoside | ||||
| Myricetin-3-glucoside | ||||
| Quercetin-galloyl-hexoside | ||||
| Quercetin-3-glucoside | ||||
| Quercetin-3-xyloside | ||||
| Myricetin | ||||
| Quercetin | ||||
| Mulberry extracts | Anthocyanins | 0.34 | 3.6 kDa dialysis membrane | Liang et al. (2012) |
| Phenolics | 7.33 | |||
| Encoding gene | Transporter name | Distribution | Protein expression level | Direction | Phenolic substrates | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| More information about protein expression level are available from online database “The Human Protein Atlas” (https://www.proteinatlas.org/). | |||||||
| Active transporters | |||||||
| ABCC1 | MRP 1 | Small intestine (basal) | Moderate | Efflux | Conjugated and unconjugated phenolic anions: quercetin, daidzein qucertin/resveratrol/naringenin/ferulic acid conjugates, curcuminoids) | Matsson and Bergström (2015), Schinkel and Jonker (2003), Chen et al. (2016), Kobayashi et al. (2013), Kullak-Ublick et al. (2000). | |
| Large intestine (basal) | Low | ||||||
| Liver (basal) | ND-low | ||||||
| Kidney (basal) | Moderate-high | ||||||
| Brain | Low | ||||||
| Adipose | Moderate | ||||||
| ABCC4 | MRP 4 | Large intestine (basal) | Low | Efflux | Conjugated and unconjugated phenolic anions | Milbury (2009), Wu et al. (2011), Russel (2010). | |
| Liver (basal) | Low | ||||||
| Kidney (apical) | — | ||||||
| Brain | Low | ||||||
| ABCC3 | MRP 3 | Stomach (basal) | Moderate | Efflux | Conjugated and unconjugated phenolic anions | Milbury (2009), Wu et al. (2011), Russel (2010). | |
| Small intestine (basal) | Moderate | ||||||
| Large intestine (basal) | High | ||||||
| Liver (basal) | Low-high | ||||||
| Kidney (basal) | Moderate | ||||||
| Heart | Low | ||||||
| Pancreatic islet | Low | ||||||
| Skeletal muscle | Low | ||||||
| ABCC2 | MRP 2 | Stomach (apical) | High | Efflux | Conjugated and unconjugated phenolic anions (epicatechin, phloridzin, quercetin-4′-β-glucoside, genistein-7-glucoside, quercetin, daidzein, qucertin/resveratrol/naringenin/ferulic acid conjugates | Schinkel and Jonker (2003), Chen et al. (2016), Kobayashi et al. (2013), Sandusky et al. (2002), Russel (2010) | |
| Small intestine (apical) | Moderate | ||||||
| Large intestine | Moderate | ||||||
| Liver (apical) | High | ||||||
| Kidney (apical) | Low-moderate | ||||||
| Brain | Moderate | ||||||
| Adipose | Low | ||||||
| Skeletal muscle | Moderate | ||||||
| ABCB1 | MDR 1 | Small intestine (apical) | Low-moderate | Efflux | Conjugates and unconjugated phenolic cations, phenolic cations (daidzein) | Matsson and Bergström (2015), Schinkel and Jonker (2003), Chen et al. (2016), Kobayashi et al. (2013), Kullak-Ublick et al. (2000). | |
| Large intestine (basal) | Low | ||||||
| Liver (apical) | Moderate | ||||||
| Kidney (apical) | Low | ||||||
| Brain (apical) | Low | ||||||
| ABCG2 | BCRP | Small intestine (both) | Moderate | Efflux | Conjugates and unconjugated phenolic anions (dihydroferulic acid, ferulic acid/quercetin/resveratrol/genistein conjugates, quercetin, chrysin, daidzein, and coumestrol) | Matsson and Bergström (2015), Kobayashi et al. (2013), Estudante et al. (2013), Schinkel and Jonker (2003), Chen et al. (2016), Sesink et al. (2005). | |
| Large intestine | Moderate | ||||||
| Liver (apical) | Low to moderate | ||||||
| Kidney (apical) | Low | ||||||
| Brain (apical) | Low | ||||||
| Heart | Low | ||||||
| Smooth muscle | Moderate | ||||||
| SLC16A3 | MCT 4 | Stomach | Moderate | Efflux | Phenolic acid and phenolic acid conjugate anions | Ziegler et al. (2016), Lafay and Gil-Izquierdo (2008). | |
| Small intestine (basal) | Low-moderate | ||||||
| Large intestine (basal) | Moderate | ||||||
| Liver | Low-moderate | ||||||
| Kidney | High | ||||||
| Heart | Moderate | ||||||
| Smooth and skeletal muscle | Low-moderate | ||||||
| Brain | Low | ||||||
| Adipose | Low | ||||||
| SLC16A1 | MCT 1 | Stomach (apical) | High | Influx | Phenolic acids, phenolic acid conjugate anions (ferulic acid, ferulic acid conjugate, dihydroferluric acid, salicylic acid, m-coumaric and 3-(m-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acids) | Matsson and Bergström (2015), Ziegler et al. (2016), Lafay and Gil-Izquierdo (2008). | |
| Small intestine (both) | Moderate-high | ||||||
| Large intestine (both) | High | ||||||
| Liver | Moderate | ||||||
| Kidney | Moderate | ||||||
| Brain | Low | ||||||
| Heart | Moderate | ||||||
| Smooth and skeletal muscle | Low-moderate | ||||||
| SLC5A8 | SMCT 1 | Small intestine (both) | Moderate | Both | Sodium-coupled phenolic acid | Ziegler et al. (2016), Poquet et al. (2008), Cui and Morris (2009), Rhoden (2012), Martin et al. (2007). | |
| Large intestine (both) | Moderate | ||||||
| Kidney (both) | Low | ||||||
| Brain | Low | ||||||
| SLC47A1 | MATE 1 | Stomach | Low | Influx | Cationic compounds efflux and phenolics influx* (quercetin, kaempferol, luteolin, apigenin. Less prefer to phenolic glucosides and conjugates) | Matsson and Bergström (2015), Lee et al. (2014), Domínguez-Avila et al. (2017), Russel (2010). | |
| Small intestine (apical) | Moderate-high | ||||||
| Large intestine | Moderate | ||||||
| Kidney (apical) | High | ||||||
| Liver (apical) | Low | ||||||
| Adipose | Low | ||||||
| Heart | Low | ||||||
| Smooth/skeletal muscle | Low | ||||||
| Brain | Low | ||||||
| SLC5A1 | SGLT 1 | Small intestine (apical side) | High | Influx | Phenolic glycosides (phlorizin, calycosin-7-O-β-D-glucoside quercetin 4′-O-β-glucoside) | Williams et al. (2004), Sabino-Silva et al. (2010), Shi et al. (2016), Walgren et al. (2000b), Yu et al. (2012). | |
| Liver | Low | ||||||
| Kidney | Low | ||||||
| Brain | — | ||||||
| Heart | — | ||||||
| - | Bilitranslocase | Stomach (apical) | — | Influx | Phenolic glycosides and aglycones: quercetin, malvidin 3-glucoside, baicalein | Passamonti et al. (2009), Maestro et al. (2009). | |
| Small intestine (both) | — | ||||||
| Large intestine | — | ||||||
| Liver (basal) | — | ||||||
| Kidney | — | ||||||
| Brain | — | ||||||
| SLCO1A2 | OATP1A2 | Small intestine (apical) | — | Influx | Amphipathic phenolics, large hydrophobic organic anions, phenolic anions (quercetin) | Cheng et al. (2012), Matsson and Bergström (2015), Glaeser et al. (2014), Tamai (2012), Cheng et al. (2012), Gao et al. (2000) | |
| Kidney (both) | Low | ||||||
| Liver (basal) | Moderate-high | ||||||
| Brain (basal) | High | ||||||
| SLCO2B1 | OATP2B1 | Stomach | Moderate | Influx | Amphipathic phenolics, large hydrophobic organic anions, phenolic anions (quercetin, daidzein-7-glucuronide) | Matsson and Bergström (2015), Glaeser et al. (2014), Tamai (2012), Cheng et al. (2012), Grosser et al. (2015), Russel (2010). | |
| Small intestine (apical) | — | ||||||
| Large intestine (apical) | — | ||||||
| Kidney (basal) | ND-Low | ||||||
| Liver (basal) | Low | ||||||
| Brain (basal) | Moderate | ||||||
| Heart | Moderate | ||||||
| Skeletal muscle | Moderate | ||||||
| Pancreas islet | Low | ||||||
| SLC10A6 | SOAT | Stomach | Moderate | Influx | Daidzein monosulfates | Grosser et al. (2015) | |
| SLC10A1 | NTCP | Liver (basal) | Moderate | Influx | Daidzein monosulfates, daidzein-7,4′-disulfates. | Grosser et al. (2015) | |
| SLC22A7 | OAT 1 | Kidney (basal) | Moderate-high | Influx | Phenolic and phenolic conjugate anions (morin, silybin, caffeic acid, ferulic acid, caffeic acid-3-O-glucuronide/sulfate, caffeic acid-4-O-glucuronide/sulfate, dihydrocaffeic acid, dihydroferulic acid, dihydrocaffeic acid-3-O-glucuronide/sulfate, dihydrocaffeic acid-4-O-glucuronide/sulfate, dihydroferulic acid-4-O-sulfate, ferulic acid-4-O-glucuronide/sulfate, genistein-4′-O-sulfate/glucuronide, isoferulicacid-3-O-glucuronide/sulfate, quercetin-3-O-glucuronide, quercetin-3′-O-sulfate/glucuroside, quercetin-7-O-glucuronide) | Passamonti et al. (2009), Wang and Sweet (2013). | |
| Liver | High | ||||||
| brain | Low | ||||||
| Muscle | Low | ||||||
| Adipose | Low | ||||||
| SLC22A8 | OAT3 | Kidney (basal) | High | Influx | Phenolic and phenolic conjugate anions (caffeic acid, caffeic acid-3-O-glucuronide/sulfate, caffeic acid-4-O-glucuronide/sulfate, dihydrocaffeic acid, dihydroferulic acid, dihydrocaffeic acid-3-O-glucuronide/sulfate, dihydrocaffeic acid-4-O-glucuronide/sulfate, dihydroferulic acid-4-O-sulfate, ferulic acid-4-O-glucuronide/sulfate, genistein-4′-O-sulfate/glucuronide, isoferulic acid-3-O-glucuronide/sulfate, quercetin-3-O-glucuronide, quercetin-3′-O-sulfate/glucuroside, quercetin-7-O-glucuronide, daidzein-7-O-glucuronide, daidzein-7,4′-O-disulfate, genistein-7-O-glucuronide, glycitein-7-O-glucuronide) | Passamonti et al. (2009), Wang and Sweet (2013), Faria et al. (2012), Koepsell and Endou (2004). | |
| Brain (basal) | Low | ||||||
| Skeletal Mucsle | — | ||||||
| SLC22A9/SLC22A11 | OAT 4 | Kidney (apical) | High | Caffeic acid-3-O-sulfate, caffeic acid-4-O-sulfate, ferulic acid-4-O-sulfate, isoferulic acid-3-O-sulfate, daidzein monosulfates | Passamonti et al. (2009), Wang and Sweet (2013), Kullak-Ublick et al. (2000), Chen et al. (2005), Grosser et al. (2015). | ||
| SLC22A1 | OCT 1 | Stomach | Low-moderate | Influx | Low-molecular-weight phenolic cations (quercetin and quercetin conjugates) | Estudante et al. (2013), Glaeser et al. (2014), Russel (2010) | |
| Small intestine (basal) | Low-moderate | ||||||
| Large intestine (basal) | Low-moderate | ||||||
| Liver (basal) | Moderate-High | ||||||
| Kidney (both) | Low-moderate | ||||||
| Brain | Low | ||||||
| Heart | Moderate | ||||||
| Skeletal muscle | Moderate | ||||||
| Pancreas islet | Low | ||||||
| SLC22A2 | OCT 2 | Small intestine (basal) | Low | Influx | Low-molecular-weight phenolic cations | Estudante et al. (2013), Faria et al. (2012), Kullak-Ublick et al. (2000), Zhou et al. (2007). | |
| Liver (basal) | Low | ||||||
| Kidney (basal) | Moderate-high | ||||||
| Brain (basal) | Moderate | ||||||
| SLC22A4 | OCTN 1 | Small intestine (apical) | — | Both | phenolic cations and anions | Estudante et al. (2013), Domínguez-Avila et al. (2017), Koepsell et al. (2004). | |
| Large intestine (apical) | — | ||||||
| Liver (only fetal, apical) | — | ||||||
| Kidney (apical) | — | ||||||
| Skeletal muscle | — | ||||||
| Brain | Low | ||||||
| Facilitated transporters | |||||||
| SLC2A1 | GLUT 1 | Brain | Low | Influx | quercetin | Passamonti et al. (2009), Wood and Trayhurn (2003), Cunningham et al. (2006). | |
| Liver | ND-low | Influx | |||||
| Adipose | Low | Influx | |||||
| Skeletal and smooth muscle | Low | Influx | |||||
| Erythrocyte | Low | Influx | |||||
| SLC2A4 | GLUT 4 | Adipose | Moderate | Influx | Genistein, myricetin, quercetin, and catechin-gallate | Passamonti et al. (2009), Wood and Trayhurn (2003), Gould and Holman (1993), McCall et al. (1997). | |
| Heart | high | ||||||
| Skeletal and smooth muscle | Moderate | ||||||
| Brain | Low | ||||||
| SLC2A2 | GLUT 2 | Small intestine (both) | Moderate | Both | Quercetin 3-glucoside, anthocyanins | Passamonti et al. (2009), Wood and Trayhurn (2003), Gould and Holman (1993), Wenzel (2013), Freitas et al. (2005), Fernandes et al. (2014). | |
| Liver | High | ||||||
| Kidney (basal) | Moderate | ||||||
| Pancreas islet | Low | ||||||
| Passive diffusion | All the tissues | Depends | Lipophilic and amphipathic small molecule (genistein, daidzein, quercetin, catechin, EGCG, ECG, EGC, dihydrogenistein, dihydrodaidzein, quercetin-3-O-glucuronide, quercetin-7-O-glucuronide) | Kobayashi et al. (2013) | |||
| Paracellular transport | All the tissues | Depends | Small molecules/ions (various phenolic acids and phenolic acid metabolites: chlorogenic acid, 3-hydroxybenzoic acid, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylpropionic acid, caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid; catechin, proanthocyanidin dimer/trimer ) | Deprez et al. (2001), Lafay and Gil-Izquierdo (2008), Domínguez-Avila et al. (2017) | |||
| Endocytosis/exocytosis | All the tissues | — | Phenolic-protein complexes | Tarahovsky et al. (2014) | |||
| Transporter name | Location on capillary endothelial cells | Orientation | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| MRP 1 | Both | Endothelium to blood, endothelium to brain | Faria et al. (2012), Milbury (2009). |
| MRP 4 | Both | Endothelium to blood, endothelium to brain | Milbury (2009), Sier (2015). |
| MRP 2 | Both | Endothelium to blood, endothelium to brain | Faria et al. (2012), Milbury (2009). |
| MDR 1 | Luminal | Endothelium to blood | Faria et al. (2012) |
| BCRP | Luminal | Endothelium to blood | Faria et al. (2012), Cheng et al. (2012). |
| MCT 1 | Both | Blood to endothelium, brain to endothelium | Faria et al. (2012) |
| MATE 1 | — | — | Geier et al. (2013) |
| SGLT 1 | Abluminal | Brain to endothelium | Faria et al. (2012) |
| OCT 2 | Luminal | Blood to endothelium | Faria et al. (2012) |
| OAT 3 | Abluminal | Brain to endothelium | Faria et al. (2012) |
| OATP1A2 | Luminal | Blood to endothelium | Cheng et al. (2012) |
| OATP2B1 | Both | Blood to endothelium, Endothelium to brain | Faria et al. (2012), Cheng et al. (2012). |
| GLUT 1 | Both | Blood to endothelium, endothelium to brain | Faria et al. (2012) |
| GLUT 4 | — | — | McCall et al. (1997) |
| Category | Main Enzymes | Common Reactions | Products |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adapted from Timbrell and Marrs (2009), Smart and Hodgson (2018), Shimada et al. (2006), and Hodgson et al. (2001). | |||
| Oxidation | Alcohol oxidases; Aldehyde oxidases; Xanthine oxidases; Monoamine oxidases; Flavin-containing monooxygenases; Cytochrome P450s. | Aromatic C-oxidation; Aliphatic C-oxidation; N- and S-oxidation. Epoxidation; Dehydrogenation; N-, O- and S-dealkylations. | Phenols; Alcohols; Ketones; Aldehydes; Epoxides; Ketenes; Acids; N- and S-oxides; Amines; Thiols. |
| Hydrolysis | Carboxylesterases; Peptidases; Epoxide hydrolases; Cholinesterases; Paraoxonases. | Hydrolysis of esters, amides, epoxides. | Alcohols; Acids; Amines. |
| Reduction | Alcohol Dehydrogenases; Carbonyl Reductases; NADPH-quinone oxidoreductases; NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductases. | Reduction of azo, nitro groups, carbonyl Groups, sulfoxides and N-oxides, quinones; Reductive Cleavage of Heteroaromatic Compounds; Disulfide reduction and reductive dehalogenation. | Phenols; Alcohols; Ketones; Sulfides; Acids; Amines; Thiols. |
| Substrate | Enzymes | Product(s) | Enzyme source | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Galangin | CYP2C9*, CYP1A1,CYP1A2 | Kaempferol | Human liver microsomes | Otake and Walle (2002b) |
| Kaempferide | CYP1A2*, CYP1A1, CYP2C9 | Kaempferol | Human liver microsomes | |
| Kaempferol | CYP1A1 | Quercetin | Hamster high-expressed CYP-450s ovary cell | Silva et al. (1997) |
| Chrysin | CYP1A1, CYP1A2 | Apigenin (major), scutellarein and isoscutellarein | Aroclor 1254-induced rat liver microsomes | Nielsen et al. (1998), Gradolatto et al. (2004). |
| Naringenin | CYP1A | Eriodictyol | Aroclor 1255-induced rat liver microsomes | |
| Hesperetin | CYP1A | Eriodictyol | Aroclor 1256-induced rat liver microsomes | |
| Apigenin | CYP1A | Luteolin | Aroclor 1257-induced rat liver microsomes | |
| Tamarixetin | CYP1A | Quercetin | Aroclor 1258-induced rat liver microsomes | |
| α-Naphthoflavone | CYP-450c, epoxide hydrolase | 7,8-Dihydro-7,8-dihydroxy-α-naphthoflavone 5,6-Dihydro-5,6-dihydroxy-α-naphthoflavone 5,6-Oxide-α-naphthoflavone 6-Hydroxy-α-naphthoflavone 9-Hydroxy-α-naphthoflavone | Rat liver microsomes. | Andries et al. (1990), Vyas et al. (1983). |
| Tangeretin | CYP1A | Demethyl tangeretin or multi-demethyl tangeretin | Rat and human liver microsomes. | Canivenc-Lavier et al. (1993) |
| β-Naphthoflavone | Unknown CYP-450s | 8-Hydroxy-β-naphthoflavone | Rat liver microsomes. | Vyas et al. (1983) |
| β-Naphthoflavone | CYP-450c, epoxide hydrolase | Trans-7,8-dihydro-7,8-dihydroxy-β-naphthoflavone Trans-5,6-dihydro-5,6-dihydroxy-β-naphthoflavone 5-Hydroxy-β-naphthoflavone | Rat liver microsomes. |
| Substrate | Human liver microsomes | Recombinant CYP-450s | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CYP1A2 | CYP2C9 | CYP1A1 | ||||||||||
| Km (μM) | Vmax(pmol/mg/min) | Vmax/Km (μl/min/mg) | Km (μM) | Vmax(pmol/mg/min) | Vmax/K (μl/min/mg) | Km (μM) | Vmax(pmol/mg/min) | Vmax/Km (μl/min/mg) | Km (μM) | Vmax(pmol/mg/min) | Vmax/Km (μl/min/mg) | |
| Adapted from Otake et al. (2002a). | ||||||||||||
| Galangin | 9.5 ± 0.4 | 129 ± 11 | 13.6 ± 1.1 | 2.5 | 81 | 32 | 0.4 | 23 | 58 | 1.1 | 10.8 | 10.2 |
| Kaempferide | 17.8 ± 3.5 | 181 ± 32 | 10.8 ± 1.9 | 4.3 | 89 | 21 | 8.1 | 41 | 5.1 | 6.4 | 12.4 | 1.9 |
| Enzyme Source | Km (μM) | Vmax (pmol/mg of protein/min) | Vmax/Km (μl/min/mg) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak 1 | Peak 2 | Peak 1 | Peak 2 | Peak 1 | Peak 2 | ||
| Adapted from Otake et al. (2002a). | |||||||
| Recombinant UGTs | Human liver microsomes | 3.6 ± 0.7 | 221 ± 31 | 1,521 ± 252 | 34,333 ± 2,167 | 427 ± 26 | 155 ± 30 |
| UGT1A9 | 1.1 | 31.8 | 721 | 3,594 | 655 | 113 | |
| UGT1A1 | N.D. | 6.3 | N.D. | 388 | N.D. | 62.1 | |
| UGT2B15 | N.D. | 15.7 | N.D. | 538 | N.D. | 34.3 | |
| Recombinant SULTs | SULT1A1 | 0.21 | 3,270 | 15,572 | |||
| SULT1A3 | 37.1 | 822 | 22.2 | ||||
| SULT1E1 | 1.13 | 948 | 839 | ||||
| Hamster kidney cytosol | Recombinant COMT from Porcine liver | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rate (pmol/mg/min) | Rate (pmol/mg/min) | Km (μM) | Vmax (pmol/mg/min) | Vmax/Km (μl/min/mg) | |
| Adapted from Zhu et al. (1994). | |||||
| Quercetin | 109 ± 11 | 9,100 ± 47 | 6.1 | 14,870 | 2,438 |
| Fisetin | 119 ± 8 | 13,100 ± 101 | 4.8 | 17,700 | 3,687 |
| 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 32 ± 3 | 2,206 ± 21 | 16.2 | 4,123 | 255 |
| 4-Hydroxyestradiol | 9 ± 2 | 414 ± 11 | 23.4 | 2,560 | 109 |
| Epinephrine | ND | 16 ± 2 | 1,036 | 2,754 | 2.66 |
| Norepinephrine | ND | 9 ± 2 | 1,149 | 1,990 | 1.73 |
| Dopamine | ND | 31 ± 3 | 1,018 | 5,182 | 5.09 |
| Enzyme | Isoforms | Expression level (RNA and Protein expression mixed) | Substrates | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal tract | Liver | Kidney | Muscle | Brain | |||
| Cited from Court et al. (2012), Rowland et al. (2013), Jancova et al. (2010), Cheng et al. (1999), Margaillan et al. (2015), Wong et al. (2009), Finel et al. (2005), King et al. (1999), Mostaghel et al. (2016), King et al. (2000), Teubner et al. (2007), Cheng et al. (1998), Cheng et al. (1999), Barbier et al. (2000), Knights et al. (2013), Chimalakonda et al. (2011), Riches et al. (2009), Ghosh et al. (2013), Sakamoto et al. (2015), Lu et al. (2015), Guidry et al. (2017), Kurogi et al. (2017), Hui et al. (2015), and Collins et al. (1973). | |||||||
| SULTs | SULT1A1 | high | high | moderate | low | trace | Various phenolics (monocyclic phenols, naphtols, benzylic alcohols, hydroxylamines, dopamine, p-nitrophenol and iodothyronines, naringenin, genistein,), aromatic amines, drugs (afimoxifene, endoxifen, raloxifene, and fulvestrant), opioids (buprenorphine, norbuprenorphine, pentazocine, naloxone) |
| SULT1A2 | high | low | low | low | trace | Aromatic hydroxylamines, opioids (buprenorphine, norbuprenorphine, pentazocine, naloxone) | |
| SULT1A3 | high | none | moderate | none | trace | Norepinephrine, catechols, aromatic molecules, and monocyclic phenolics (catecholamines, dopamine, demethoxycurcumin, curcumin, vanillin), opioids (pentazocine, naloxone) | |
| SULT1A4 | high | low | low | low | trace | — | |
| SULT1B1 | high | moderate | moderate | — | — | Thyroid hormones, phenolics (1-naphtol and 4-nitrophenol, curcumin, bisdemethoxycurcumin) | |
| SULT1C2 | high | none | moderate | none | none | 4-Nitrophenol and N-hydroxy-2-acetylaminofluoren | |
| SULT1C3 | none | none | none | none | none | 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural, ethanol, hydroxyl chlorinated biphenyls, bile acids, and thyroid hormones | |
| SULT1C4 | trace | moderate | low | low | low | Phenolics (demethoxycurcumin, curcumin, bisdemethoxycurcumin, 1-naphthol, catechol estrogens (genistein, daidzein, chrysin, apigenin, and 6,4′-dihydroxyflavone)), drugs (doxorubicin, epirubicin, afimoxifene, endoxifen, raloxifene, and fulvestrant), opioids (pentazocine, naloxone) | |
| SULT1E1 | moderate | moderate | none | none | trace | Estrogen (17β-estradiol), iodothyronines, pregnenolon, phenolics (1-naphtol, p-nitrophenol demethoxycurcumin, curcumin, bisdemethoxycurcumin, naringenin, genistein), 4-hydroxytamoxifen, opioids (pentazocine, naloxone) | |
| SULT2A1 | moderate | high | low | none | low | Androgens (dehydroepiandrosterone, epiandrosterone, androsterone, testosterone, E2), opioids (pentazocine, buprenorphine) | |
| SULT2B1 | moderate | low | none | moderate | none | Cholesterol, dehydroepiandrosterone | |
| UGTs | UGT1A1 | low | moderate | low | — | none | Drugs (bilirubin, estradiol, etoposide, ethynylestradiol, raloxifene, buprenorphine, SN-38 (active metabolite of irinotecan)), retinoic acid, opioid (naltrexone, buprenorphine, paracetamol), complex phenolics |
| UGT1A3 | low | moderate | none | — | none | Aliphatic or aromatic carboxylic acids, amines, phenolics (flavonoids, 7-hydroxycoumarins, anthraquinones), opioids, estrone (2-hydroxycatechol estrogens), drugs (telmisartan) | |
| UGT1A4 | moderate | moderate | none | — | Existence (no amount data) | Tertiary amines, androgens, progestins, plant steroids (sapogenins), drugs (lamotrigine, olanzapine, trifluoperazine) | |
| UGT1A5 | low | low | — | — | Existence (no amount data) | SN-38, scopoletin, 4-methylumbelliferone, 1-hydroxypyrene | |
| UGT1A6 | moderate | moderate | high | — | Existence (no amount data) | Simple phenolics (4-nitrophenol) and primary amines (5-hydroxytryptamine), drugs (paracetamol ) | |
| UGT1A7 | moderate | none | none | none | none | Phenols, benzo(α)pyrenes, and coumarins | |
| UGT1A8 | low | none | none | none | none | Catechol estrogens, primary and secondary amines, sapogenins, retinoids, coumarins, phenolics (nitrophenol, flavonoids, anthraquinones), and opioids | |
| UGT1A9 | trace | low | high | none | none | Carboxylic acids, amines (N-hydroxy arylamines, N-hydroxy-naphthylamine), complex phenolics (flavonoids, anthraquinones), steroids, drugs (paracetamol, frusemide, mycophenolic acid, phenylbutazone, propofol, raloxifene, retigabine, sulfinpyrazone) | |
| UGT1A10 | high | none | none | none | moderate | Phenolics (flavonoids), bile acids, steroids, fatty acids, retinoids, and other drugs (ciprofibrate, furosemide, and diflunisal) | |
| UGT2A1 | none | none | none | none | moderate | Carboxylic acids, monoterpenoid, aliphatic alcohols, phenolics, coumarins | |
| UGT2A3 | high | moderate | moderate | trace | — | Bile acids (hyodeoxycholic acid) | |
| UGT2B4 | low | high | high | trace | none | Hyodeoxycholic acid, steroids (androstanediol, androsterone) | |
| UGT2B7 | high | high | high | trace | trace | Carboxylic acids, azido deoxythymidine, catechol estrogens, Androgens (3α-hydroxyandrogens, 3α-pregnanes), hyodeoxycholic acid, NSAIDs (fenoprofen, ketoprofen, naproxen), and opioids (codeine, morphine, naloxone), valproic acid, zidovudine, carbamazepine, chloramphenicol, epirubicin, gemfibrozil, | |
| UGT2B10 | none | high | none | none | Existence (no amount data) | Steroids (testosterone, androstanediol, androsterone), tertiary amines (cotinine and nicotine) | |
| UGT2B11 | low | moderate | none | none | none | Androgens (3α-hydroxyandrogens, 3α-pregnanes), estrogen (oestriol) | |
| UGT2B15 | high | high | Existence (no amount data) | trace | — | Phenolics (flavonoids), estrogens, androgens (testosterone, dihydrotestosterone, androstanediol), drugs (lorazepam, oxazepam, temazapam, sipoglitazar ) | |
| UGT2B17 | high | low | — | trace | — | 4-Methylumbelliferone, eugenol, and the endogenous steroids (testosterone, androstanediol, androsterone, dihydrotestosterone) | |
| UGT2B28 | high | none | none | none | none | Androgens (testosterone, androstanediol, androsterone) | |
| COMT | moderate | moderate | high | low | moderate | Catechol amines (dopamine, salsolinol, tetrahydropapaveroline, norepinephrine) catechol estrogens, various phenolics, various drugs, plant steroids | |
| Specifications | Oral cavity | Esophagus | Stomach | Small intestine | Large intestine | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duodenum | Jejunum | Illeum | Cecum | Colon | Rectum | |||||
| Data from Jandhyala et al. (2015), Gibbons and Houte (1975), Proano et al. (1990), Camilleri et al.(1989), Pei et al. (2004), Bik et al. (2006), Kroes et al. (1999), Dewhirst et al. (2010), Fujio-Vejar et al. (2017), Dethlefsen et al. (2006), Berg (1996),Booijink et al (2007), Li et al. (2014), Wang et al. (2005), Stearns et al. (2011), Zoetendal et al. (2012), Li et al. (2015), Li et al (2018), eHOMD (http://www.homd.org/) and NIH Human Microbiome Project (https://www.hmpdacc.org/hmp/). | ||||||||||
| pH | 7.0 | 4.0–7.0 | 1.0–4.0 | 5.5–7.0 | 6.5–7.5 | 6.5–7.5 | 5.9–6.4 | 5.5–7.0 | 7.0–7.5 | |
| Microbiota density (cells/ml or g contents) | 107–109 | — | < 103 | 103–105 | 105–107 | 107–108 | 108–1012 | |||
| Stay time of food residue | 0.5–1 min | 5–10 seconds | 0.5–5 hours | 3–5 hours | 4–72 hours (36 hours) | |||||
| Bacteria diversity | Phyla detected in different individuals | Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, Fusobacteria, Bacteroidetes, TM7, Chlamydiae, Chloroflexi, Spirochaetes, SR1, Synergistetes, Tenericutes, Deferribacteres, Acidobacteria, Cyanobacteria, Chlorobi, Deinococcus-Thermus, Verrucomicrobia, GN02, WPS-2, WS6, Elusimicrobia Total phylum amount: ∼29 | Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Fusobacteria, TM7, Spirochaetes, Tenericutes, SR1, Synergistetes, GN02, Chloroflexi, Cyanobacteria, Armatimonadetes, Thermotogae, TM6, WPS-2, WS6, Chlamydiae, Verrucomicrobia, Gemmatimonadetes, Acidobacteria Total phylum amount: ∼29 | Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Fusobacteria, TM7, Deferribacteres, Acidobacteria, Chloroflexi, Cyanobacteria, Deinococcus-Thermus Total phylum amount: ∼15 | Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, Fusobacteria, Verrucomicrobia, Cyanobacteria, Deinococcus-Thermus, SR1, Spirochaetes, TM7, Tenericutes, Lentisphaerae, Thermotogae, Chloroflexi, Acidobacteria, OP10, Synergistetes, Planctomycetes, Gemmatimonadetes, Deferribacteres, OD1, Aquificae Total phylum amount: ∼23 | Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Verrucomicrobia, Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, Spirochaetes, Cyanobacteria, Tenericutes, Fusobacteria, Lentisphaerae, Acidobacteria, Deinococcus-Thermus, SR1, Synergistetes, TM7, Thermotogae, Nitrospira, Gemmatimonadetes, OD1, Aquificae, Deferribacteres Total phylum amount: ∼21 | ||||
| Partially named Genera detected in different individuals (The amount of named species) | Streptococcus (49), Deinococcus (1), Lactococcus (1), Enterococcus (4), Granulicatella (2), Abiotrophia (1), Dolosigranulum (1), Alloiococcus (1), Lactobacillus (19), Gemella (4), Paenibacillus (2), Bacillus (4), Listeria (1), Staphylococcus (4), Erysipelothrix (1), Bulleidia (1), Solobacterium (1), Mollicutes class sp. (1), Mycoplasma (9), Eubacterium (9), Mogibacterium (5), Peptostreptococcus (2), Filifactor (1), Parvimonas (3), Finegoldia (1), Anaerococcus (2), Peptoniphilus (6), Clostridiales order sp. (6), Pseudoramibacter (1), Johnsonella (2), Butyrivibrio (1), Catonella (3), Shuttleworthia (1), Oribacterium (5), Peptococcus (2), Selemonomas (22), Centipeda (1), Mitsuokella (3), Veillonella (5), Anaeroglobus (1), Megasphaera (2), Dialister (5), Actinomyces (24), Mobiluncus (1), Actinobaculum (1), Arcanobacterium (1), Rothia (3), Kocuria (1), Arsenicococcus (1), Microbacterium (1), Propioibacterium (7), Mycobacterium (3), Dietzia (1), Turicella (1), Corynebacterium (5), Gardnerella (1), Biofidobacterium (1), Parascardovia (1), Scardovia (2), Slackia (1), Crytobacterium (1), Eggerthella (1), Atopobium (7), Olsenella (4), Fusobacterium (9), Sneathia (2), Leptotrichia (19), Prevotella (56), Bacteroides (4), Tanerella (3), Porphyromonas (12), Bergeyella (3), Capnocytophaga (16), Neisseria (19), Eikenella (2), Kingella (5), Acromobacter (1), Bordetella (1), Lautropia (1), Burkholderia (2), Rhodocyclus (1), Ralstonia (1), Delftia (1), Variovorax (1), Leptothrix (3), Stenotrophomonas (1), Xanthomonas (1), Cardiobacterium (2), Pseudomonas (6), Acinetobacter (2), Moraxella (2), Enterobacter (3), Klebsiella (1), Escherichia (1), Yesinia (1), Proteus (1), Haemophilus (6), Terrahaemophilus (1), Aggregatibacter (7), Desulfobulbus (1), Desulfovibrio (2), Desulfomicrobium (1), Bdellpvibiro (1), Erythromicrobium (1), Sphingomonas (4), Brevundimonas (1), Caulobacter (1), Afipia (3), Bradyrhizobium (1), Agrobacterium (1), Bartonella (1), Ochrobactrum (1), Defluvibacter (1), Rhizobium (1), Helicobacter (1), Campylobacter (7) Treponema (49), Chlamydophila (1), Jonquetella (1), Pyramidobacter (1), Rickettsia (1), Brucella (1), Borrelia (1), Chlamydia (2), Ruminococcus (2), Zymophilus (1), Schwartzia (1), Nocardia (1), Arthrobacter (1), Micrococcus (1), Kingella oralis, Weeksella (1) Total genera amount: ∼365 Total species amount: ∼784 | Streptococcus (12), Prevotella (17), Veillonella (3), Granulicatella (2), Lactobacillus (5), Gemella (3), Bulleidia (1), Paenibacillus (1), Eubacterium (1), Mogibacterium (1), Filifactor (1), Peptostreptococcus (1), Megasphaera (1), Micronuciformis (1), Selenomonas (1), Centipeda (1), Clostridiales (7), Atopobium (2), Rothia (1), Actinomyces (4), Comamonas (1), Delftia (1), Achromobacter (1), Neisseria (3), Shewanella (1), Yersinia (1), Haemophilus (5), Campylobacter (2), TM7 (3), Bacteroidetes AJ289174 (1), Bacteroides (1), Tannerella (1), Porphyromonas (3), Leptotrichia (2), Fusobacterium (4), Staphylococcus (2), Candida (1), Escherichia (1), Enterobacter (1) Total genera amount: ∼594 Total species amount: − | Eubacterium (5), Deinococcus (1), Bergeyella (1), Chryseobacterium (1), Capnocytophaga (1), Cytophagales (1), Prevotella pallens (20), Porphyromonas (2), Tannerella (2), Fusobacterium (5), Leptotrichia (5), Streptococcus (12), Granulicatella (1), Abiotrophia (1), Enterococcus (1), Lactobacillus (2), Weissella (1), Gemella (1), Veillonella (2), Megasphaera (1), Selenominas (1), Mogibacterium (1), Filifactor (1), Lachnospiraceae (1), Firmicutes phylum sp. (1), Cryptobacterium (1), Atopobium (2), Rothia (2), Actinomyces (4), Corynebacterium (2), Flexistipes (1), Neisseria (3), Kingella (1), Delftia (1), Acidovorax (1), Comarmonas (1), Lautropia (1), Alcaligenes (2), Ralstonia (1), Moraxella (1), Acinetobacter (2), Escherichia (1), Haemophilus (3), Actinobacillus (1), Brevundimonas (1), Caulobacter (1), Blastobacter (1), Pedomicrobium (1), Sphingomonas (4), Campylobacter (3), Helicobacter (1), TM7 phylum sp. (3) Total genera amount: ∼100 Total species amount: ≤262 | Aquifex (1), Thermus (1), Deinococcus (2), Leifsonia (1), Trophetyma (1), Bifidobacterium (1), Propionibacterium (1), Thermobifida (1), Streptomyces (2), Frankia (1), Corynebacterium (4), Norcadia (1), Mycobacterium (4), Streptococcus (9), Leptospira (1), Borrelia (2), Treponema (2), Dehalococcoides (2), Gloeobacter (1), Prochlorococcus (1), Symbiobacterium (1), Moorella (1), Desulfitobacerium (1), Mycoplasma (12), Lactobacillus (5), Enterococcus (1), Lactococcus (1), Listeria (2), Bacillus (3), Acidobacerium (1), Desulfovibrio (2), Syntrophus (1), Bdelloviobrio (1), Anaeromyxobacter (1), Geobacter (2), Pelobacer (1), Sulfurimonas (1), Campylobacer (1), Wolinella (1), Helicobacter (2), Erythrobacter (1), Anaplasma (2), Rickettsia (5), Wolbachia (2), Ehrlichia (2), Caulobacer (1), Gluconobacer (1), Sphingopyxis (1), Rhizobium (1), Sinorhizobium (1), Rhodopseudomonas (1), Bradyrhizobium (1), Brucella (5), Burkholderia (3), Ralstonia (7), Bordetella (3), Chromobacterium (1), Xanthomonas (3), Xylella (1), Nitrosococcus (1), Methylococcus (1), Coxiella (1), Legionella (1), Thiomicrospira (1), Francisella (1), Psychrobacter (2), Hahella (1), Chromohalobacter (1), Pseudomonas (4), Saccharophagus (1), Shewanella (2), Vibrio (4), Colwellia (1), Photobacerium (1), Pectobacterium (1), Francisella (1), Yersinia (2), Buchnera (1), Candidatus (1), Salmonella (2), Shigella (4), Escherichia (1), Mannheimia (1), Pasteurella (1), Photohabdus (1), Idiomarina (1), Lawsonia (1), Desulfovibrio (2), Campylobacter (1), Wolbacchia (2), Zymomonas (1), Jannaschia (1), Slicibacter (2), Agrobacterium (1), Bartonella (2), Aromatoleum (1), Dechloromonas (1), Polaromonas (1), Methylobacillus (1), Rhodoferax (1), Sodalis (1), Baumannia (1), Wigglesworthia (1), Butyrivibrio (1), Clostridium (23), Eubacterium (5), Coprococcus (1), Dorea (1), Ruminococcus (5), Roseburia (1), Faecalibacterium (1), Oscillospira (1), Megasphaera (1), Veillonella (1), Dialister (1), Selenomonas (1), Propionispira (1), Mogibacterium (1), Peptostreptococcus (1), Porphyromonas (3), Bacteroides (19), Prevotella (11), Rikenella (1), Micrococcus (1), Escherichia (1), Haemophilus (1), Acinetobacter (3), Sutterella (1), Neisseria (2), Fusobacterium (3), Verrucomicrobium (1), Akkermansia (1) Total genera amount: ∼400 Total species amount: ∼400–500 | Thermotoga (1), Aquifex (1), Propionibacterium (2), Bradyrhizobium (2), Listeria (2), Ethanoligenens (1), Cellulosilyticum (1), Staphylococcus (1), Burkholderia (3), Deinococcus (2), Vibrio (4), Neisseria (1), Nitrobacter (3), Shewanella (1), Finegoldia (1), Proteobacterium (1), Mycoplasma (1), Bacillus (1), Yersinia (1), Exiguobacterium (1), Acinetobacter (1), Mobiluncus (1), Leuconostoc (1), Catonella (1), Paenibacillus (3) Achromobacter (1), Moraxella (1), Pediococcus (2), Edwardsiella (1), Oenococcus (3), Abiotrophia (1), Filifactor (1), Rahnella (1), Sodalis (1), Brachyspira (1), Methanobrevibacter (1), Methanosphaera (1), Bifidobacterium (11), Atopobium (4), Collinsella (3), Eggerthella (4), Olsenella (1), Slackia (2), Bacteroides (41), Odoribacter (1), Parabacteroides (3), Porphyromonas (3), Paraprevotella (1), Prevotella (21), Alistipes (3), Capnocytophaga (7), Enterococcus (4), Lactobacillus (25), Weissella (1), Lactococcus (1), Streptococcus (36), Clostridium (20), Anaerococcus (2), Parvimonas (2), Peptoniphilus (4), Eubacterium (6), Pelotomaculum (1), Acetivibrio (1), Mobiluncus (1), Lawsonia (1), Caulobacter (1), Epulopiscium (1), Anaerostipes (2), Ruminococcus (7), Thermoanaerobacterium (1), Blautia (2), Butyrivibrio (1), Coprococcus (3), Dorea (2), Roseburia (3), Oscillibacter (1), Peptostreptococcus (2), Pseudoflavonifractor (1), Anaerotruncus (1), Faecalibacterium (3), Coprobacillus (2), Holdemania (1), Solobacterium (1), Turicibacter (2), Acidaminococcus (3), Phascolarctobacterium (1), Centipeda (1), Dialister (1), Megasphaera (3), Mitsuokella (1), Selenomonas (4), Veillonella (5), Fusobacterium (7), Acidovorax (1), Comamonas (1), Oxalobacter (2), Parasutterella (1), Sutterella (1), Bilophila (1), Desulfovibrio (3), Campylobacter (5), Helicobacter (1), Aeromonas (4), Succinatimonas (1), Gardnerella (1), Grimontia (1), Subdoligranulum (1), Anaerofustis (1), Anaerobaculum (1), Xenorhabdus (1), Ralstonia (1), Shuttleworthia (1), Oribacterium (3), Citrobacter (4), Cronobacter (2), Enterobacter (9), Escherichia (10), Klebsiella (4), Proteus (2), Providencia (4), Salmonella (2), Shigella (5), Actinobacillus (3), Aggregatibacter (3), Basfia (1), Haemophilus (8), Histophilus (1), Mannheimia (1), Pasteurella (2), Treponema (1), Pyramidobacter (1), Akkermansia (1), Victivallis (1), Gemella (1), Mycobacterium (2), Laribacter (1), Corynebacterium (4), Granulicatella (1), Cardiobacterium (1), Leptotrichia (2), Marvinbryantia (1), Eikenella (1), Dysgonomonas (1), Bartonella (1), Arcobacter (1), Ureaplasma (1), Brucella (1), Pelobacter (2) Total genera amount: ∼400 Total species amount: ∼400–500 | |||||
| Phenolic category | Catabolites | Known bacteria | Known enzymes | Sources | Citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flavonols | |||||
| Quercetin | 3,4-Dihydroxytoluene, 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propionic acid, 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid, o-hydroxyphenylacetic acid, m-hydroxyphenylacetic acid, protocatechuic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, phloroglucinol, | Eubacterium oxidoreducens, Clostridium orbiscindens, Eubacterium ramulus, Enterococcus gilvus, Stretococcus lutetiensis, Escherichia coli, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Weissella confusa, Clostridium perfringens, Bacteroides fragilis, Butyrivibrio spp. | — | Pig caecum, human feces, rat feces | Zhang et al. (2014), Labib et al. (2004), Labib et al. (2006), Rechner et al. (2004), Serra et al. (2012). |
| Rutin and quercetin rhamnoside | Hydrogenated rutin, quercetin-3-glucoside, leucocyanidin, 5,7,3,4-tetrahydroxy flavonone, 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propionic acid, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, 3-hydroxyphenylacetic acid, 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid, phenylacetic acid, protocatechuic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, phloroglucinol | Baceroides distasonis, Bacteroides uniformis, Bacteroides ovatuis, Bacillus sp. 52, Bacteroides sp. 45, 42, 22, Veillonella sp. 32, Eubacterium ramulus | β-D-glucosidase β-L-rhamnosidase | Human feces, rat feces | Yang et al. (2012), Serra et al. (2012). |
| Myricetin | Phenylacetic acid, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, 3-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propionic acid | — | — | Rat feces | Serra et al. (2012), |
| Galangin | Phloroglucinol, phenylacetic acid | — | — | Pig caecum | Labib et al. (2006) |
| Kaempferol | Phloroglucinol, 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid, 4-hydroxytoluene | Clostridium orbiscindens, Clostridium difficile, Lactobacillus spp. | p-hydroxyphenylacetate decarboxylase | Pig caecum | Labib et al. (2006) |
| Kaempferol rutinoside | Phenylacetic acid, o-hydroxyphenylacetic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid | — | — | Rat feces | Serra et al. (2012) |
| Flavonones | |||||
| Hesperetin | Eriodictyol, 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid, phloroglucinol | — | — | Pig caecum | Labib et al. (2004) |
| Naringenin | 3-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)propionic acid, 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid, 3-phenylpropionic acid, phenylacetic acid, p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid, o-hydroxyphenylacetic acid, protocatechuic acid, | Clostridium scindens, Eubacterium desmolans | — | Pig caecum, rat feces, human feces | Labib et al. (2004), Serra et al. (2012), Selma et al. (2009). |
| Flavone | |||||
| Chrysin | — | — | — | Pig caecum | Labib et al. (2006) |
| Tangeretin | 4′,6,7-Trihydroxy-5,8-dimethoxyflavone, 4′,7-dihydroxy-5,6,8-trimethoxyflavone, 4′,6-dihydroxy-5,7,8-trimethoxyflavone, 4′-hydroxy-5,6,7,8-tetramethoxyflavone, 6-hydroxy-4′,5,7,8-tetramethoxyflavone, 5,6-dihydroxy-4′,7,8-trimethoxyflavone | — | demethylase | Rat gut | Nielsen et al. (2000) |
| Luteolin | 3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)propionic acid, 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-propionic acid | — | — | Rat feces, pig caecum | Serra et al. (2012), Labib et al. (2006). |
| Apigenin | 3-Phenylpropionic acid, 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-propionic acid, 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-propionic acid | — | — | Pig caecum | Labib et al. (2006) |
| Hispidulin | 3-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid, scutellarein | — | demethylase | Pig caecum | Labib et al. (2006) |
| Isoflavonols | |||||
| Daidzein | Dihydrodaidzein, equol, O-desmethylangolensin | Adlercreutzia equolifaciens, Slackia isoflavoniconvertens, Slackia equolifaciens, Lactococcus garvieae, Bacteroide ovatus spp., Streptococcus intermedius spp., Ruminococcus productus, SNU-Julong 732 (AY310748), Enterococcus faecium EPI1, Lactobacillus mucosae EPI2, Finegoldia magna EPI3, and Veillonella spp. EP | — | Rat gut | Matthies et al. (2011), Selma et al. (2009). |
| Genistein | Dihydrogenistein, 5-hydroxy-equol, 6′-hydroxy-O-desmethylangolensin | Slackia isoflavoniconvertens, Slackia equolifaciens, Enterorhabdus mucosicola | — | Rat gut | Matthies et al. (2011) |
| Flavanols | |||||
| Catechin/epicatechin | 4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid, 3-(3′-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid, 5-(3′,4′-dihydroxyphenyl)-γ-valeric acid, 5-(3′,4′-dihydroxyphenyl)-γ-valerolactone, 5-phenyl-γ-valerolactone, phenylpropionic acid | Clostridium coccoides and Eubacterium rectale co-cultured | — | Human gut, human urine, human feces | Roowi et al. (2009), Tzounis et al. (2008). |
| Epigallocatechin | 4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid, 5-(3′,4′,5′-trihydroxyphenyl)-γ-valerolactone, 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid | — | — | Human gut, human feces, human urine | Roowi et al. (2009) |
| Epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate | Pyrocatechol, pyrogallol, 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid, 5-(3′,4′,5′-trihydroxyphenyl)-γ-valerolactone, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid | — | — | Human gut, human feces, human urine | Roowi et al. (2009) |
| Phenolic acids | |||||
| Gallic acid | Pyrogallol, phloroglucinol, resorcinol | Klebsiella aerogenes, Pelobacter massiliensis, Eubacterium oxidoreducens | Decarboxylase, transhydroxylase (pyrogallol-phloroglucinol isomerase) | Human gut | Grant and Patel (1969), Heider and Fuchs (1997), Fuchs (2008). |
| Chlorogenic acid, feruloyquinic acid | Ferulic acid, caffeic acid, quinic acid, dihydroferulic acid, dihydrocaffeic acid, 3-(3′,4′-dihydroxyphenyl)propionic acid, 3-(3′-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid, 3-(4′-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid, 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid, phenylacetic acid, benzoic acid, 3-hydroxybenzoic acid, 3′-hydroxyphenylacetic acid, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, 3-phenylpropionic acid, | — | — | Human feces | Rechner et al. (2004), Ludwig et al. (2013). |
| Protocatechuic acid | Catechol | Klebsiella aerogenes, Lactobacillus plantarum | 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoate decarboxylase | Yogurt, fruit, human gut | Grant and Patel (1969), Landete et al. (2008). |
| Vanillic acid | 2-Methoxyphenol | Bacillus subtilis | Vanillate decarboxylase | Human gut | Lupa et al. (2008) |
| 2/3/4-Hydroxybenzoic acid | Phenol | Bacillus subtilis | 4-Hydroxybenzoate decarboxylase | Human gut | Lupa et al. (2008) |
| Dihydroxybenzoic acid | Dihydroxybenzene | Klebsiella aerogenes, Clostridium sp. with a Campylobacter sp. co-cultured | Decarboxylase | Human gut, Human gut (Clostridium) and chicken gut (Campylobacter) | Grant and Patel (1969), Kluge et al. (1990). |
| p-Coumaric acid, caffeic acid | 4-Vinyl phenol, 3-(4′-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid, 3-phenylpropionic acid, phenylacetic acid, 4-ethyl phenol | Lactobacillus plantarum, Bacillus subtilis, Enterobacter cloacae strain DG-6 | Decarboxylase, putative phenolic acid reductase or vinyl phenol reductase | Yogurt, fruit, human gut | Barthelmebs et al. (2000), Young and Frazer (1987). |
| Ferulic acid | 4-Vinylguaiacol, dihydroferulic acid, 4-ethylguaiacol, vanillin, vanillyl alcohol | Lactobacillus collinoides, Lactobacillus plantarum, Oenococcus oeni, Lactobacillus brevis, Pediococcus damnosus, Bacillus coagulans, Saccharomyces cerevisiae (yeast), Brettanomyces anomalus (yeast) | Phenolic acid decarboxylase, phenolic acid reductase, acid phenol reductase | Yogurt, fruit, human gut, wine | Knockaert et al. (2012), Bloem et al. (2007). |
| Tannins | |||||
| Punicalagin | Ellagic acid, gallic acid, urolithin C, urolithin A, isourolithin A | — | — | Human feces | González-Barrio et al. (2011b) |
| Ellagic acid | Urolithin C, urolithin A, urolithin B | — | — | Human feces | González-Barrio et al. (2011b) |
| Proanthocyanidin | 2-(4′-Hydroxyphenyl)acetic acid, 3-phenylpropionic acid, 2-(3′-hydroxyphenyl)acetic acid, 3-(4′-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid, 5-(3′-hydroxyphenyl)valeric acid, 3-(3′-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid | — | — | Human feces | Déprez et al. (2000) |
| Tannic acid | Gallic acid, pyrogallol, resorcinol | Enterococcus faecalis | tannase | Goat feces | Goel et al. (2011) |
| Lignans | |||||
| Secoisolariciresinol diglucoside, pinoresinol diglucoside, pinoresinol, medioresinol, syringaresinol, sesamin | Lariciresinol, secoisolariciresinol, 8-hydroxypinoresinol, 2,3-bis(3,4-dihydroxybenzyl)butene-1,4 diol, sesamol, seco, enterodiol, enterolactone, 2,3-bis(3,4-dihydroxybenzyl)butyrolactone | Butyribacterium, methylotrophicum, Eubacterium callanderi, Eubacterium limosum, Peptostreptococcus productus, Clostridium scindens, Eggerthella lenta | deglycosidase, demethylase, dehydroxylase | Human feces | Heinonen et al. (2001), Gaya et al. (2016), Xie et al. (2003), Clavel et al. (2006). |
| Anthocyanidins | |||||
| Cyanidin-3-glucoside, cyanidin-3-rutinoside | Cyanidin, protocatechuic acid, protocatechuic acid glucoside, vanillic acid, 4-coumaric acid, 2,4,6-trihydroxybenzaldehyde, caffeic acid, hydroxybenzoic acid, catechol, tartaric acid | — | α,L-rhamnosidase, β,D-glycosidase | Human feces, human gut, rat gut | Aura et al. (2005), Flores et al. (2015), Chen et al. (2017). |
| Delphinidin-3-glucoside, delphinidin rutinoside | Gallic acid, 2,5-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, 4-coumaric acid, sinapic acid, 2,4,6-trihydroxybenzaldehyde, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, pyrogallol | Bifidobacterium lactis BB-12, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus casei, | β-glycosidase | Yogurt, human gut, human feces, rat gut | Flores et al. (2015), Ávila et al. (2009). |
| Malvidin-3-glucoside | Syringic acid, gallic acid, 2,5-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, 4-coumaric acid, sinapic acid | Bifidobacterium lactis BB-12, Lactobacillus plantarum, IFPL722, Lactobacillus casei LC-01 | β-glycosidase | Yogurt, human gut, human feces | Flores et al. (2015), Ávila et al. (2009). |
| Peonidin | Vanillic acid | — | — | Human gut | Williamson and Clifford (2010) |
| Pelargonidin | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid | — | — | Human gut | Williamson and Clifford (2010) |
| Malvidin | Syringic acid | — | — | Human gut | Williamson and Clifford (2010) |
| Cyanidin | Protocatechuic acid, caffeic acid, 3-(3′,4′-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid, 3-(3′-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid, 3-(4′-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid, 3′,4′-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, 4′-hydroxyphenylacetic acid, 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid, pyrogallol, catechol, resorcinol, | Lactobacillus plantarum GIM 1.35, Streptococcus thermophiles GIM 1.321, | — | Yogurt, human gut, human feces | Williamson and Clifford (2010), Cheng et al. (2016) |
| Chalcone | |||||
| Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone | Hesperetin dihydrochalcone 4′-β-d-glucoside, hesperetin dihydrochalcone, 3-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)propionic acid, 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propionic acid, phloroglucinol | Eubacterium ramulus, Clostridium orbiscindens | β-glucosidase, phloretin hydrolase | Human gut | Braune et al. (2005) |
| Others | |||||
| Curcumin | Tetrahydrocurcumin, demethoxycurcumin, bisdemethoxycurcumin, dihydroferulic acid, 1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-propanol, bis-hydroxylated demethyl dihydrocurcumin, methylated tetrahydrocurcumin, hydroxylated and demethylated dihydrocurcumin, 3,5-tetrahydropyrandione derivative, dehydroxyl demethyl 3,5-tetrahydropyrandione derivative, hexahydrocurcumin | Escherichia coli., Bacillus megaterium DCMB-002, Bifidobacterium longum BB536, Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum G4, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus casei shirota, Enterococcus faecalis JCM 5803, Escherichia coli K-12 | NADPH-dependent curcumin/dihydrocurcumin reductase | Human feces, mice feces | Tan et al. (2015), Hassaninasab et al. (2011), An et al. (2017), Ireson et al. (2002). |
| Oleuropein | Hydroxytyrosol | Lactobacillus plantarum | β-glucosidase, esterase | Olive brines, could be found in human gut | Landete et al. (2008), Marsilio and Lanza (1998). |
| Coumarin | Dihydrocoumarin, 2-hydroxyphenylpropionic acid, 2-hydroxyphenylacetic acid | — | — | Rat feces, rat caecal, rabbit feces | Scheline (1968b) |
| Quinic acid | Protocatechuic acid, catechol | — | — | Rat gut | Scheline (1968a) |
| Precursors | Products | Enzymes | Species | Source | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quercetin glucoside and rutin | Quercetin | β-Glucosidase, β-rhamnosidase | Bacteroides distasonis, Bacteroides uniformis, Bacteroides ovatus, Enterococcus casseliflavus, Bacteroides JY-6, Enterococcus faecium, Selenomonas ruminatium, Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens D1, Peptostreptococcus sp. B178, Coprococcus sp. P15, Streptococcus milleri | Human feces | Aura et al. (2002), Rechner et al. (2004), Schneider et al. (1999) |
| Rutin, quercitrin | Quercetin | Glycosidases | Butyrivibrio sp. C3 | Human gut, bovine rumen | Cheng et al. (1969) |
| Quercetin | 4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid (ring B), 3, 4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (ring B), 3,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde (ring B), phloroglucinol (ring A), CO2 | — | Butyrivibrio sp. C3 | Human gut, bovine rumen | Cheng et al. (1969) |
| Quercetin glucuronidates | Quercetin | β-Glucuronidases | Human feces | Aura et al. (2002) | |
| Naringenin | 4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid (ring B), phloroglucinol (ring A) | — | Butyrivibrio sp. C3 | Human gut, bovine rumen | Cheng et al. (1971) |
| Quercetin glucoside | Quercetin, 3,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde (ring B), 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (ring B), phloroglucinol (ring A), butyrate, acetate, lactate | Eubacterium ramulus, Butyrivibrio sp. C3, Eubacterium oxidoreducens | Human feces, bovine rumen | Schneider et al. (1999) | |
| Robinin | Kaempferol | Desmolase (β-glycosidase) | Bacteroides distasonis | Human gut | Winter et al. (1989) |
| Hesperetin dihydrochalcone 4′-β-d-glucoside | Hesperetin dihydrochalcone | β-Glucosidase | Eubacterium ramulus | Human gut | Braune et al. (2005) |
| Hesperetin dihydrochalcone | 3-(3-Hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)propionic acid | phloretin hydrolase | Eubacterium ramulus, Clostridium orbiscindens | Human gut | Braune et al. (2005) |
| Kaempferol, quercetin | 4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid (ring B), 3, 4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (ring B), phloroglucinol (ring A) | — | Clostridium orbiscindens, Butyrivibrio sp. C3, Eubacterium oxidoreducens | Human feces | Winter et al. (1991), Schneider et al. (1999). |
| Malvidin glucoside | Syringic acid, gallic acid (ring B), 2,5-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (ring B), p-coumaric acid (ring B), sinapic acid (ring B) | — | Bifidobacterium lactis BB-12, Lactobacillus plantarum IFPL722, Lactobacillus casei LC-01 | Human feces | Ávila et al. (2009) |
| Delphinidin glucoside | Syringic acid (ring B), gallic acid (ring B), 2,5-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (ring B), p-coumaric acid (ring B), sinapic acid (ring B) | — | Bifidobacterium lactis BB-12, Lactobacillus plantarum IFPL722, Lactobacillus casei LC-01 | Ávila et al. (2009) | |
| Formononetin | Daidzein | Demethylase | Eubacterium limosum | Human gut | Hur and Rafii (2000) |
| Biochanin A | Genistein | Demethylase | Eubacterium limosum | Human gut | Hur and Rafii (2000) |
| Glycitein | 6,7,4′-Trihydroxyisoflavone | Demethylase | Eubacterium limosum | Human gut | Hur and Rafii (2000) |
| 4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid | 4-Hydroxytoluene | p-Hydroxyphenylacetate decarboxylase | Clostridium difficile ATCC 9689, Lactobacillus spp. | Swine feces | Labib et al. (2006) |
| 3, 4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid | 3,4-Dihydroxytoluene | p-Hydroxyphenylacetate decarboxylase | Clostridium difficile | Human gut | Labib et al. (2006) |
| Hispidulin, glycitein, biochanin A, formononetin | Scutellarein, 6,7,4′-trihydroxyisoflavone, genistein, daidzein | Demethylase | Eubacterium limosum | Pig caecum | Labib et al. (2006) |
| 3-(4′-Hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid | 3-Phenylpropionic acid | Dehydroxylase | — | Human feces | Labib et al. (2006) |
| 3-(4′-Hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid | 4-Ethylphenol | Decarboxylase | — | — | Young and Frazer (1987) |
| 3-(3′,4′-Dihydroxyphenyl)propionic acid | 3-(3-Hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid | Dehydroxylase | Escherichia coli and Streptococcus faecalis var. liquifaciens co-cultured | Human feces | Labib et al. (2006) |
| Hydroxybenzoic acid | Benzoic acid, acetyl group, CO2 | Hydroxybenzoyl-CoA reductase, benzoyl-CoA reductase, 2-hydroxyglutaryl-CoA dehydratase | Acidaminococcus fermentuns, Eubacterium ramulus | Human, piglet gut | Ricaboni et al. (2017), Schneider et al. (1999) |
| Hydroxybenzoic acid | Phenol | 4-Hydroxybenzoate decarboxylase | Klebsiella pneumoniae | Rumen animals | He and Wiegel (1995) |
| Phloroglucinol | 1,3-Dioxo-5-hydroxy-cyclohexane | Phloroglucinol reductase | Eubacterium ramulus | Human gut | Schneider et al. (1999) |
| Phloroglucinol | 1,3-Dioxo-5-hydroxy-cyclohexane, acetate, butyrate | — | Eubacterium oxidoreducens | Human gut | Winter et al. (1989) |
| Resorcinol | 1,3-Cyclohexanedione | Resorcinol reductase | Clostridium sp. with a Campylobacter sp. Co-cultured | Human gut (Clostridium) and chicken gut (Campylobacter) | Kluge et al. (1990) |
| Secoisolariciresinol diglucoside | Secoisolariciresinol | Deglycosidase | Clostridium sp., Bacteroides ovatus, Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides distasonis, B. fragilis, C. cocleatum, Clostridium ramosum | Human gut | Clavel et al. (2006) |
| Secoisolariciresinol | 2,3-Bis(3,4-dihydroxybenzyl)butene-1,4 diol | Demethylase | Butyribacterium methylotrophicum, Eubacterium callanderi, Eubacterium limosum, Peptostreptococcus productus, Bacteroides methylotrophicum | Human gut | Clavel et al. (2006) |
| 2,3-Bis(3,4-dihydroxybenzyl)butene-1,4 diol | Enterodiol | Dehydroxylase | Clostridium scindens, Eggerthella lenta, Peptostreptococcus productus | Human gut | Clavel et al. (2006) |
| Enterodiol | Enterolactone | Dehydrogenase | Clostridium amygdalinum, Clostridium saccharolyticum, Strain ED-Mt61/PYG-s6 | Human gut | Clavel et al. (2006) |
| 2,3-Bis(3,4-dihydroxybenzyl)butene-1,4 diol | 2,3-Bis(3,4-dihydroxybenzyl)butyrolactone | Dehydrogenase | Strain ED-Mt61/PYG-s6 | Human gut | Clavel et al. (2006) |
| Isoxanthohumol | 8-Prenylnaringenin | Demethylase | Eubacterium limosum | Human feces | Possemiers et al. (2005) |
| Protocatechuic acid | Catechol | 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoate decarboxylase | Klebsiella aerogenes | Human feces | Grant and Patel (1969) |
| Vanillic acid | 2-Methoxyphenol | Vanillate decarboxylase | Bacillus subtilis | Human gut | Lupa et al. (2008) |
| 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid | Phenol | 4-Hydroxybenzoate decarboxylase | Bacillus subtilis | Human gut | Lupa et al. (2008) |
| 2,4/6-Dihydroxybenzoic acid | resorcinol | Decarboxylase | Clostridium strain KN245 and Campylobacter sp. Co-cultured | Sludge (Clostridium strain KN245), Bird gut (Campylobacter sp.) | Young and Frazer (1987) |
| Gallic acid | Pyrogallol | Decarboxylase | Klebsiella aerogenes | Human gut | Grant and Patel (1969) |
| Pyrogallol | Phloroglucinol | Transhydroxylase (pyrogallol-phloroglucinol isomerase) | Pelobacter massiliensis, Eubacterium oxidoreducens | Human gut | Heider and Fuchs (1997), Fuchs (2008) |
| Pyrogallol | Resorcinol | Dehydroxylase | — | Rabbit feces, rat feces | Scheline (1968a) |
| Phloroglucinol | dihydrophloroglucinol | Phloroglucinol reductase | Eubacterium oxidoreducens | Could be extracted from human gut | Krumholz et al. (1987) |
| Dihydrophloroglucinol | 3-hydroxy-5-oxohexanoate | Dihydrophloroglucinol hydrolase | Eubacterium oxidoreducens | Could be extracted from human gut | Krumholz et al. (1987) |
| 3-hydroxy-5-oxohexanoate. | 3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA, acetyl-CoA | CoASH | Eubacterium oxidoreducens | Could be extracted from human gut | Krumholz et al. (1987) |
| 3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA | acetate and butyrate | p-Hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase, CoA transferase, butyryl-CoA dehydrogenase, acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase, enoyl-CoA hydrase, phosphate acetyltransferase, acetate kinase, butyrate kinase | Eubacterium oxidoreducens | Could be extracted from human gut | Krumholz et al. (1987) |
| 2/3/4-Hydroxybenzoic acid | Phenol | Dehydroxylase | Clostridium sp. with a Campylobacter sp. Co-cultured | Human gut (Clostridium) and chicken gut (Campylobacter) | Kluge et al. (1990) |
| Dihydroxybenzoic acid | Dihydroxybenzene | Decarboxylase | Klebsiella aerogenes, Clostridium sp. with a Campylobacter sp. Co-cultured | Human gut, Human gut (Clostridium) and chicken gut (Campylobacter) | Grant and Patel (1969), Kluge et al. (1990). |
| p-Coumaric acid | 4-Vinyl phenol | Decarboxylase | Lactobacillus plantarum, Bacillus subtilis | could be found in human gut | Barthelmebs et al. (2000) |
| Ferulic acid | 4-Vinylguaiacol | Phenolic acid decarboxylase | Lactobacillus collinoides, Lactobacillus plantarum, Oenococcus oeni, Lactobacillus brevis, Pediococcus damnosus, Pediococcus spp. | Yogurt, fruit, human gut | Knockaert et al. (2012), Bloem et al. (2007) |
| Ferulic acid | Dihydroferulic acid | Phenolic acid reductase | Lactobacillus plantarum | Yogurt, fruit, human gut | Knockaert et al. (2012) |
| Caffeic acid | 4-Vinylcatechol | Decarboxylase | Streptococcus faecium, Lactobacillus sp., Enterobacter aerogenes, Bacillus sp. | Young and Frazer (1987) | |
| 4-Vinylguaiacol | 4-Ethylguaiacol | Acid phenol reductase | Lactobacillus plantarum | Yogurt, fruit, human gut | Knockaert et al. (2012) |
| Ferulic acid | Vanillin | — | Lactobacillus plantarum, Oenococcus oeni, Lactobacillus brevis, Pediococcus damnosus | Yogurt, fruit, human gut | Bloem et al. (2007) |
| Vanillin | Vanillyl alcohol | — | Oenococcus oeni, Bacillus coagulans, Saccharomyces cerevisiae (yeast), Brettanomyces anomalus (yeast) | Wine | Bloem et al. (2007) |
| Methyl gallate | Gallic acid | Esterase | — | Rat caecal | Scheline (1968a) |
| Oleuropein | Oleuropein-aglycone | β-Glucosidase | Lactobacillus plantarum B21 | Olive brines | Marsilio and Lanza (1998) |
| Oleuropein-aglycone | Hydroxytyrosol, elenolic acid | Esterase | Lactobacillus plantarum B21 | Olive brines | Marsilio and Lanza (1998) |
| Curcumin | Dihydrocurcumin | NADPH-dependent curcumin/dihydrocurcumin reductase | Escherichia coli. DH10B | Human feces | Hassaninasab et al. (2011) |
| Dihydrocurcumin | Tetrahydrocurcumin | NADPH-dependent curcumin/dihydrocurcumin reductase | Escherichia coli. DH10B | Human feces | Hassaninasab et al. (2011) |
| Dihydrocoumarin | 2-Hydroxyphenylpropanoic acid | Esterase | — | Rat caecal, | Scheline (1968b) |
| Substrate | Substrate concentration in diluted rat fecal inoculum, pM | Percentage (%) remained after incubation, h | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 4 | 24 | 48 | ||
| Adapted from Serra et al. (2012). | ||||||
| Rutin | 23.0 | 95.7 ± 9.1 | 87.0 ± 7.4 | 75.5 ± 6.1 | 1.5 ± 0.1 | 1.4 ± 0.1 |
| Quercetin rhamnoside | 7.3 | 111.0 ± 10.7 | 108.2 ± 10.4 | 27.4 ± 2.6 | 7.7 ± 0.4 | 0.8 ± 0 |
| Quercetin | 1.0 | 64.0 ± 3.0 | 110.0 ± 11.0 | 370.0 ± 31.0 | 33.0 ± 2.0 | 0 |
| Kaempferol-rutinoside | 9.0 | 97.8 ± 9.7 | 98.9 ± 7.2 | 87.8 ± 3.6 | 0.2 ± 0 | 0 |
| Naringenin | 13.0 | 100 ± 0.9 | 76.9 ± 7.6 | 36.2 ± 2.5 | 50.8 ± 4.9 | 0 |
| Luteolin | 32.0 | 93.8 ± 9.4 | 90.6 ± 6.6 | 46.9 ± 4.4 | 29.7 ± 2.9 | 15.6 ± 1.5 |
| Gallic acid | 43.0 | 148.8 ± 14.2 | 155.8 ± 14.0 | 134.9 ± 1.3 | 74.4 ± 7.2 | 65.1 ± 5.3 |
| Protocatechuic acid | 296.0 | 95.9 ± 8.1 | 97.3 ± 5.7 | 89.5 ± 7.1 | 92.2 ± 8.4 | 85.8 ± 7.1 |
| Substrate | Substrate concentration in diluted pig caecal inoculum, mM | Percentage (%) remained after incubation, h | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 24 | ||
| Adapted from Labib et al. (2006). | |||||||
| Galangin | 125 | 95.8 ± 8.8 | 83.3 ± 5.9 | 54.2 ± 5.8 | 19.8 ± 4.4 | 7.3 ± 1.5 | 0 |
| Kaempferol | 125 | 55.5 ± 13.7 | 33.3 ± 5.9 | 5.6 ± 0.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Apigenin | 175 | 94.4 ± 1.9 | 91.0 ± 4.9 | 78.5 ± 6.9 | 78.4 ± 1.0 | 67.4 ± 1.0 | 59.0 ± 0.9 |
| Luteolin | 175 | 95.8 ± 1.9 | 81.6 ± 1.9 | 86.1 ± 3.9 | 82.6 ± 4.9 | 65.3 ± 7.9 | 56.2 ± 4.9 |
| Quercetin | 125 | 53.7 ± 1.5 | 38.9 ± 1.5 | 18.9 ± 3.0 | 5.3 ± 1.5 | 0 | 0 |
| Chrysin | 175 | 100.0 ± 3.9 | 99.9 ± 6.0 | 98.6 ± 9.9 | 100.7 ± 1.0 | 98.6 ± 4.0 | 99.9 ± 5.9 |